For an engineer, wheel bearing design and selection can be a balancing act between durability, cost and fuel economy. A large bearing might be great to safeguard against the impact of potholes and/or accommodate heavy loads; but there is only so much room in the hub and knuckle. In addition, the larger bearing might have increased rolling resistance due to a larger sealing surface. On the other hand, if the bearing is too small in diameter, it might not be able to stand up to loads and there might not be enough room for the axle. The smaller hub may lack the stiffness to control movement of the flange and rotor.
But here is some encouraging news. Two technologies are now being used on new vehicles and in aftermarket replacement hub units that allow engineers to put better bearings in smaller packages. These technologies will change the way you replace and diagnose wheel bearings.
Better designs are needed to accommodate large-diameter wheels, which apply a heavier bending moment on the hub’s flange. Many of today’s vehicles also have twice the power compared to new models of just a decade ago. This extra power can cause stress on the splines and stub axle.
Axial (Face) Spline Design
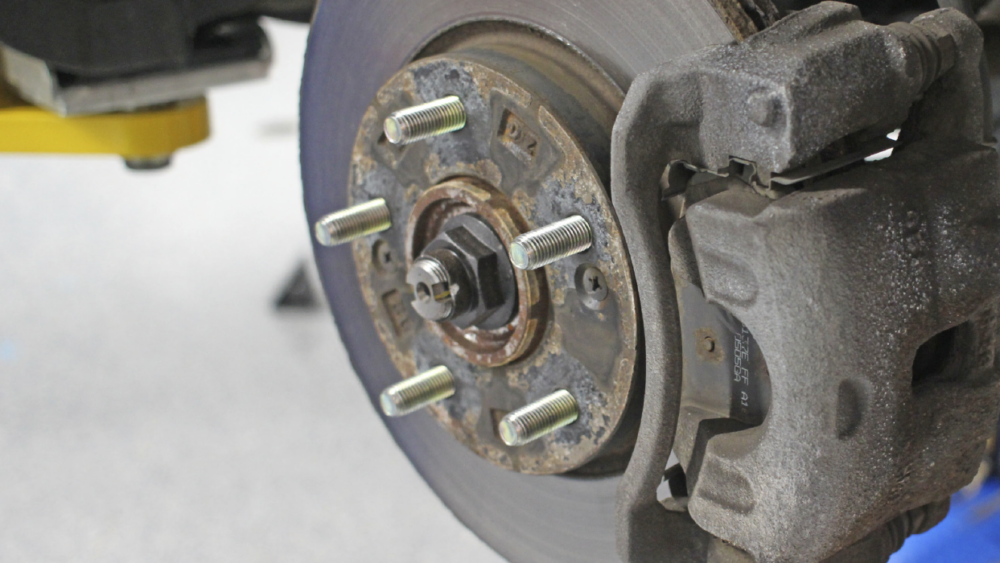
Most driven wheel bearing hubs have a male-splined axle that slides through a matching female-splined hole in the hub. The whole thing is held together with an axle nut. This design has been used for more 60 years.
Splines have their limits when it comes to the size of the hub and the amount of power and load that can be transmitted to the wheels. Increasing the number of splines and the diameter of the stub axle can make the hub unit too large for the knuckle and increase rolling resistance.
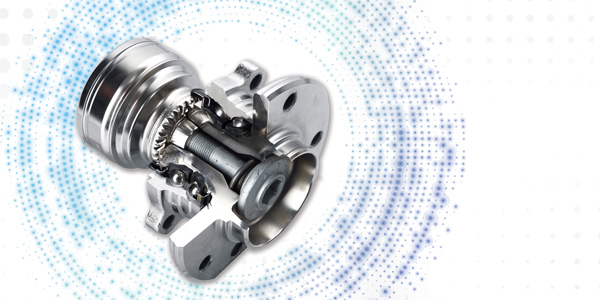
The latest hub design moves the splines from inside the bearing races to the back of the hub. Axial- or face-spline hubs have what looks like gear teeth on the backside of the hub assembly unit. Matching axial gear teeth are formed on the end of the CV joint, and the whole unit is held in place with a long bolt.
The axial-spline arrangement allows higher torque transmission over the traditional splined CV method, primarily because the gear teeth operate on a much larger pitch circle.
This design allows for a smaller diameter hole in the center that can improve the stiffness of the bearing and its durability. It also can reduce brake pedal pulsation and travel.
These units come preassembled and preloaded from the manufacturer. The preload is set by cold rolling the inner race under many tons of pressure.
AsymmetricAL/Hybrid Design
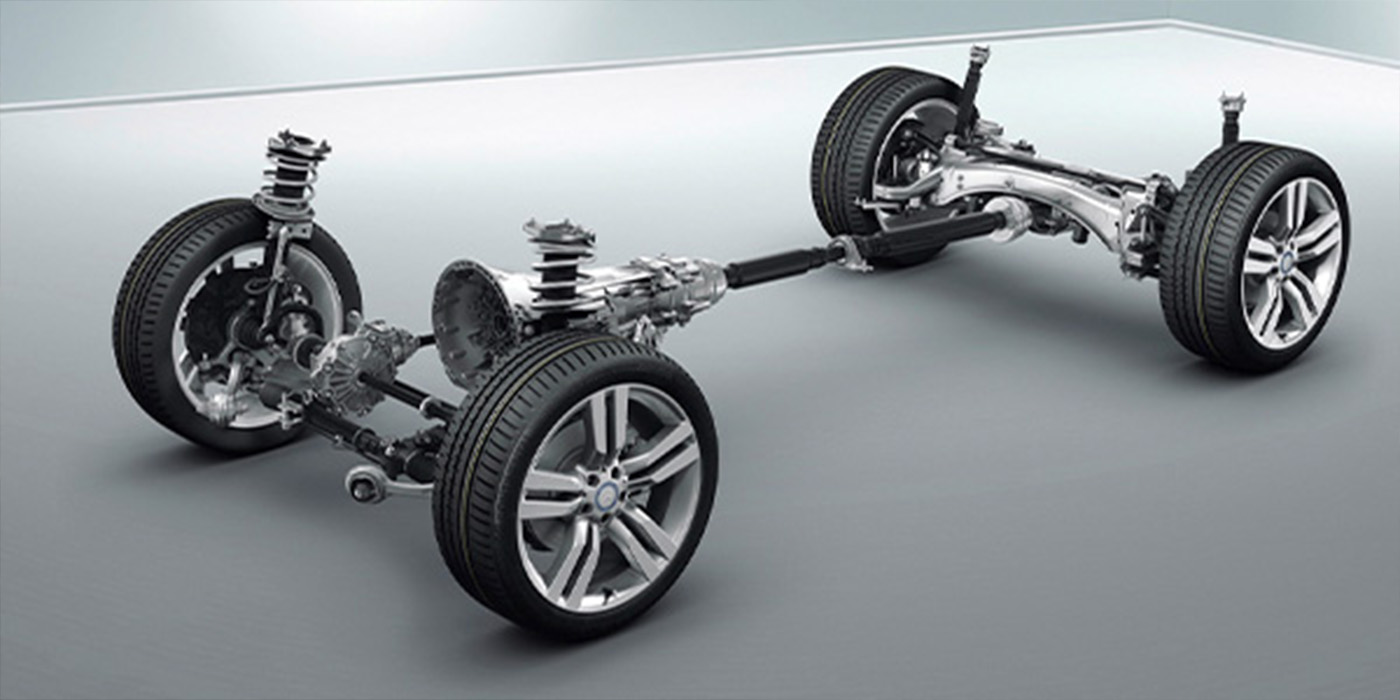
Asymmetrical wheel bearing hubs use different bearing row diameters to improve load capacity and overall stiffness. The hub’s outboard row has a larger diameter than the inner row and more rollers or balls. Hybrid asymmetrical designs use both rollers and ball bearings in the two rows.
The design increases the bearing load capacity, and the unit is stiffer than a conventional hub of the same size. This stiffness prevents the brake rotor from flexing and tilting while the vehicle is cornering. It also reduces brake caliper piston knockback that can cause a long brake pedal. This can also lower the chances of runout and disc thickness variation.
Installation Tips
Both axial and asymmetrical bearings need to be installed using either the correct service or bearing manufacturer installation information. Hub units are typically preassembled and are simply bolted to the suspension. These are “maintenance-free” and non-serviceable units that are pre-set, pre-greased and pre-sealed. Some applications use torque-to-yield bolts that stretch and maintain constant tension. These bolts may attach the hub unit to the knuckle. In the case of axial-splined hubs, a torque-to-yield bolt holds the hub to the axle. These bolts can’t be used twice.
While it may appear to be easier to use an impact wrench to tighten the axle nut or bolt, it is not recommended. Instead, use a torque wrench. Impact wrenches can damage the axle nut, threads and components. These can also create a false sense of security when adjusting a nut or bolt, which may be under- or over-torqued. This can leave a hub assembly susceptible to failure.
Article courtesy Brake & Front End.