Technicians and customers have pretty much accepted that the accessory serpentine drive belt should be replaced between 90,000 to 100,000 miles. It is a “slam dunk” sale to just replace the belt, but does that replacement belt have the same chance to survive the same mileage?
Chances are in the next 90,000 to 100,000 miles the replacement belt will have to deal with problems the original belt did not — a worn tensioner, idler pulley bearing failure or component alignment issue.
This is why selling the complete serpentine belt job is important. If just the belt is replaced, the customer could end up replacing the belt sooner than normal and replacing other components when they fail, which could leave them stranded.
Belt-On Inspection
Noise is the first sign that more components than the belt need attention. Listen to the belt before proceeding with the rest of the inspection. The first clue is a belt squeal heard during engine startup. The second clue might be a belt squeal heard during parking maneuvers or during an alternator load test.
While the engine is running, watch the different runs of the belt and look for flutter or excessive movement from the automatic tensioner. This can indicate that the tensioner is worn and/or the pulley or decoupler on the alternator needs further inspection. A spray bottle can be used to wet the belt to isolate typical belt noise from tensioner, idler pulley and attached component noises.
 Visual inspection of serpentine belts is changing. In the past, cracked and missing pieces were easy to spot. With better materials, cracks and fraying occur less often within the 90,000-100,000 mile timeframe. For the majority of modern belts, the replacement specification is the depths of the grooves. When the belt is past the wear specification, the top of the groove bottoms out on the pulleys. The walls of the grooves on the belt are no longer able to grip and drive the accessories.
Visual inspection of serpentine belts is changing. In the past, cracked and missing pieces were easy to spot. With better materials, cracks and fraying occur less often within the 90,000-100,000 mile timeframe. For the majority of modern belts, the replacement specification is the depths of the grooves. When the belt is past the wear specification, the top of the groove bottoms out on the pulleys. The walls of the grooves on the belt are no longer able to grip and drive the accessories.
Inspect the outside of the tensioner for rust bleed seeping from inside the tensioner. This is an indication that the dampener or other internal parts have failed and metal-on-metal wear is happening. Some tensioners have marks on the housing that indicate tension and belt stretch, but not the health of the tensioner.
Look for leaking oil or accumulation of dirt around the idler and decoupler pulleys. This is an indication the seals and possibly the bearings have failed.
Belt-Off Inspection
Place a wrench on the tensioner and move the arm its entire range of motion at least three times. Feel for spring tension along with a fluid motion throughout. Any sticking or notching movement may indicate a problem with the spring or pivot bearing. The arm should only move up and down. Any lateral movement could indicate a bad bearing or spring.
Spin the pulleys on the tensioner and idlers. They should spin freely without bearing noise, but they shouldn’t spin too freely. A “free-wheeling” bearing is a sign that the seals have failed. Any significant amount of noise is an indication that the components are at the end of their life.
With the belt off, it is possible to check the alignment of the pulleys. Belt manufacturers and tool companies offer laser alignment tools for accessory drive systems that can be very helpful in eliminating drive belt noise due to misaligned pulleys. These tools typically connect onto a reference pulley like the crankshaft, so the technician can view where the laser pattern falls on the pulleys.
It is possible to make adjustments by moving the pulley on the shaft or adjusting the placement of the components in their brackets. Check the service information for possible adjustments.
 Automatic Belt Tensioner
Automatic Belt Tensioner
Almost all automatic belt tensioners have a dampening mechanism that absorbs shocks, belt load changes and crankshaft speed. On some import applications, the dampener looks just like a miniature shock absorber. On some tensioners, it is a friction dampener inside the housing. The bottom line is the tensioner mechanism is a wear part with a limited life span.
A worn automatic belt tensioner has consequences beyond a loose belt. When an automatic belt tensioner wears out, the belt and attached accessories will start to take an extra pounding because the tensioner can no longer dampen the power pulses of the crankshaft. The effect on these components is similar to when a car has bad shocks that slowly destroy the suspension.
A worn tensioner can cause the alternator pulley or decoupler to work harder and wear out sooner. The drive accessories can be damaged by the uneven tension and the hammering of the belt. This can damage the bearings inside the alternator and idler pulleys.
Idler Pulleys
Replacing idler pulleys is cheap insurance against a comeback. If you miss a bad idler pulley, the life of the belt is compromised. Typically a worn idler will produce a chirping noise. Belt manufacturers and specialty parts suppliers have kits that include all possible wear items — the belt, idler pulleys and tensioner. Often these kits include updated parts that can solve belt noise problems.
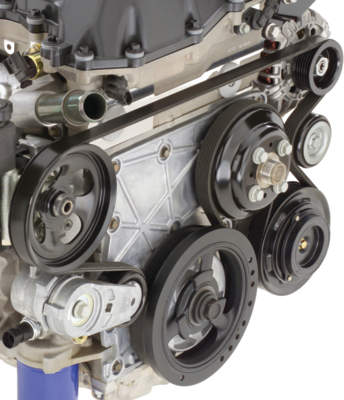 Decouplers and Pulleys
Decouplers and Pulleys
When an alternator decoupler or pulley is compromised, it can no longer absorb the same level of abuse, which has a trickledown effect throughout the system. Belts and tensioners are then much more likely to overstress and fail.
Alternator decouplers and pulleys should be inspected every 10,000 miles for wear. Early design versions have provided service life of 40,000 to 60,000 miles, with more recent versions lasting more than 100,000 miles.
When inspecting a decoupler or pulley, there are two signs that replacement is needed. First, after shutting down the engine, if there is an audible buzzing, the bearings in the pulley have likely failed. The second sign depends on whether the vehicle has a one-way clutch (OWC), overrunning alternator pulley (OAP) or decoupler (OAD).
With the inspection cap/cover removed and the center locked, turn the pulley or decoupler with the appropriate tool. If it is an OAP or OWC, the pulley can only be turned in the clockwise direction. If it is an OAD, a counterclockwise turn will reveal a noticeable increase in spring force and a clockwise turn will only have slight resistance. If these functions are not operational, the OWC, OAP or OAD needs to be replaced.
Anyone can replace the original belt (most quick lubes are actively selling belts), but to make the next belt last just as long as the original, there is more work required beyond the easy sale.
Courtesy Underhood Service.