For most repair shops, brake pedal pulsation or brake vibration is one of the most frequent brake performance complaints coming through the door.
For most repair shops, brake pedal pulsation or brake vibration is one of the most frequent brake performance complaints coming through the door.
If a customer complains of pedal pulsation or steering wheel shimmy when the brakes are applied, the most common assumption is that heat, wear, corrosion or mechanical stress is causing a variation in braking torque to occur that’s directly proportionate to wheel speed.
While servicing disc brake rotors might seem like “old hat” to some brake technicians, the reduced mass of modern brake rotors, plus changes in the composition and materials of modern brake pad materials, make correct brake rotor service more important than ever. The reduced mass of modern brake rotors often causes them to be less tolerant of dimensional inaccuracies and poor installation procedures than are earlier systems.
Solving a one-time occurrence is one thing, solving a chronic or repeat instance of pedal
pulsation is quite another. After all, it’s your reputation on the line and, while your customer doesn’t mind paying a fair price for service, he or she will begin to take notice when they appear to be paying for the same repair twice.
Consequently, any case of brake pedal pulsation should be approached in a methodical manner that, not only provides a remedy, but determines the cause of repeat cases.
 Understand the Issue
Understand the Issue
When diagnosing a brake pedal pulsation complaint, remember that the frictional coefficient between the tire and the road surface is just as important to stopping the vehicle as the frictional coefficient between the brake pad and the rotor. Although tire casings have become much more reliable in recent years, it’s still possible for a steel belt to cause a brake pull by shifting position off-center or a broken tire casing to imitate brake pedal pulsation when the brakes are applied.
It’s also important to examine the wheels, especially aftermarket wheels, for proper fit around the lug bolts and axle hubs. If the axle studs establish concentricity, a snug fit must exist between the studs and the holes in the wheels. If the axle hub establishes concentricity, the fit must similarly be sufficient to hold the wheel in a concentric manner.
Last, remember that the rear brakes may also cause brake pedal pulsation. In most cases, using the park brake pedal or lever to apply the rear brakes while the vehicle is rolling along at slow speeds in a low-traffic area will quickly determine if the rear brakes are pulsating.
On occasion, rear brake drums can be forced out-of-round if the rear drums are overheated and the park brake is left in the applied position. In this case, the drum cools to an out-of-round condition when the vehicle is parked.
 RTV & Runout
RTV & Runout
Rotor thickness variation (RTV) or the lack of parallelism between the rotor surfaces is the major cause of pedal pulsation. In general, RTV in a rotor should be less than 0.001” or less than manufacturer’s specifications.
In contrast, runout is simply the amount of “wobble” or lateral rotational variation a rotor exhibits as it turns. Because of design differences in calipers and caliper mountings, maximum runout specifications may vary among manufacturers.
But, in the larger picture, the high points of a rotor with excessive runout wear away as the spinning rotor contacts the brake pad. It doesn’t take long for runout in an out-of-specification rotor to cause a variation in rotor thickness by wearing away several thousandths of material from the outer perimeter of the rotor surface.
RTV becomes apparent during light braking applications as the brake pad begins to contact the brake rotor. In this situation, the steering wheel may begin to oscillate slightly and the vehicle may begin to roll unevenly as the brakes are applied.
The Runout Issue
Not all pedal pulsation issues can be solved by installing new brake rotors. In many cases, an accumulation of rust around the wheel studs or a slight amount of runout at the wheel hub can cause rotor runout. Keep in mind that minor runout at the hub will cause major runout at the rotor’s outer perimeter.
The first step is to measure the thickness of the rotor to ensure it has at least 0.020 inches of removable stock per side for truing the surfaces. Next, inspect the rotor for hard spots and “black” rust. Neither condition can be remedied by resurfacing, so the rotor should be replaced.
Re-torque the rotor hat to the hub using flat nuts to duplicate wheel nut torque. All wheel nuts should be torqued in a star pattern and in two-step increments using an accurate torque wrench. If the threads on the wheel studs are rusty, they should be cleaned with a thread chaser and lubricated with a drop or two of non-detergent motor oil.
Remember that accurate torque readings are impossible if lubricants that contain a friction modifier are used. If torque values aren’t increasing in direct relation to the angular rotation of the wheel nut, both the wheel nut and stud are defective or a friction modifier is present on their threads.
Next, remove all traces of rust from around the wheel studs and hub using a scraper, wire brush or mild abrasive wheel. An old 1/4” wood chisel works well for this purpose. Thoroughly clean the rotor-mounting surface inside the rotor hat using an abrasive pad or wheel.
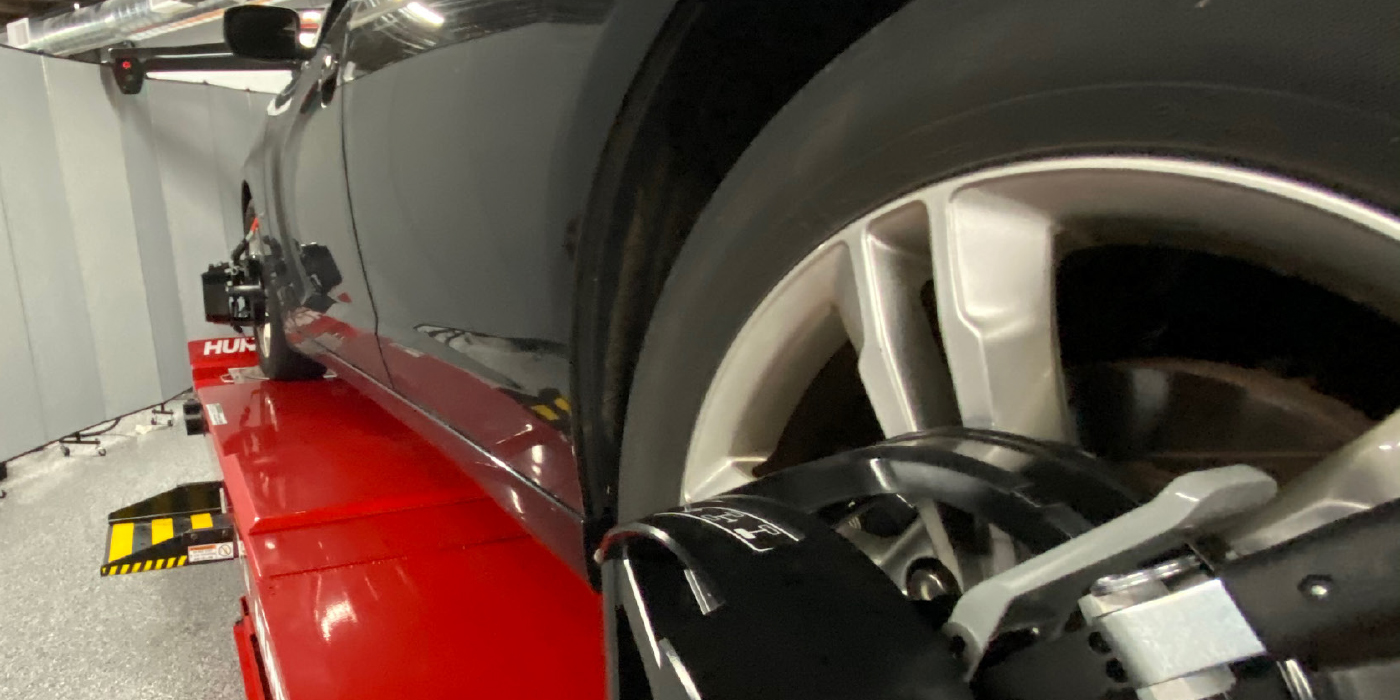
After torquing the wheel nuts, the end play on the wheel bearings and the runout on the brake rotor should be checked with a dial indicator. Most wheel bearings should have less than 0.002 inches end play and rotate quietly and smoothly. The high point of runout should be marked on the rotor and indexed to a wheel stud or to the hub itself.
For diagnostic purposes, remove the rotor and re-mount it as close to 180 degrees from its original position as possible. If the runout is nearly the same, the runout condition is caused by the rotor. If the runout changes significantly, the runout condition is caused by the wheel bearing hub.
If runout is within specifications, the rotor should be removed and its thickness measured at a minimum of eight different points at the center of the rotor surface. The measurements should be written on the rotor with a felt marking pen and, if the differences between the highest and lowest values exceed OE specifications, the rotor should be resurfaced or replaced.
Off-Vehicle Brake Lathes
Mounting a rotor on an off-vehicle brake lathe is a critical part of rotor service. In short, the high point of runout indexed on the rotor should be the same high point of runout as indicated by the brake lathe.
If the high points significantly differ, either the wheel hub or the brake lathe has excessive runout. In any case, the runout of the brake lathe arbor should be occasionally tested with a dial indicator. The tolerance should be nearly zero at the rotor-mounting point.
Similarly, all hub adapters and other centering fixtures should be checked for dimensional inaccuracies or damage. In many cases, a bent lathe arbor or worn arbor bearings actually increase, rather than decrease, minor cases of rotor runout.
On-Car Resurfacing
Although tapered shims are available for many applications to correct wheel hub runout, the fastest and most certain method to correct for minor amounts of hub runout is to turn the rotor on the vehicle.
Excessive hub runout should, however, be corrected to avoid machining excess stock from new rotors. Although some import manufacturers allow caliper-mounted on-car lathes to be used, most recommend modern lathes that machine rotors independently of the caliper mounts.
‘Finishing’ Up
While rotor finish has more to do with keeping the brakes quiet than with preventing pedal pulsation, keep in mind that it’s especially important to use a fine tool feed to reduce torn metal during machining.
Remaining torn metal is removed by applying a non-directional “crosshatch” finish to the rotor with finishing stones or an abrasive pad. Thoroughly washing the rotor with soapy water and drying with a paper towel will remove metal particles.