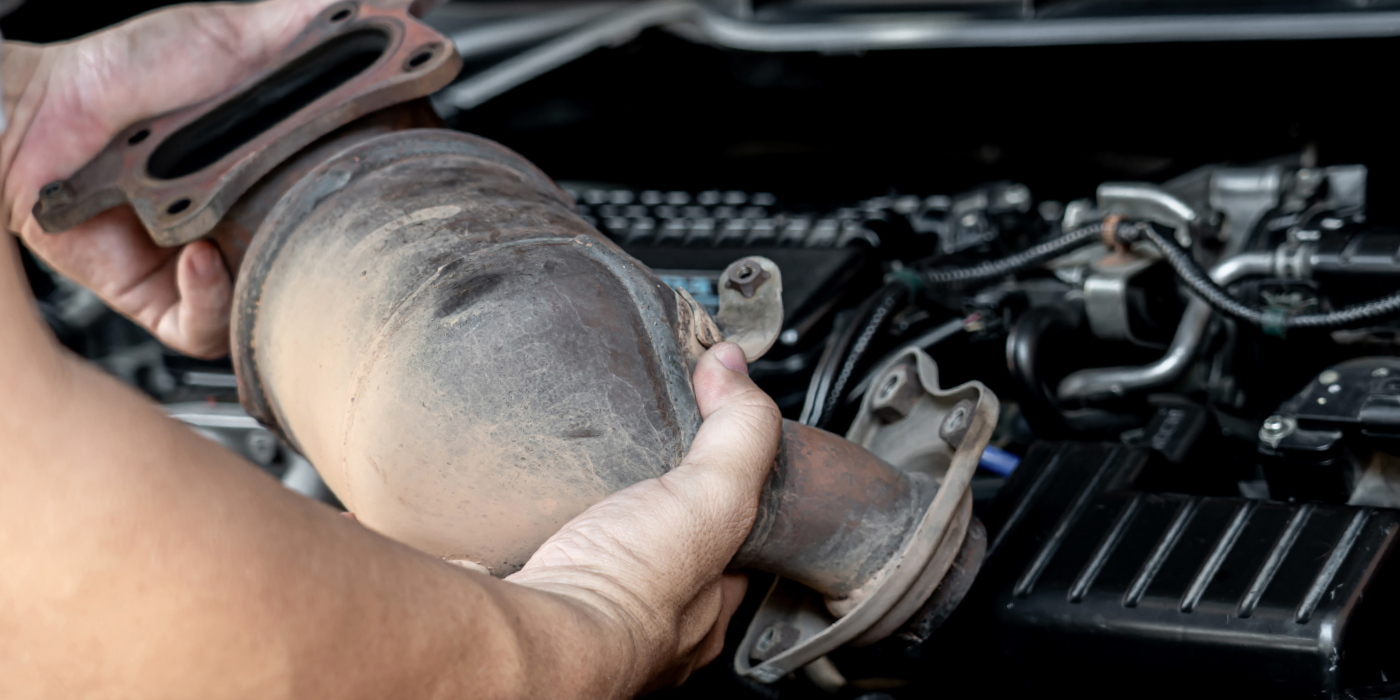
Understanding catalytic converter efficiency codes can be a long diagnostic road that can either lead to a happy customer or an expensive comeback. Chances are the original converter didn’t fail on its own, but conditions upstream hastened its demise.
Almost every part on the engine determines how long the catalytic converter will last. It could be a faulty line of computer codes that pulses an injector too long or it could be a stuck piston ring allowing oil to be sucked into the combustion chamber. These little details can limit the life or efficiency rating of a catalytic converter.
The Code
For a catalyst efficiency code to be set, a number of criteria must be met. The specific enabling criteria is different for almost every vehicle. For a code to be set, the oxygen or air/fuel sensor and the rear oxygen sensor must see a reduction in the efficiency of the converter. In other words, if the oxygen levels before and after the converter do not change, the converter is not working.
But, this is not an automatic pass or fail. The oxygen sensors need to see this loss in efficiency over a number of drive cycle conditions. This is why it might take a few hours or a few days for the light to come back on after a code is erased.
On most vehicles, an efficiency code will not be set if an oxygen sensor heater code or any oxygen sensor-related code is set. Even if the converter is operating below 95% efficiency or the oxygen sensor is bad, the chances of the light coming right back on are slim.
What is Efficiency?
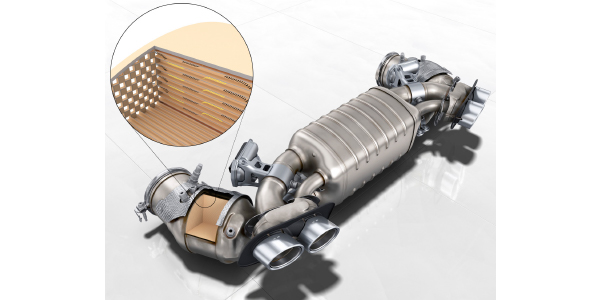
The converter has an efficiency rating that is computed by the vehicle. This number rates the amount of reduction that is occurring in the converter and its ability to store oxygen. But, the efficiency of the converter is tied to the fuel trim of the engine. Most engines minutely alter the fuel trim to replenish the oxygen in the converter and to add fuel for reduction. This helps to keep the converter at the correct temperature for the most efficient operation.
If an engine is running too rich, it cannot store oxygen. If it is running too lean, the reduction process might not occur due to an inability to heat up. If the engine is dealing with a leaking vacuum hose or a stuck injector, it can’t switch the fuel mixture properly to replenish oxygen and reduce harmful contaminates.
Converter efficiency can be checked with some scan tools along with the process of switching between rich and lean. Most converters start out at about 99% efficiency when new, and quickly taper off to about 95% efficiency after 4,000 miles or so of driving. As long as efficiency doesn’t drop off more than a few percentage points, the converter will do a good job of cleaning up the exhaust. But if efficiency drops much below 92%, it will usually turn on the MIL lamp.
Article courtesy Brake & Front End.