CC:
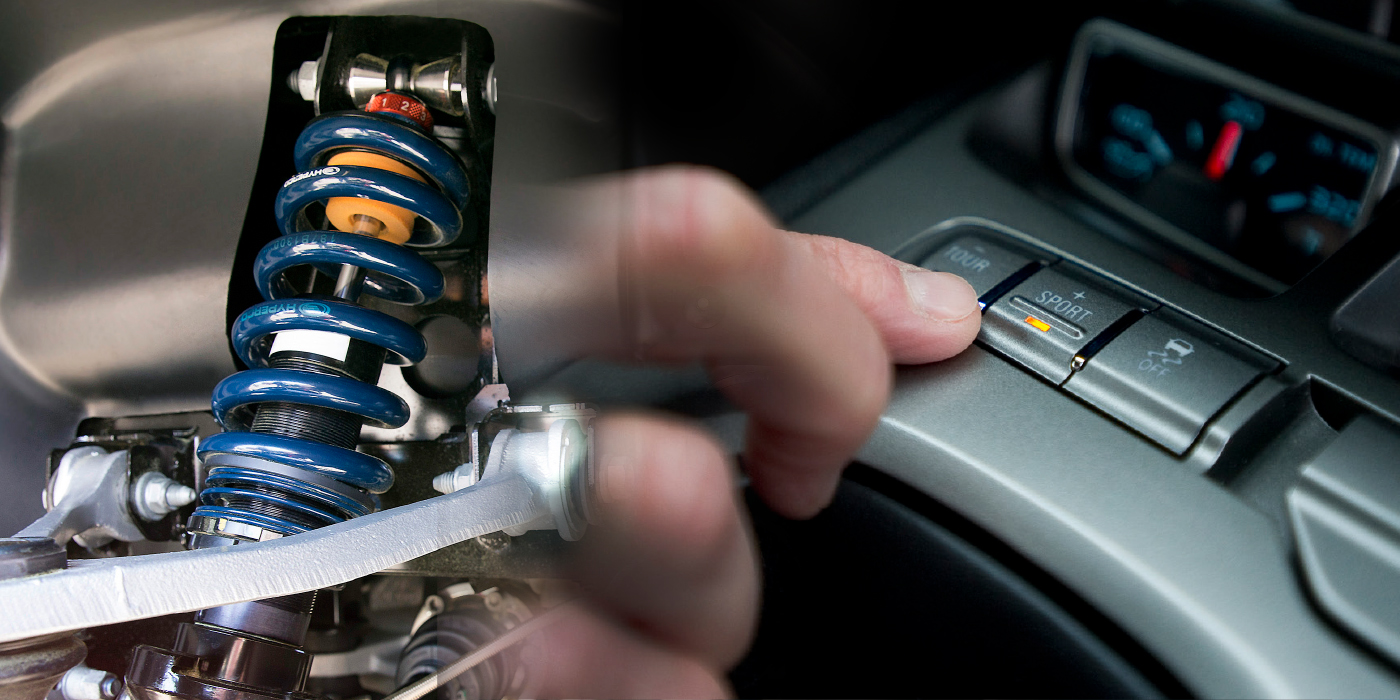
What if I told you there was a technology that could prevent wheels from falling into potholes, reduce stopping distances and offer new levels of comfort and control for a driver, you might think this is a future technology. But, the reality is that some cars and trucks have been equipped with this technology for more than 20 years. The technology is called Continuous Dampening Control, or CDC for short.
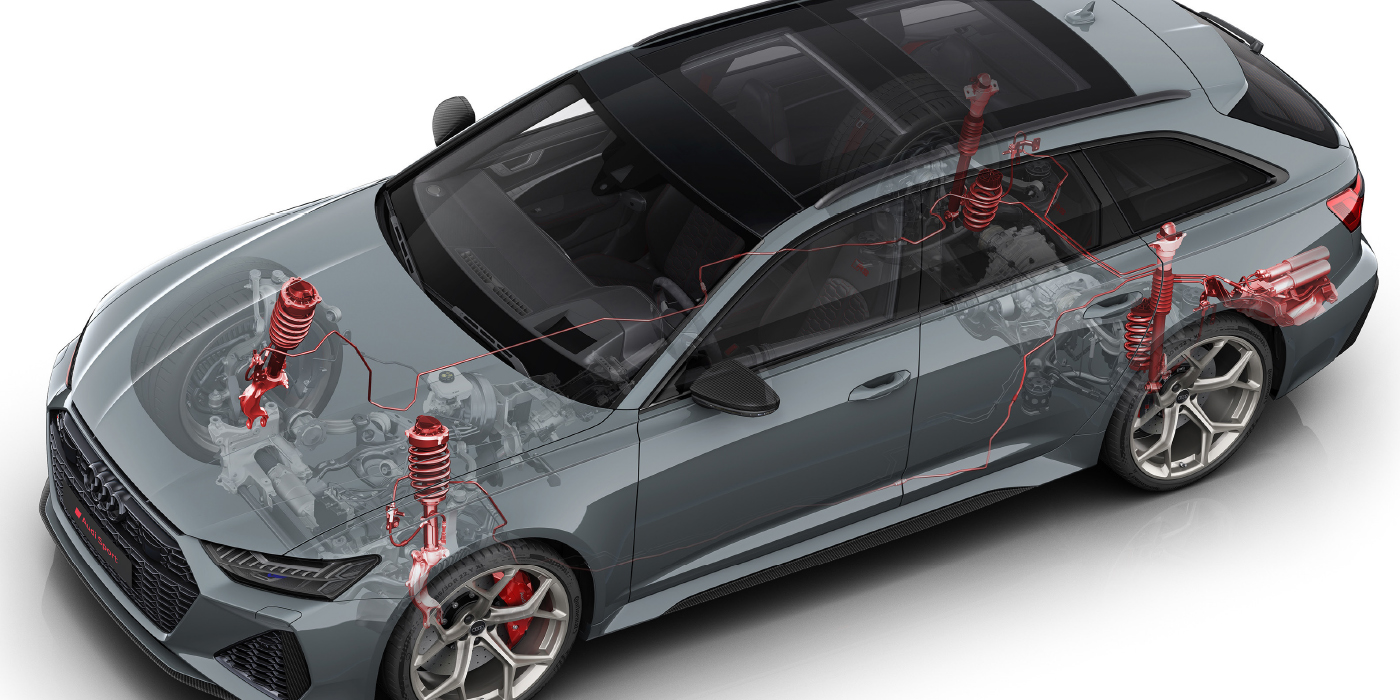
These units use electronically controlled valving that is adjusted in milliseconds to control the compression and rebound of the dampener. For example, the unit can increase rebound when a pothole is detected by either the wheel displacement sensors or a camera. This prevents the wheel from dropping down in the pothole and hitting the backside of the hole. For braking, a CDC dampener can increase compression in the front and increase rebound in the rear to prevent nosedive
The heart of the system is the valving located in the piston or base of the shocks. Inside is an electromagnetically controlled valve that controls the size of the opening of the valve. The opening size is calculated by a module connected to sensors and other systems on the vehicle.
The primary sensor for CDC is the wheel displacement or position sensor. These are not ride height sensors. Instead, these sensors continuously measure the position of the suspension relative to the road and body. The CDC control module will also use data from the ABS, stability control and electric power steering modules for further information on vehicle dynamics.
CDC shocks and struts use conventional mono-tube and twin-tube oil-filled dampeners. The rods, gas chambers and pistons have the same construction as passive units. Just like passive units, they can be damaged internally and externally. Also, they can wear out just like passive units.
When inspecting CDC units, the same rules as conventional units apply. Look for leaks on the surfaces, especially around the shaft seal. Look at the condition of the boot and bumpers. Scrutinize the condition of the shaft for any signs of impacts and corrosion.
The knee on the bumper test is not a valid test for CDC units. Since the valving is variable depending on speed and vehicle dynamics, a static test in your bay may yield inconsistent results. A test drive under controlled conditions is the best tool to assess the condition of the system.
For CDC diagnostics, it requires a scan tool. Just like an engine, a CDC system has diagnostic trouble codes. When the vehicle is first started, the CDC system will perform a self-diagnostic. If there is an issue with the actuators or the CDC module is not communicating with the other modules, diagnostic trouble codes will be set.
For CDC replacement, it is advisable to replace CDC units in pairs. You might be tempted to replace a CDC unit with a conventional passive unit that is listed in a catalog for the same model. This will disable the CDC system and compromise the safety of the vehicle. Also, the spring rates for the CDC and passive units are different and could cause handling and ride quality problems.
CDC shocks and struts represent a considerable opportunity for shops. Replacement units can return a car or truck to its full capabilities for safety and comfort.
This video is sponsored by Sachs.