Adapted from Gary Goms article in ImportCar
Adapted from Gary Goms article in ImportCar
Veteran auto mechanics, and probably even many of your auto instructors, well remember the days of oil-bath air filters, cartridge-type oil filters and sediment-bowl fuel filters. While these early-design filters would work well under a narrow range of circumstances, most were woefully inefficient and inadequate in the long term.
All were subject to careless installation and dirt contamination during servicing.
As disposable “paper” filters were popularly introduced in the late 1950s and made standard equipment in the 1960s, service procedures became more simplified and efficient. Filter housings, for example, no longer were being washed in a dirty solvent tank or exposed to grit and grime during installation. So, just from the aspect of their simplified service requirements and more efficient operation, paper-type filters represented a major advance in automotive maintenance.
They’re All the Same, Right?
Wrong. At the outset, it’s important to know that, although most filters meet original equipment (OE) standards, not all filters are created equal in terms of reliability and overall capacity.
When looking at cutaways of various filters, it’s easy to compare the numbers and depths of the pleats in the filter media, the structural integrity of the filter assembly, and the presence of quality materials in their construction. In addition, keep in mind that the old-fashioned paper-based media has given way to a much stronger and effective media made from synthetic fibers and resins.
Unfortunately, not all of the differences are visual. A cheaply made air filter, for example, might catch fire from an engine backfire or lose structural integrity when exposed to moisture from rain or snow. Worse still, a cheaply made air filter may also shed paper filaments that stick to the hot-wire sensors built into many modern air flow meters.
Similarly, oil filters with cheap paper-based media can collapse or split open when clogged with sludge. When exposed to water draining from a leaking cylinder head gasket, a paper-based filter might disintegrate altogether and clog an engine’s lubrication system.
Despite their relative simplicity, fuel filters aren’t exempt from quality-related issues. The media in a cheaply made fuel filter must resist fuel pressures in excess of 90 pounds per square inch and must also resist long-term exposure to water and various fuel additives.
As for the economics of quality fuel filters, keep in mind that a cheaply made fuel filter may burst under high fuel pressure and allow dirt to clog an expensive set of fuel injectors!
Expert Service
The most misunderstood part of an air filtration system is the air flow capacity of the air filter itself. To illustrate, a correctly designed air filter system operates the majority of the time at only a small percentage of its total airflow capacity.
Unless clogging from extremely dusty operating conditions is an issue, the OE filter is fully capable of supplying an adequate volume of air at peak open-throttle engine speeds throughout its estimated service life.
In addition, many modern air intakes are designed to reduce turbulence and resonances that can affect the ability of the air flow sensor to accurately meter air flow into the engine. Consequently, the seemingly simple act of modifying an intake system for better performance isn’t always a case of “bigger is better.”
Many air filters are designed to be replaced at 30,000-mile intervals. Some experts discourage routine filter inspections because many air filter housings are susceptible to breakage, warpage or dirt contamination. Areas in which rodent contamination is prevalent, however, may require more frequent inspection.
Paved highway driving may require fewer inspections and replacement intervals, while driving on rural gravel roads may obviously require more frequent inspections and replacements.
Unless the air box and seals are cleaned before installation, dust may seep around the air filter and damage the engine. In all cases, debris should be removed using a shop vacuum or a compressed air-operated hand vacuum available through most tool dealers.
If the filter seals against a rubber gasket, the gasket should be firmly attached to the filter housing. If the gasket is loose, it should be reinstalled using an appropriate adhesive.
Last, the popular aftermarket filters using an oil-coated filter medium should be cleaned using the manufacturer’s detergent-based soil-release agent. While using gasoline or solvent may remove the oil, enough dirt is left in the filter medium to reduce airflow and invite rapid clogging.
The filter must also be sparingly re-oiled to prevent excess oil from contaminating or permanently damaging the airflow sensor.
Did You Know…
Perhaps the most destructive air filter service practice is using compressed air to blow dirt out of the filter media. In all cases, compressed air perforates the media in the delicate pleated area. The resulting pinholes allow dirt to pass through the media, which eventually contaminates the airflow sensor and abrades the piston rings and cylinder walls.
 Hide the CAF
Hide the CAF
They call it the “hidden filter” because many motorists don’t realize their vehicles have separate air filters for the passenger compartments. Cabin air filters (CAF) first appeared back in the mid-1980s.
The earliest applications were on Audi and other European makes. Today, about 80% of all new import and domestic vehicles have a cabin air filter — or a slot where one can be installed.
Cabin air filters are put there for the health of the vehicle’s occupants. The filter can trap pollen, dust, smoke and other pollutants that would otherwise enter the vehicle and possibly irritate the nose and lungs of the driver and passengers.
But look out — They also can be a comfortable place for small rodents to nest. (See Photo 1)
Cabin air filters also prevent leaves, dirt, bugs and other debris from entering the HVAC (Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning) system. This prevents the fan and control doors from becoming jammed with debris that could cause fan noise or affect the operation of the heater, air conditioner and defroster.
Keeping the HVAC system clean also helps reduce the growth of odor-causing mold and other microbes on the A/C evaporator.
Some cabin air filters also trap odors and are called “combination” filters. These type of filters have an extra layer of activated carbon that reacts with odors and other airborne pollutants to neutralize them before they become objectionable.
The filters can even reduce the levels of carbon monoxide and oxides of nitrogen from the exhaust of other vehicles. The levels of these pollutants can be quite high in heavy stop-and-go traffic, and it’s not unusual for the concentration of these pollutants to be several times higher inside a vehicle than outside. Studies have shown that driver reaction times are slower when the driver is being affected by poor air quality.
 Trapped Clues
Trapped Clues
Oil filters are usually removed, replaced and discarded without any thought as to their design or function. While all oil filters may appear similar from the outside, most differ internally.
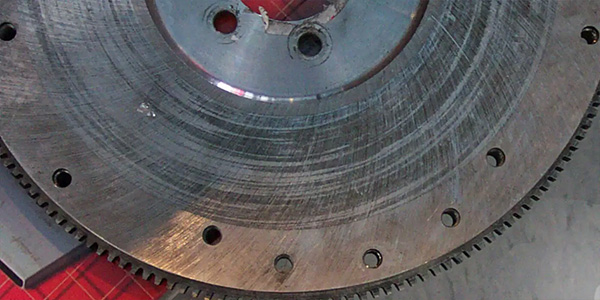
Quality oil filters usually contain an anti-drain back and filter by-pass valve. Oil filters lacking these features may cause permanent engine damage. (See Photo 2)
To better evaluate oil filter construction, an oil filter cutting tool can be used to remove the canister. (see Photo 3)
The filter cutter can also be used as a diagnostic tool to determine if metallic particles from internal engine parts are trapped in the canister and filter media. These can provide clues as to the conditions inside an engine.
 A quality oil filter will have an anti-drain-back valve to prevent oil from draining out of the engine’s oil galleries after shut-down. It will also have an oil filter bypass valve that allows oil to flow around the filtering media if the media becomes clogged or the oil becomes too viscous to flow through the media.
A quality oil filter will have an anti-drain-back valve to prevent oil from draining out of the engine’s oil galleries after shut-down. It will also have an oil filter bypass valve that allows oil to flow around the filtering media if the media becomes clogged or the oil becomes too viscous to flow through the media.
When installing an oil filter, it’s always important to routinely wipe off the oil filter mount to remove dirt and, most important, the old gasket. Next, it’s important to lubricate the gasket on the new filter with engine oil to prevent the gasket from seizing the oil filter to the mount.
Last, hand-tightening is usually recommended to avoid causing potential leakage by perforating or distorting the canister. In cramped spaces where a tool must be used, enough torque should be applied to seat the gasket, but not cause a potential leak by denting or scoring the filter canister.
 Fuel Filter Replacements
Fuel Filter Replacements
The primary symptom of a clogged fuel filter is an engine that loses power or surges under open-throttle operating conditions. In some instances, it’s handy to determine the cause of a clogging problem by cutting a fuel filter apart with a common exhaust pipe cutter.
This particular fuel filter features a spiral-wound filter media design that’s capable of absorbing a large amount of contamination without clogging. (See Photo 4). When taken apart, the inlet side of the filter reveals a thick coating of dirt, which is normal for a long-neglected fuel filter. (See Photo 5)
Fuel filter service poses several issues because many import carmakers no longer specify a filter replacement interval. In addition, a few “permanent” in-tank fuel filters require service only when the fuel pump is being replaced.
 Nevertheless, the major variable in determining any fuel filter replacement interval is the level of dirt, rust and water contamination present in the local fuel distribution system. For the sake of reliability and peace of mind, most externally mounted fuel filters should be replaced at 30,000-mile intervals.
Nevertheless, the major variable in determining any fuel filter replacement interval is the level of dirt, rust and water contamination present in the local fuel distribution system. For the sake of reliability and peace of mind, most externally mounted fuel filters should be replaced at 30,000-mile intervals.
The most important safety consideration in replacing a fuel filter is to release fuel tank pressure by first removing the fuel tank filler cap and then releasing the in-line residual fuel pressure. While most techs crack open the fuel line connections and let the residual pressure vent into a folded shop rag, some might prefer removing the fuel pump fuse and starting the engine to remove pressure.
In other cases, the pressure can be vented by depressing the Schrader valve located in the test port on the fuel injection rail.
When installing a new fuel filter, always inspect the rubber fuel lines for cracking or deterioration. In addition, always inspect the fuel hose clamps for wear. Most high-pressure fuel injection systems require a special hose clamp that applies high clamping pressure without cutting into the hose. For that reason, never substitute a worm-gear clamp for an OE fuel hose clamp.
In addition, a flare nut hex wrench should be used to remove fuel filters equipped with flare-nut connectors. During and after installation, the flare nuts should be coated with an anti-corrosion lubricant to permit easy future removal.