EPB Systems and Diagnostics
A growing number of vehicles are equipped with electronic parking brakes (EPB) that automatically engage the parking brake when the transmission is shifted into park or it detects that the vehicle is on a hill. If you are doing a brake job on a vehicle with EPB, you will need a scan tool with the proper software for the EPB system to retract pistons calipers, adjust cables and perform diagnostics.
There are no shortcuts on YouTube. You can find methods that involve removing the electric motor, jumping connectors, and excessive disassembly of the parking brake mechanism. But, these methods are very risky and can damage the vehicle and kill productivity. Unapproved EPB diagnostic methods will set malfunction codes, and the worst-case scenario is that you could damage the unit.
EPB System Types
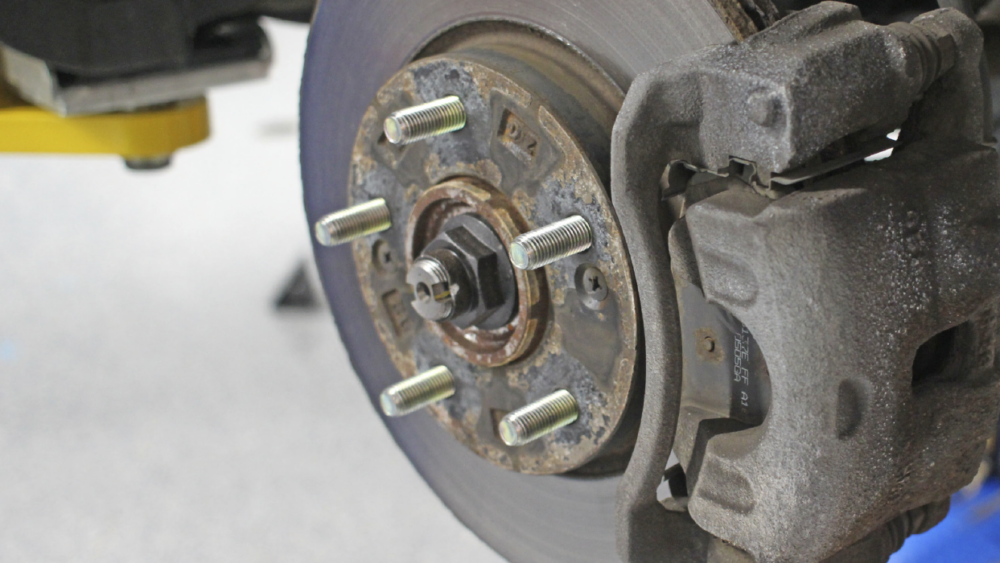
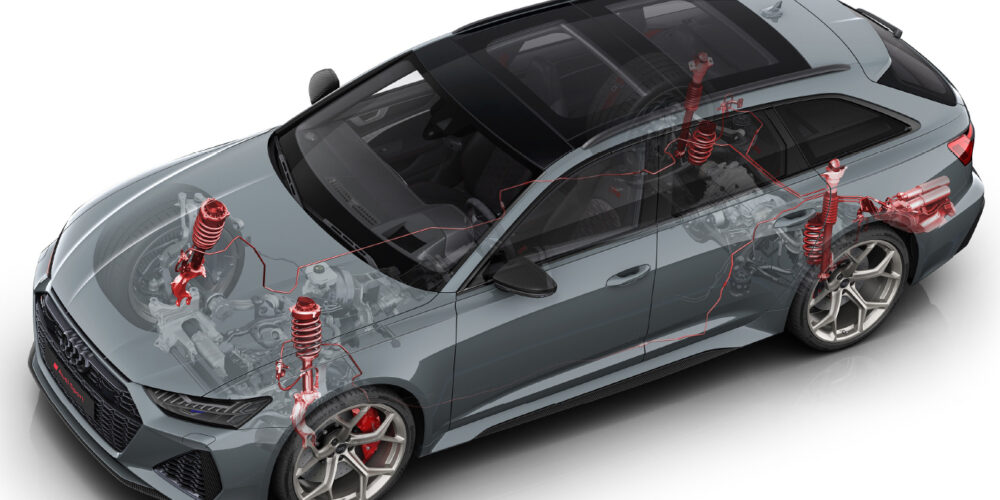
 On one end of the spectrum you have the Audi/VW EPB system that was installed on a number of platforms starting in 2004. This system has stepper motors on the back of the caliper that actuate the piston. These EPB systems require a scan tool to replace the rear brake pads.
On one end of the spectrum you have the Audi/VW EPB system that was installed on a number of platforms starting in 2004. This system has stepper motors on the back of the caliper that actuate the piston. These EPB systems require a scan tool to replace the rear brake pads.
On recent platforms, Audi/VW have outfitted the motors with a sensor that can measure brake pad wear and adjust the pads for the least amount of drag. The sensor will also adjust the pads every 621 miles when the vehicle is off. During this adjustment on some vehicles, the pad thickness is calculated.
On the other end of the spectrum, you have cable-actuated EPB systems. These EPB systems use conventional calipers, but a motor replaces the lever or pedal in the cabin. All cable systems have a built-in program that adjusts for slack in the system that runs at certain intervals. Some of these systems require the use of a scan tool to adjust the parking brake. These EPBs can recognize if the cables become elongated and will set a code.
These systems are typically manufactured by TRW, SKF or Bosch. They can be found on platforms such as GM, Ford, Jaguar, BMW, Subaru and many other domestic and import nameplate manufacturers. Performing diagnostics on these systems can be frustrating to the under-equipped and under-trained technician. The typical customer complaint is that an intermittent “parking brake fault” is displayed in the driver information center.
EPB Diagnostics
 Inspecting the caliper, cables and motors may not give you a complete picture of what is happening with an EPB system, but having access to a scan tool can reduce diagnostic time.
Inspecting the caliper, cables and motors may not give you a complete picture of what is happening with an EPB system, but having access to a scan tool can reduce diagnostic time.
The OEMs have built-in bi-directional protocols to retract the parking brake so the pads can be replaced. A dedicated brake tool or enhanced scan tool is able to command these protocols and interrogate the module for codes and faults.
The Electronic Parking Brake Module (EPBM) is a module on the CAN bus of most vehicles equipped with EPB systems. Any missing data for vehicle speed, gear position or brake pedal input will cause a problem with the system.
CAN bus information from the ESC program is responsible for the hill-holding control of the actuator. Shared information for the hill-holding feature comes from the yaw, incline and acceleration sensors along with gear selection and steering wheel position. The EPB ECU monitors the operation of the parking brake motor and places this information on the CAN bus.
Another diagnostic approach when assessing EPBs is to check the operations section of the parking brake system in the vehicle’s service information. Some EPB systems will use the parking brake for hill holding if an incline is detected, and some EPBs have an “Auto Hold” or “Roll-Away Prevention” function that will prevent the vehicle from rolling forward at stops.
Courtesy Brake & Front End.