Have you ever inspected a customer’s vehicle, and found what looks like fluid coming from one of the suspension bushings? No, your eyes are not tricking you. That bushing could be hydraulic, and it’s a good service opportunity for you and your shop.
What’s so different about hydraulic bushings?
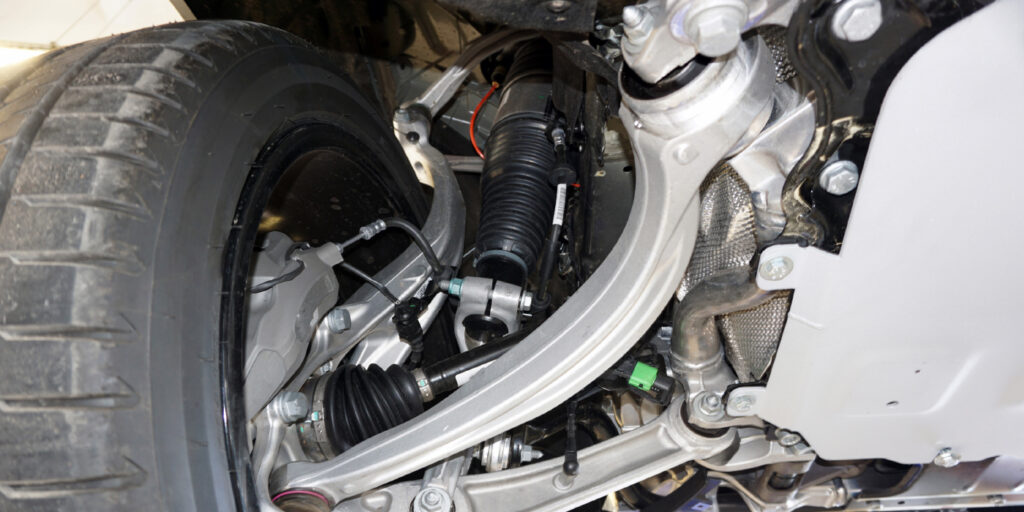
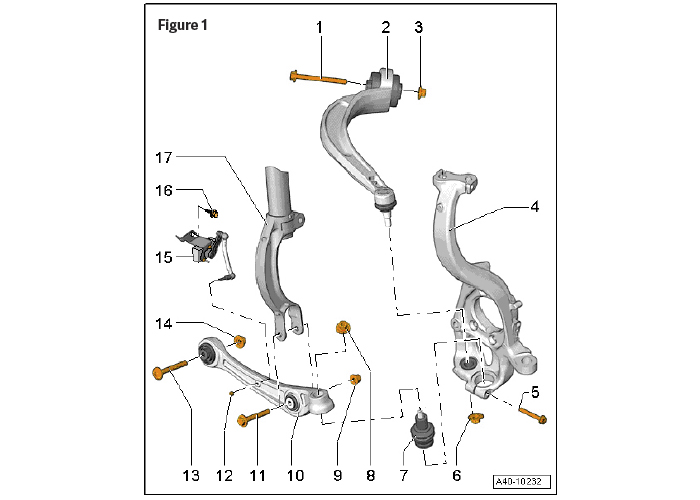
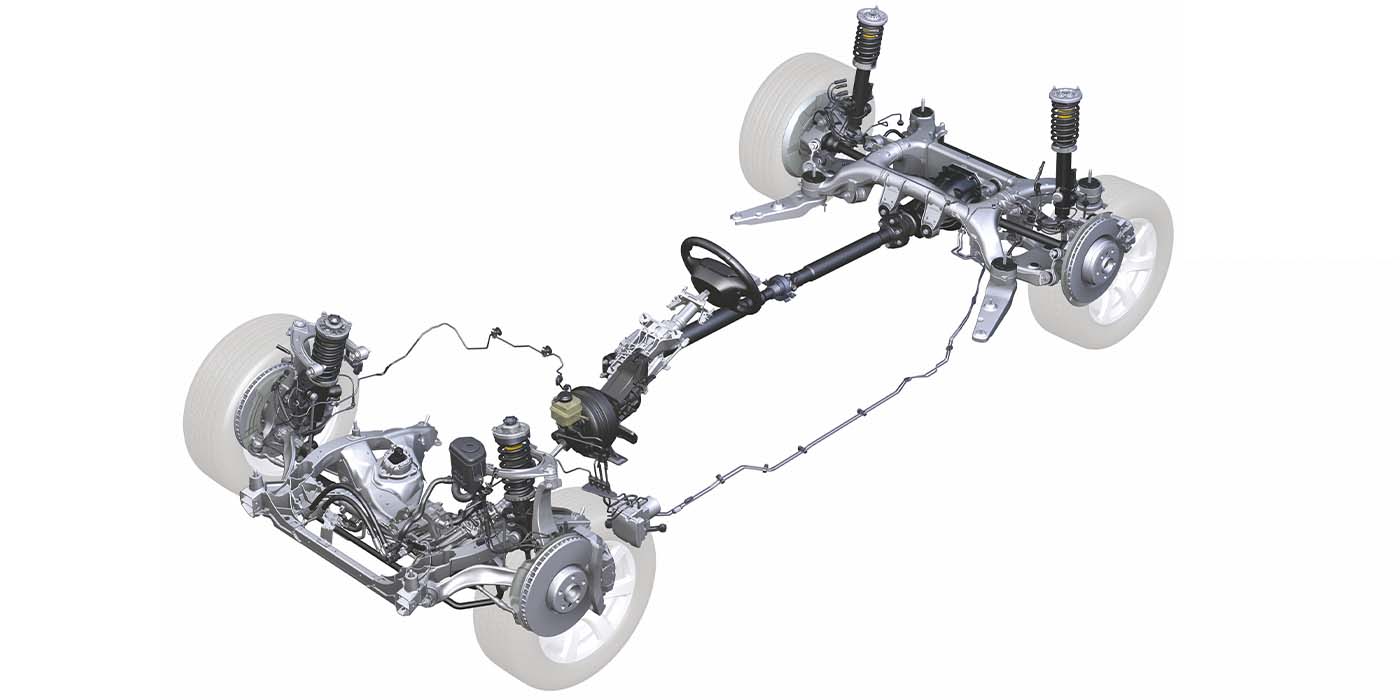
Hydraulic suspension bushings were developed in response to specific customer desires: smoother, quieter, and better-handling vehicles. Sophisticated suspension components are needed in order to achieve this. Modern suspension systems look a lot different than they used to (Figure 1), with multiple links used to maintain suspension geometry.
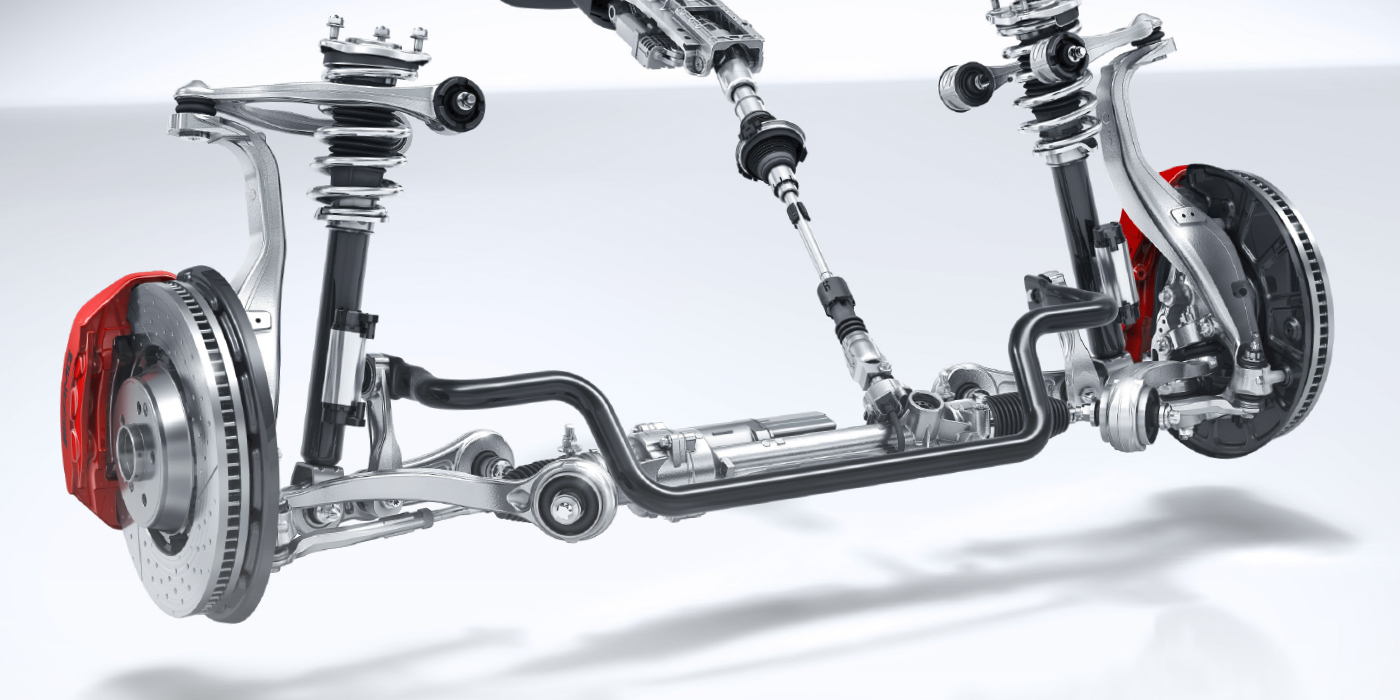
A non-hydraulic suspension bushing will typically feature a number of empty voids inside them (Figure 2). These voids are a product of clever engineering, and they allow for deflection/compression in a specific direction when placed under load. Hydraulic bushings fill those empty voids with a fluid. This fluid works like a hydraulic damper, while still allowing for deflection/compression when under load.
The word “hydraulic” might imply that hydraulic fluid or oil is used inside these bushings, but they typically use a glycol mixture instead. Oil or hydraulic fluid would break down the rubber inside the bushing and cause it to fail prematurely. If you’ve ever seen a radiator hose that got coated in engine oil, you know what I’m talking about.
These bushings are engineered with a certain tire and wheel combination in mind. This means that increasing the tire and/or wheel sizes can throw this off, and the suspension may need to be repaired more frequently.
What are the pros/cons?
Hydraulic bushings are able to isolate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) from entering the vehicle cabin more effectively than standard bushings. Hydraulic bushings can be firmer without compromising passenger comfort, leading to crisp steering response and road feel. They will deflect less under load, such as braking or hard cornering, and this means better vehicle stability.
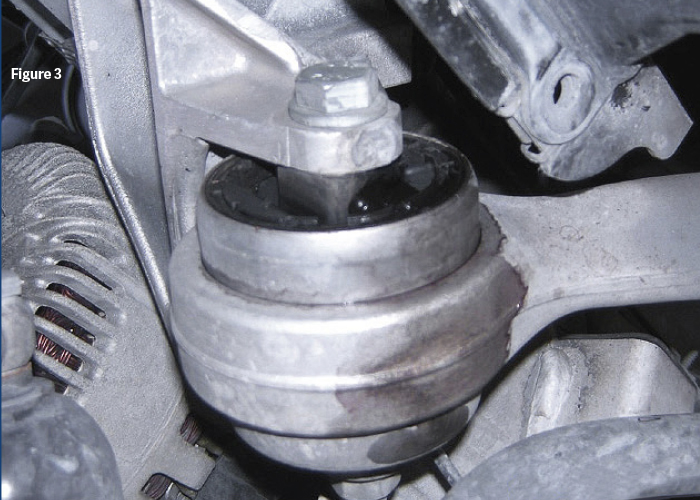
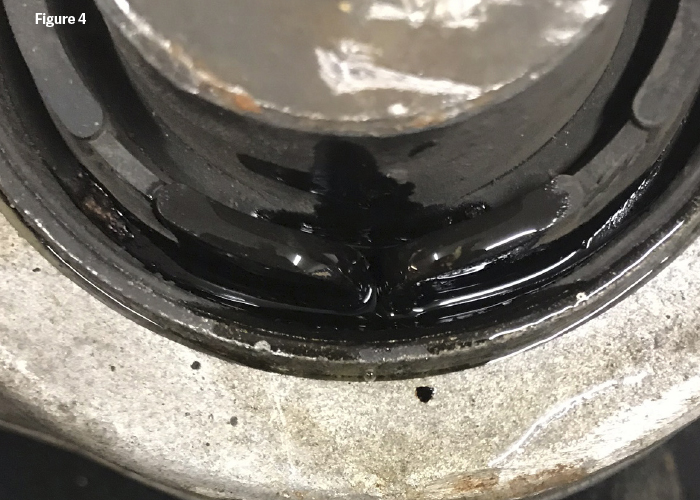
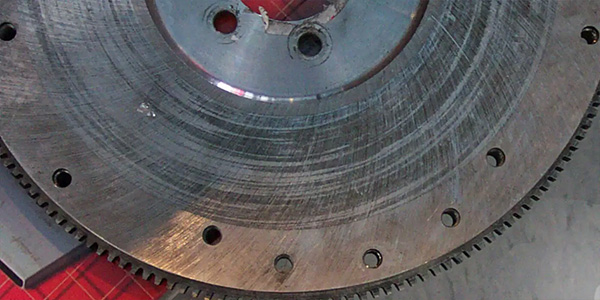
But, all bushings will eventually wear out and need to be replaced. Hydraulic bushings may crack, rip, tear, just the same as non-hydraulic bushings will. The big giveaway is the hydraulic fluid leaking from the bushing (Figure 3 & Figure 4).
Failing hydraulic bushings typically exhibit one or more of the following symptoms:
- Clunking or knocking noises while braking or turning.
- Evidence of fluid leaks coming from the bushings.
- Unwanted suspension movement.
- Tire wear (from excessive suspension movement).
- Increased NVH transferring into the vehicle cabin.
Special considerations during service
Hydraulic bushings will likely be more expensive to replace than standard bushings. Here are a few tips & tricks for servicing these unique bushings:
Let’s start with the most important tip: always check the OE service information. Even if you’ve performed this type of repair in the past, it’s still a good idea to check the service information to see if anything has been updated recently. Road test the vehicle before and after the repair.
If you are pressing a hydraulic bushing into or out of a suspension arm, be very careful not to apply force directly against the rubber part of the bushing. Doing this will most likely rupture the rubber bushing, causing the hydraulic fluid to spill all over the floor. Once this happens, the bushing is ruined and must be replaced. Be selective when choosing a tool to press the bushing, and be sure to only apply force against the outer race or sleeve.
Modern bushings will likely feature some sort of locating mark, notch, or indicator. Reference the OE service information to learn how to correctly align the bushing to the suspension arm. Doing this will allow the suspension to articulate properly. Failure to do this may cause the suspension to bind up during movement, and/or may cause the bushing to wear out or fail prematurely.
We would strongly recommend waiting to torque the fasteners down to specification until the suspension has been set to normal ride height. If you tighten the fasteners down with the vehicle in the air, the bushing will be forced to twist when the vehicle is lowered onto the ground. This means that the bushing will always be twisting at normal ride height, and this will surely lead to premature wear, tearing, and/or failure.
Perform a four-wheel alignment if the service information calls for it. Some suspension components may not require an alignment after service; it depends on the make, model, and application.