Mazda’s i-ACTIVSENSE, an umbrella term covering a series of advanced safety technologies developed in line with Mazda Proactive Safety, makes use of a variety of detection devices. Milliwave radars, lasers and cameras are mounted in the windshield, behind the badges in the grille and rear bumper cover, and first appeared in 2015.
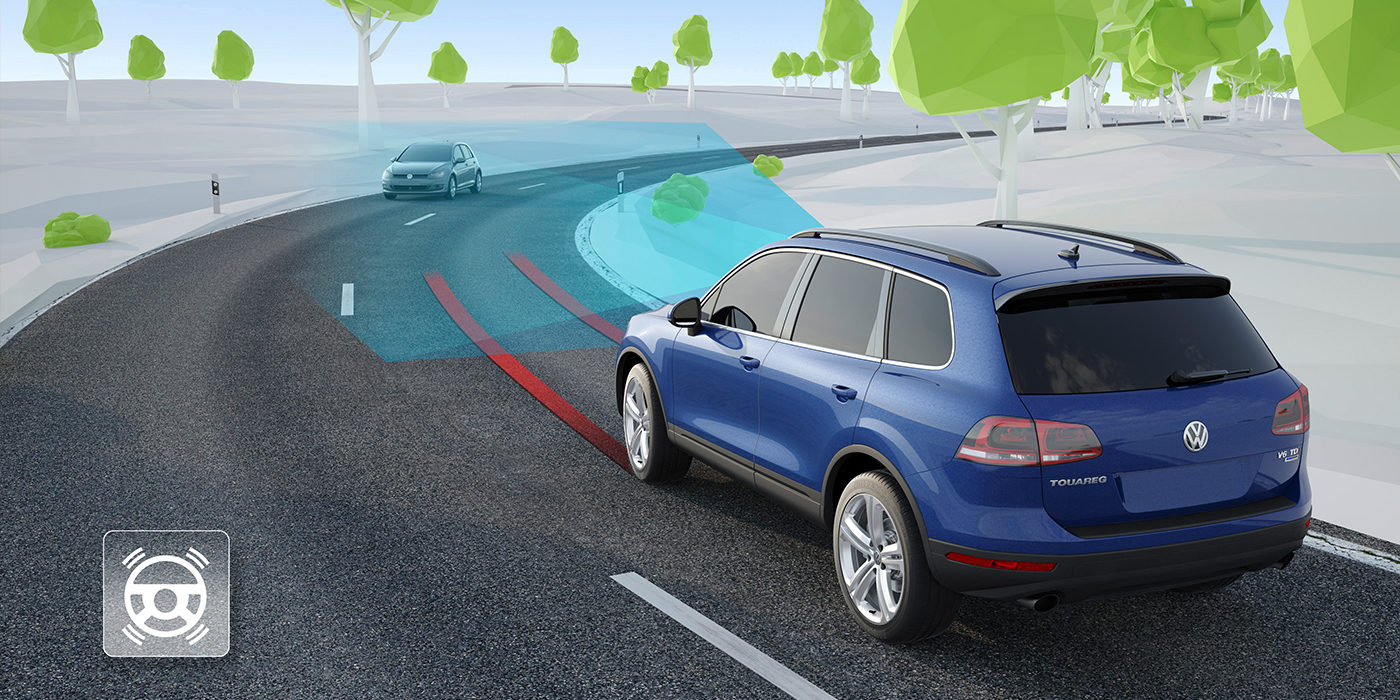
The i-ACTIVSENSE system uses the sensors for pre-braking and active braking, lane departure warnings and blind-spot detection. The i-ACTIVSENSE system is one of the more sophisticated systems on the road that classifies objects and measures distance.
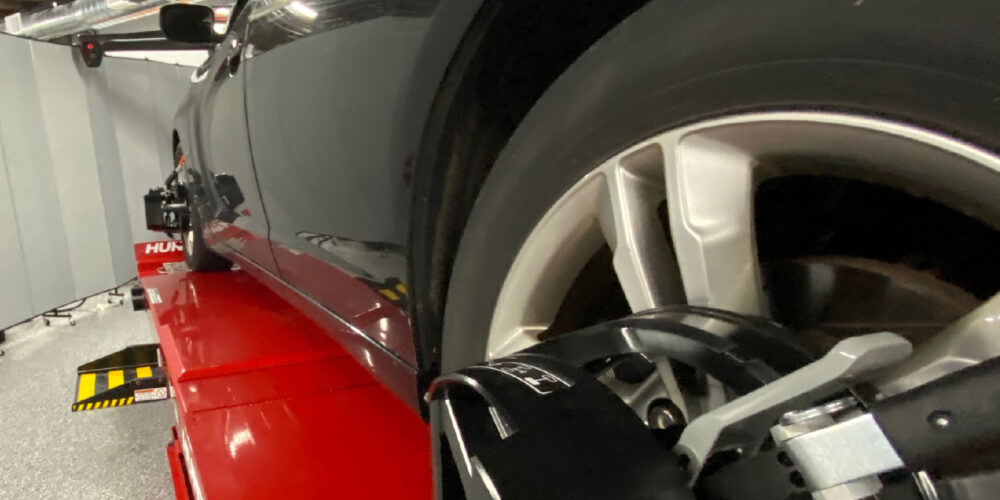
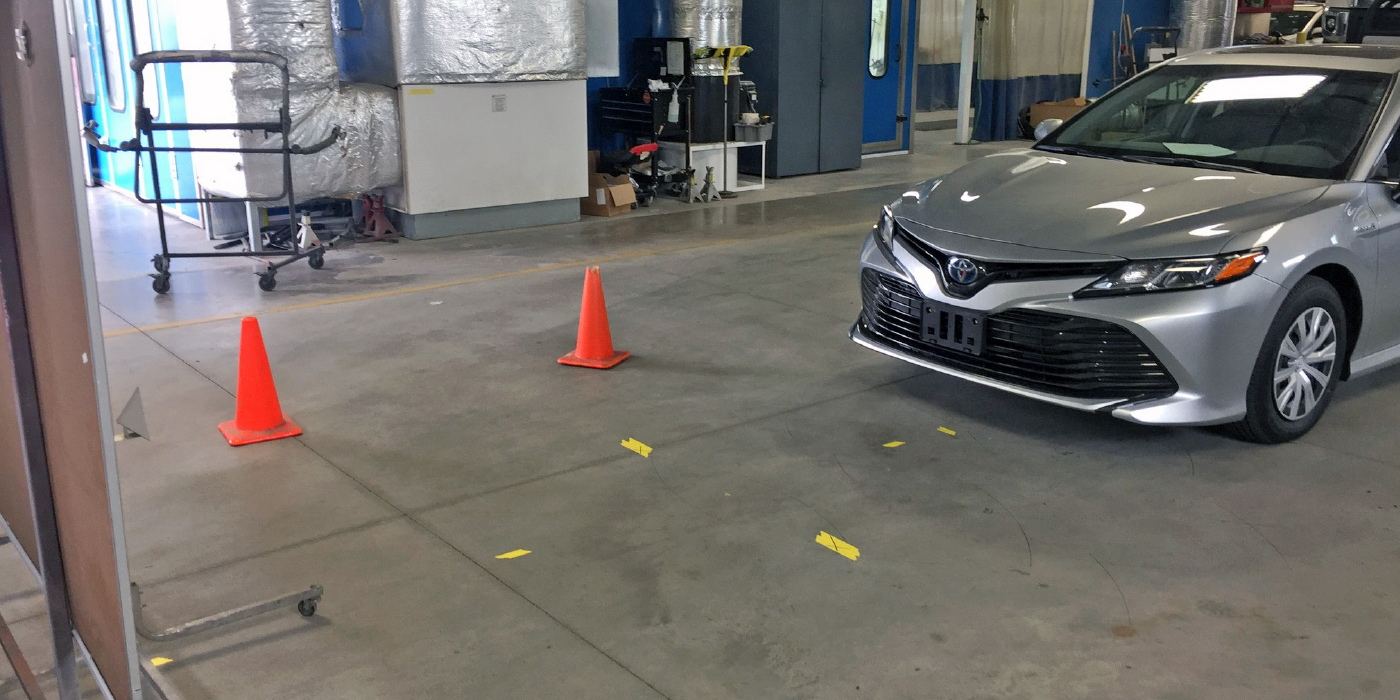
Most models require a static calibration procedure with targets mounted at precise distances. For some Mazdas, it may require three sets of targets. The systems require a scan tool to initiate the calibration of the sensors.
RADAR
Radars for the i-ACTIVSENSE system are mounted in the badges – the system operates on a vehicle traveling in front and adjacent lanes.
The radar operates on objects within the millimeter-wave emission range of the radar units placed behind the grille. The operation of the radar unit can be impaired by dirt or scratches. If the sensor is hit, the axis deviation due to impact around the radar unit can cause reduced performance or a shutdown of the system.
The system is not perfect. Driving on a continuously curving road, entrance to and exit of a curve, or narrow-lane roads due to road construction or lane closures can cause a false warning or activation of the system. Many Mazda owners complain that toll booths set off the collision avoidance system.
The other variables to consider are vehicle loads and even tire inflation. These items can change the aiming of the radar unit. Dirt on the radiator grille ornament, modifications and stickers (including transparent paint protection) can cause poor performance and abort the calibration process.
If the radar unit is installed at an incorrect angle, the radar unit cannot detect obstructions and the system may not operate normally. When installing the radar unit, verify that there is no damage or deformation to the installation part (shroud panel) and perform the installation correctly.
Two radar units that detect vehicles in the blind spots are mounted in the rear bumper cover.
Laser
Mounted behind the windshield with the cameras are two lasers to determine the distance of objects in front of the vehicle. The beam emitted is invisible – but it’s there. According to Mazda, if you try to inspect the laser with a magnifying glass, it can damage your eyes. The laser requires a static calibration using a target set at a precise distance and height from the centerline of the vehicle.
On these vehicles, the condition of the wipers is critical to the operation of the lasers. If the wipers leave streaks, it can impair the operation of the laser.
Calibration Tips
Calibration of the i-ACTIVSENSE system requires targets and a scan tool with software to communicate with the different modules. The calibration procedure can be aborted or set codes if the conditions with the vehicle and targets are not correct.
If the battery is not able to stay above 12 volts during the calibration procedure, it will also abort the process. Mazda says the voltage must remain in the range of 9.5-15.5 volts. Check for codes in all the modules. Codes in the ABS module, instrument cluster or any i-ACTIVSENSE module will prevent the calibration from being initiated.
Do not move or shake the vehicle during aiming adjustments by sitting inside or opening a door. Also, the engine needs to be off. Before starting the procedure, take the time to clean up the badges and windshield.