Nissan TPMS systems began appearing in 2003 as a standard feature or option on most models. And, for the past decade, the behavior of all Nissan TPMS systems is very consistent on all models.
There is only one trick to service Nissan TPMS systems, and that is to buy the right tools. A TPMS tool that can interface through the OBD II port is needed to profitably perform Nissan TPMS relearns and sensor replacement. Lost business and productivity will result if you try to avoid making this investment.
TPMS Light Diagnostics
The most common complaint you will get in your shop is low inflation. If you get a Nissan in your shop where the light stays illuminated, it is an indication that the system is operating normally and has detected a low tire. The first procedure should be to inflate the tires to the specified pressure and drive at speeds above 16 mph for at least three minutes to turn the light off.
If the system is malfunctioning, the light will flash for one minute and then stay on. The pattern of the flashing can indicate if a specific sensor is not activated (ID not present in the module). However, this will not indicate sensor malfunctions like low battery voltage, transmitter loss of signal or another system malfunction. Retrieving this data requires a scan tool that can communicate with the body control module (BCM). It is possible to ground a connector under the dash to read the codes by counting the flashes, but this can be like reading Morse code.
Sensor Operation
Most Nissan TPMS systems use a single receiver that detects signals from the four sensors (five if the spare tire has a sensor). The sensor transmits ID and pressure information at specified intervals or if a rapid deflation event is detected. The sensors have small accelerometers that trigger operation when the vehicle is moving.
The receiver knows where the sensor is located by the transmitted ID number and matches it to the number stored in the receiver module. The sensor may also transmit battery information if the voltage is below a specified level.
Never assume that the failure of a sensor to register means that the sensor has failed. Sensors are sensitive to how they are installed on the wheel. Changes in the mounting position of the sensor can interfere with the activation tool as well as the sensor’s transmission. Always make sure the sensor’s body is parallel to the wheel. And, if a sensor is not registering during a stationary relearn procedure, try rolling the vehicle a foot or two. This can help to position a sensor so brake or suspension components are not blocking it.
Nissan uses TPMS sensors from Continental, Schrader and Pacific. Sensor service kits and valve stems are not interchanged between the different styles. Nissan did change sensors on some vehicles in the middle of a model year, particularly in 2010 when its supplier in Thailand was flooded.
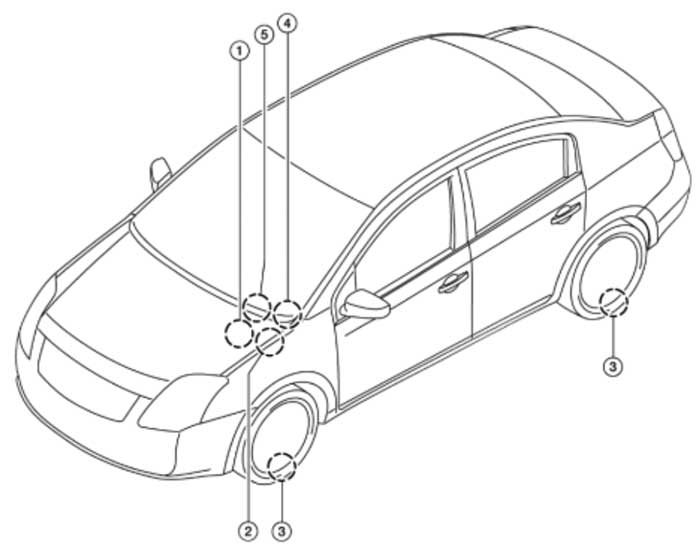
The “Corporate” Relearn
Unlike some domestic systems where a relearn procedure can be performed by just pressing a few buttons on a key fob, most Nissans require the use of an enhanced/factory scan tool or dedicated TPMS tool. The tool must be able talk to the BCM through the OBD II port to initiate a learning mode or input sensor IDs.
This is sometimes called a “corporate” TPMS relearn procedure because it once could only be performed with an OE scan tool, but now there are aftermarket tools and software that can perform the task.
The OE method is to put the BCM into a learn mode with a scan tool and activate the sensors with an activation tool. The activation tool sends a low-frequency signal to the sensor’s antenna. This “ping” tells the sensor to transmit.
With some tools, it is possible to excite the sensor with a low-frequency signal and record the information with the tool. The information can then be programmed into the TPMS module through the OBD II connection.
Another option if you do not have an activation tool is to go for a test drive with your scan tool.
First, set the tire pressures to:
Left Front: 34 psi
Right Front: 31 psi
Right Rear: 29 psi
Left Rear: 26 psi
Then, use the scan tool to put the BCM into “ID registration” mode. Drive the vehicle at 25 mph or more for several minutes until the scan tool tells you it is “done” and that all the IDs are registered and assigned to the four different tire pressures. After the test drive, inflate the tires to the correct pressure. This is a last-ditch procedure if your activation tool is not working, or if there might be issues with the sensors’ antennas.
Advanced Diagnostics
The receiver for the system is typically located under the dash. Depending on the model, the system may or may not share the antenna with the keyless entry system.
The BCM communicates with the instrument cluster through the CAN bus to turn on the TPMS light or display the tire pressures on the driver information center.
If you are pulling “no communication” codes, the TPMS problem may just be a symptom of a larger problem. For example, if the BCM is not able to communicate with the ABS or transmission module needed to determine vehicle speed, the TPMS system will not operate and turn on the light.
Nissan is the fourth largest make on U.S. roads. It is estimated more than 14 million Nissans are equipped with TPMS systems, representing a significant service opportunity for a shop. Trying to get around the investment in a proper TPMS tool by grounding wires under the dash is not a practical or efficient practice for a professional shop.