Any time you’re dealing with a combustion engine, there’s a chance it will develop a misfire. A better understanding of how computer systems analyze a misfire can make your job that much easier as the service tech.
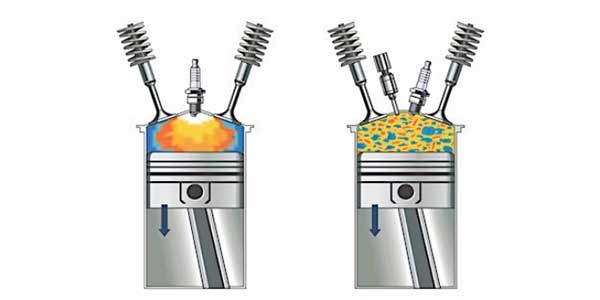
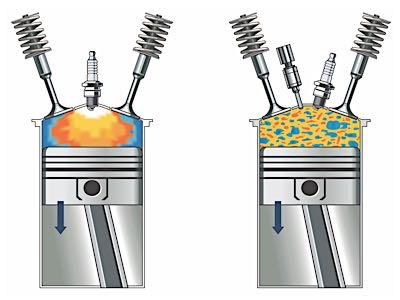
With most engines, the crank sensor is the key component in determining a misfire. The PCM calculates the time between the edges of the crank reluctor wheel teeth by receiving a signal from the CKP sensor. The crankshaft rotational velocity and acceleration are compared in the event of a power loss from each cylinder.
When a power loss is less than the calibrated value, the suspected cylinder is determined to be misfiring by the PCM. The misfire detection is enabled after certain base information is received by the PCM. Typically, engine coolant temperature, cylinder head temperature, intake air temperature and, if equipped, the mass air flow sensor (or a combination of these) are used to evaluate the condition as well as the crank and cam positions.

DTCs P0300 to P0310 indicate a random misfire per the individual cylinders. Of course there are other codes that can be related to a misfire as well. These include P1336 (crankshaft/camshaft performance), P0606 (PCM), P0315 (CKP not learned), P0316 (misfire detected at startup) and many more. Generally speaking, the rate of misfire is calculated every 200 to 1,000 revolutions.

Almost every emission problem that causes hydrocarbons to exceed 1.5 times the federal limit will cause the check engine light to come on even if there are no symptoms noticed by the driver. On some vehicles, the PCM will disable a particular cylinder’s fuel injector if the misfire is bad enough to cause raw fuel to be sent to the catalytic converter. This is generally determined by the comparison of the up and down stream O2 sensor information sent to the PCM. When the converter’s efficiency drops below a predetermined value, the service light will turn on.
False failures are just one more thing to look into. With the sensitivity of these sensors, they can generate a false misfire under certain conditions. For example, driving on a very muddy or dusty road can throw debris into the reluctor teeth (on engines with external reluctor wheels mounted on the crankshaft). Water in the fuel tank can be sent through the injectors and cause a misfire condition or even a lean condition, which can also cause the PCM to see a misfire — usually a random misfire code and not an individually isolated cylinder misfire.

Sometimes, the misfire is intermittent, which presents its own issues when it comes to diagnosing the problem. A visual check of the usual causes of a misfire and monitoring the engine with a scanner under the conditions the misfire was detected is usually the best way to determine the failure point.

Some mechanics prefer using mode 6 to monitor misfires, and in some cases, that is the only option to see individual cylinder misfires. Although it can be a bit confusing when it comes to reading mode 6 information, a scope is by far my preferred method when it comes to those engine setups. Obviously, fuel pressure, cylinder compression and all the sensors have to be in working order to keep things from misfiring.

Your job is to sort out which parts of the scenario aren’t performing correctly. Knowing the correct values and how the systems are supposed to work will greatly improve your diagnostic skills. Article courtesy Underhood Service.