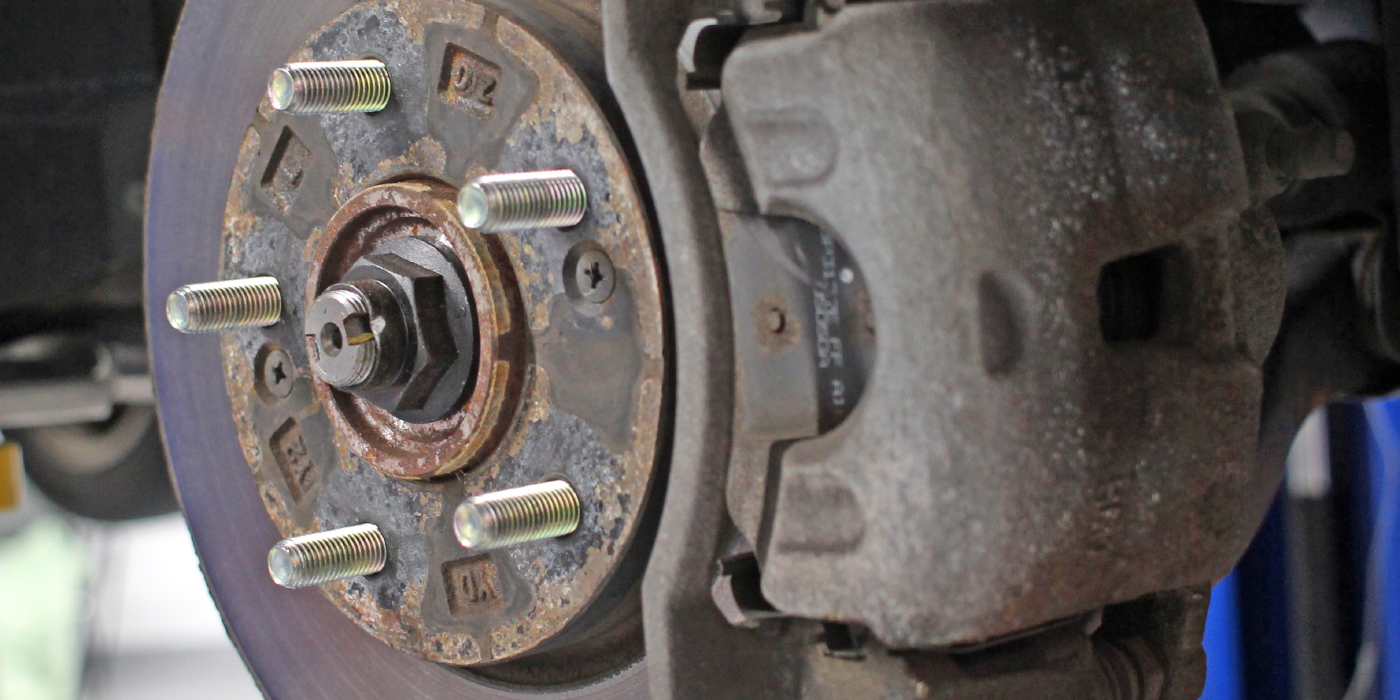
GM’s Alpha platform is a rear-wheel-drive or all-wheel-drive platform used for the sixth-generation Camaro. This generation includes a variety of engines, ranging from a 2.0L turbocharged four-cylinder to a 6.2L supercharged V8. With this wide range of powertrains, the brake systems technicians may encounter can vary depending on what is under the hood.
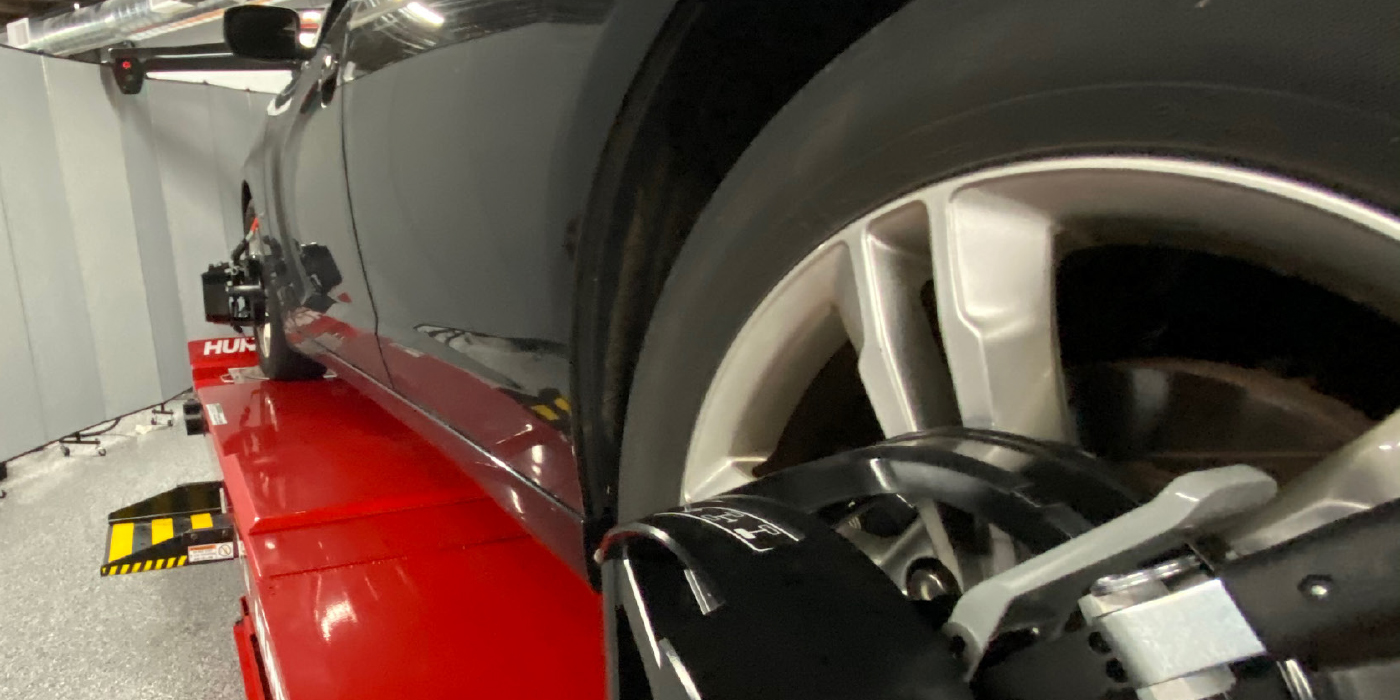
For most four-cylinder, V6 and some V8 models, the front brakes have 12.6˝ vented rotors with four-piston fixed calipers (J55) or single-piston caliper (JL9). In the rear, the rotors are 12.4˝ with single-piston floating calipers. The Brembo option or the J6G brake package uses four-piston fixed rear calipers. Sorry for all the Js, but knowing the letter can save you from ordering the wrong parts.

Rotor
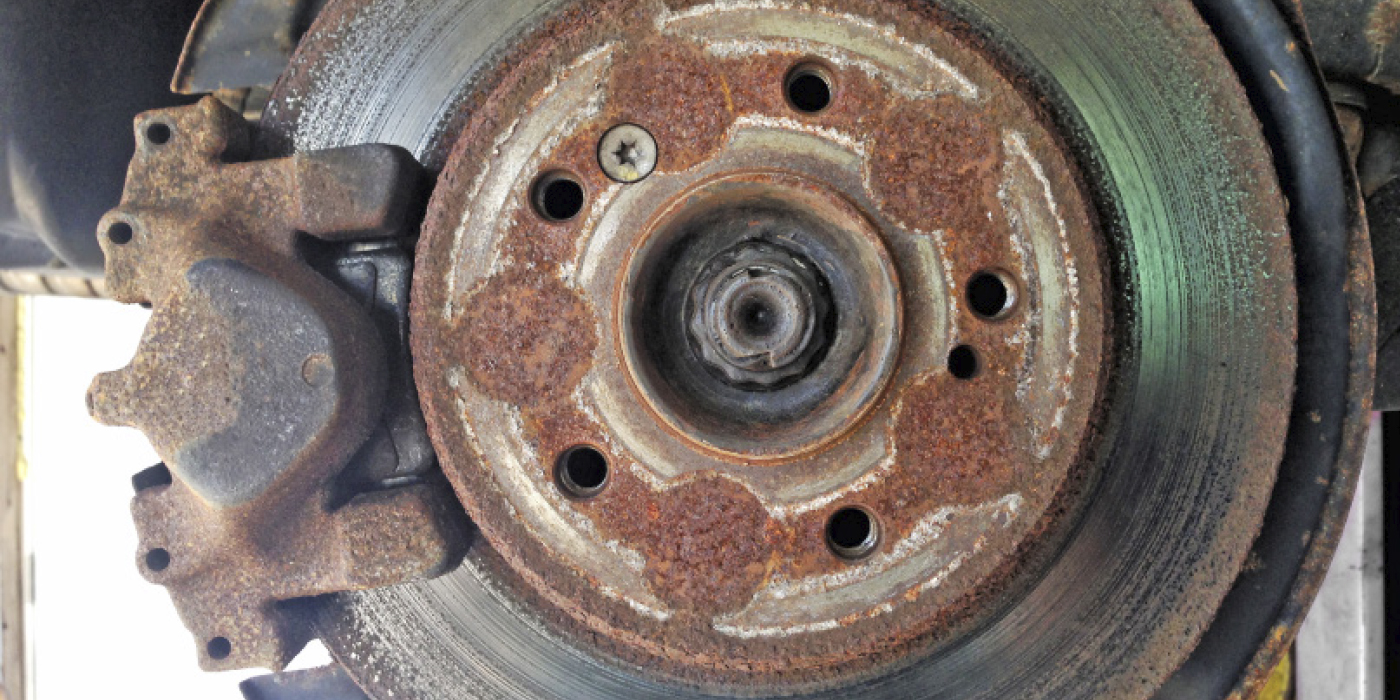
The base brake package comes with Ferritic Nitro Carburized rotors for corrosion resistance. This is an additional step in the manufacturing process of the brake rotor that creates a hardened outer layer on the surface of the rotor. This hardened outer layer reduces the amount of rotor rusting (corrosion) and it also allows the rotor to wear slower. Because this new technology protects against excessive rotor corrosion, it not only aesthetically looks better through open-spoke-type wheels, but helps reduce thickness variation, which creates pulsation specifically due to “lot rot” corrosion (when the vehicle sits on the dealer’s lot between build delivery and customer delivery).
In the service information for the Camaro, Chevrolet offers diagnostic steps in case there is a vibration concern that can’t be solved by balancing the wheels. The cause of the vibration could be the brake rotors due to their large size. The diagnostic procedure is to remove the wheels from the drive wheels (with lug nuts attached) and then run the vehicle at the speed of the reported vibration. If the vibration is present, remove the calipers and rotors and see if the vibration is gone.

GM also recommends inspecting the rotors on a tire balancer. Mount the brake rotor/drum on a balancer in the same manner as a tire and wheel assembly. Ignore the dynamic imbalance readings – use only static imbalance readings.
There is not a set tolerance for brake rotor/drum static imbalance. However, any brake rotor/drum measured in this same manner that is over 21 grams (3/4 oz) may have the potential to cause or contribute to a vibration. Rotors suspected of causing or contributing to vibration should be replaced. Any rotor that is replaced should be checked for imbalance in the same manner.

Parking Brake
The sixth-generation Camaro can have different parking brake configurations depending on the calipers. The J71 brake package uses a motor mounted on the caliper. The J77 package uses a cable puller system for the drum-in-hat parking brake. Remember J71 and J77 when you are ordering brake hardware or parking brake components.

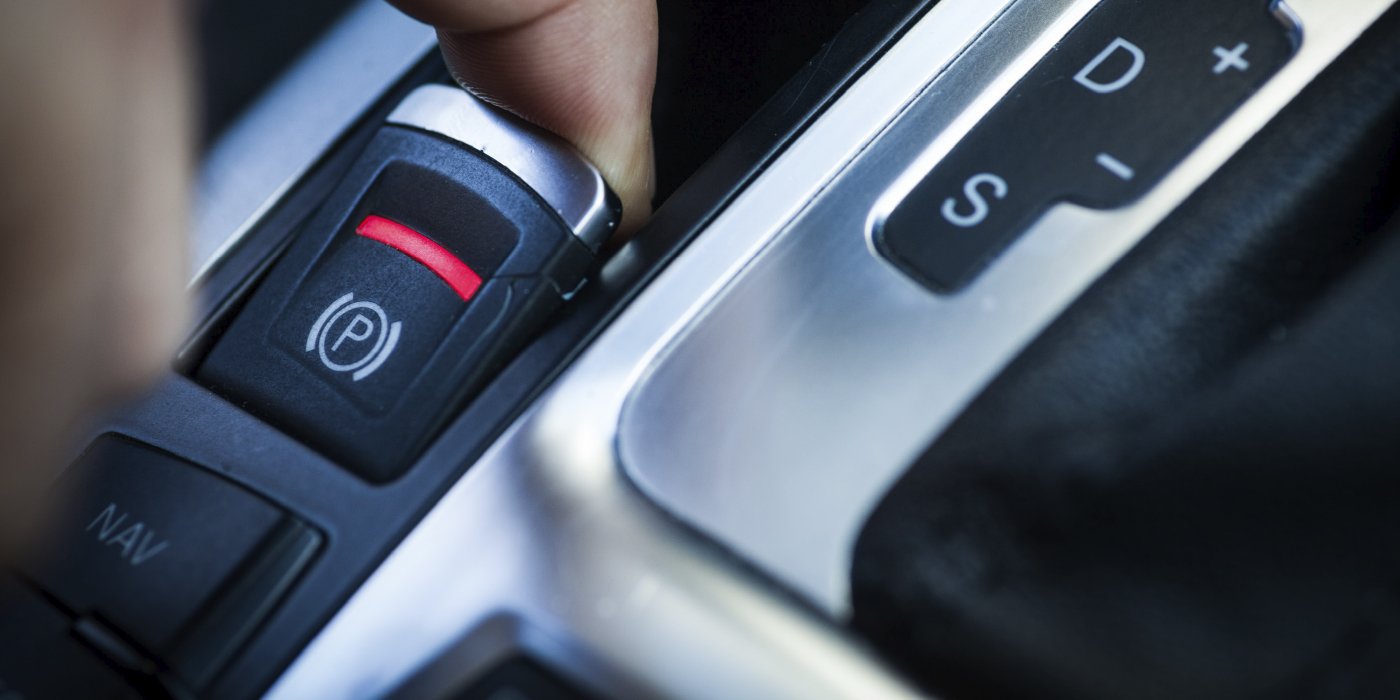
There are no workarounds in the service information to retract or adjust the rear parking brake. Use of a scan tool is required. Do not try the change the position of the pistons using mechanical methods, jumper wires or disconnecting the battery.
Brake Pads
With brake packages using the opposed piston calipers, it is a different approach when it comes to hardware and lubricants.
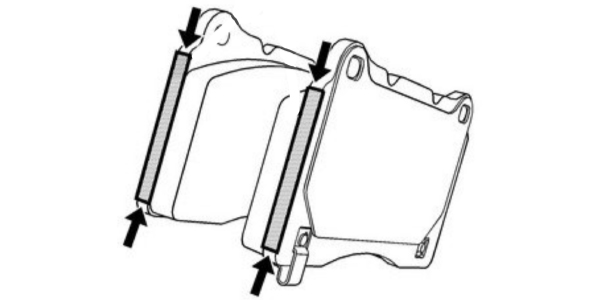
When the pads are replaced, always replace the pins and anti-rattle clips. For lubricants, apply a light coating of anti-seize or brake lubricant to the left and right edges of the backing plate.