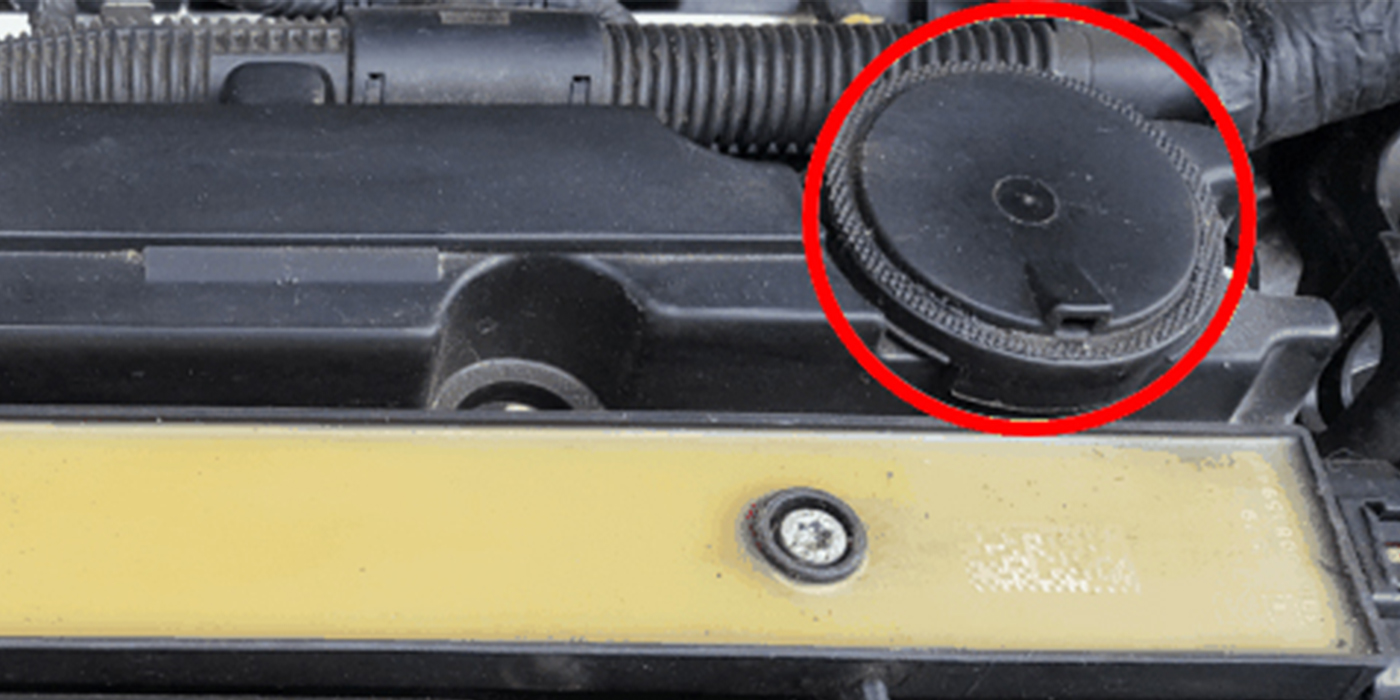
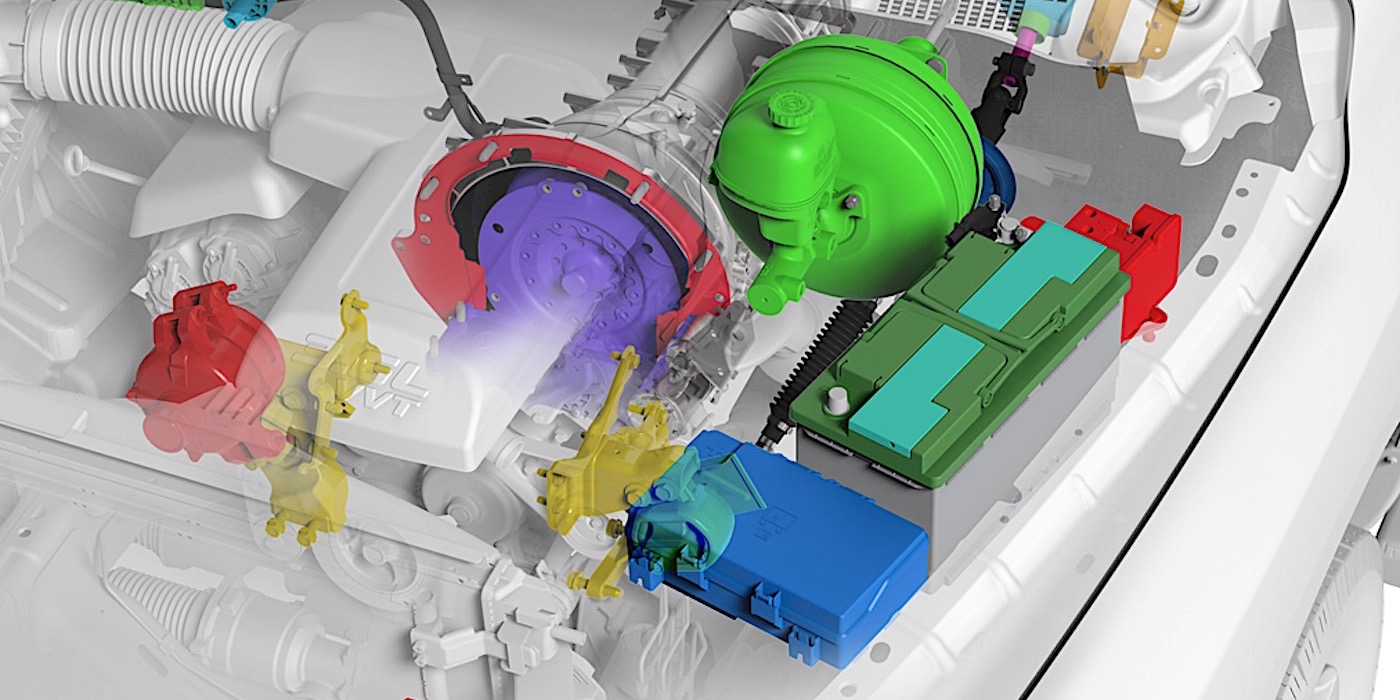
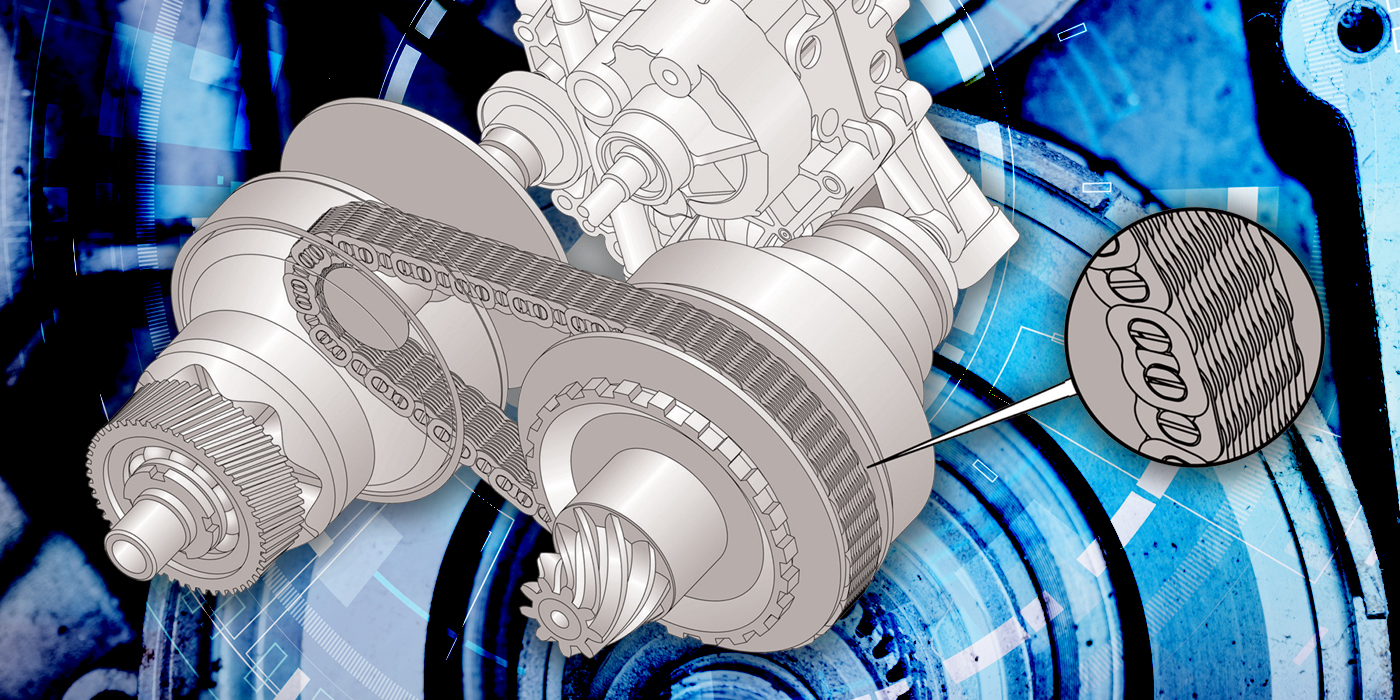
Idle quality is challenging to diagnose because it is a vague description at best on most Volkswagens. The textbook definition is an engine speed lower or higher than the specification in the service manual. For drivers, idle “quality” is more difficult to define.
Idle quality could be classified as vibration. However, vibrations can be caused by multiple components, including broken engine mounts. Running conditions that cause misfires can also cause “rough running” or a vibration felt by the driver. Capturing a driver’s complaint and replicating it is critical. Knowing when the idle quality issue occurs is just as crucial of how it feels.
How is idle speed controlled?
Volkswagen fuel injected engines can regulate the idle speed two ways. Some engines have an idle air control or idle stabilization valve. These valves are bypasses around the throttle plate. The flow is controlled by an electric motor. Most late-model Volkswagen throttle by wire systems might not have an idle control system. The angle of the throttle plate is used to control idle speeds. The amount of air allowed to pass for the idling of the engine is typically displayed as a data PID that can be a percentage or angle on a scan tool.
Changing the amount of air means changing the amount of fuel. To create the optimal idle mixture, the engine control module will adjust the open time of the injectors. If the mixture is too rich or too lean, the resulting misfire will create a rough idle.
How is idle speed setting determined?
Idle is not just a number that the engine control module tries to match. The goal of the ECU is to keep the idle speed consistent under changing engine loads from the A/C compressor, alternator and other components. These loads are predictable and anticipated. When an A/C compressor is given the command to engage, the ECM will increase airflow and fuel to the engine. This is usually undetectable by the driver. There are expected loads, and unexpected loads or changes inside the engine that change the idle.
The ECM knows how much suction should be produced by the throttle position data for the engine speed. The amount of air sucked in can change if the pump is not operating correctly. Changes to camshaft timing, restriction in the exhaust or burnt intake valves can change the amount of air required to keep the engine idling smoothly.
The air is measured by a manifold air pressure (MAP)or mass airflow sensor (MAS). A MAP measures negative pressure. A MAS measures the amount of air flowing through intake before the throttle plate. Some engines have both a MAP and MAS.
Some of the greatest idle quality killers are leaks in the intake manifold. To a MAS sensor, the air coming through is unmetered, and the ECU thinks the engine is running too lean so it adds fuel. To a MAP sensor, the leak is seen as a signal the engine is using less air so it takes away fuel. These strategies can result in a change in the quality of the idle. A MAS-only system may have a high idle. A MAP system might stumble and run rough. Modern systems are better at controlling the idle and compensating for the problem, so it will not leave the driver stranded. But, it will still run rough and it will turn on the check engine light.
Misfires
Between combustion events, every engine slows down just a tiny amount. If a cylinder is not firing, it slows down even more but still has to speed up when the next cylinder is fired. This makes for a very poor idle. The cylinder can often be isolated using misfire codes or using the misfire counters.
Courtesy of Brake & Front End.