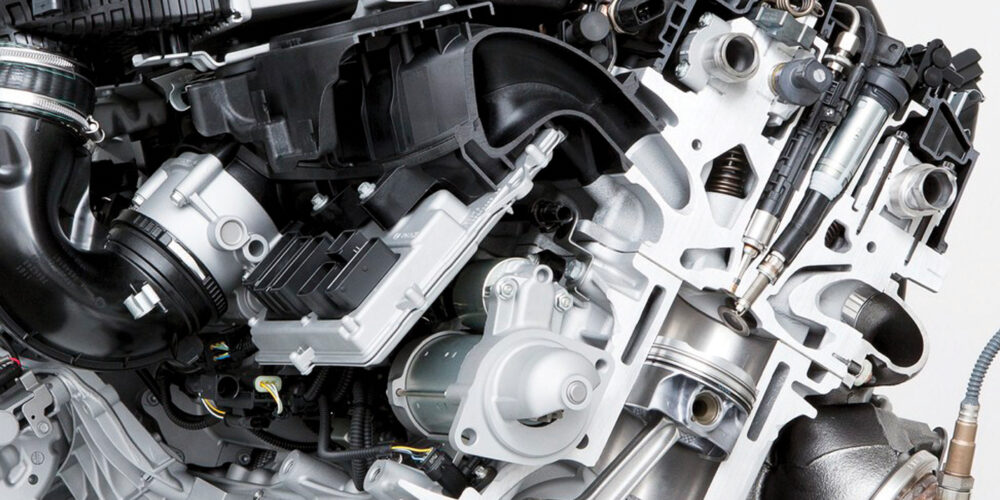
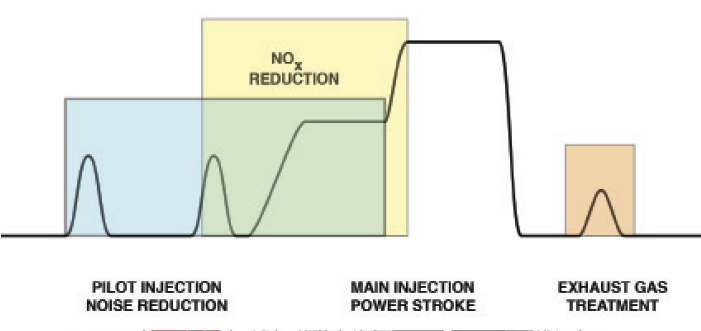
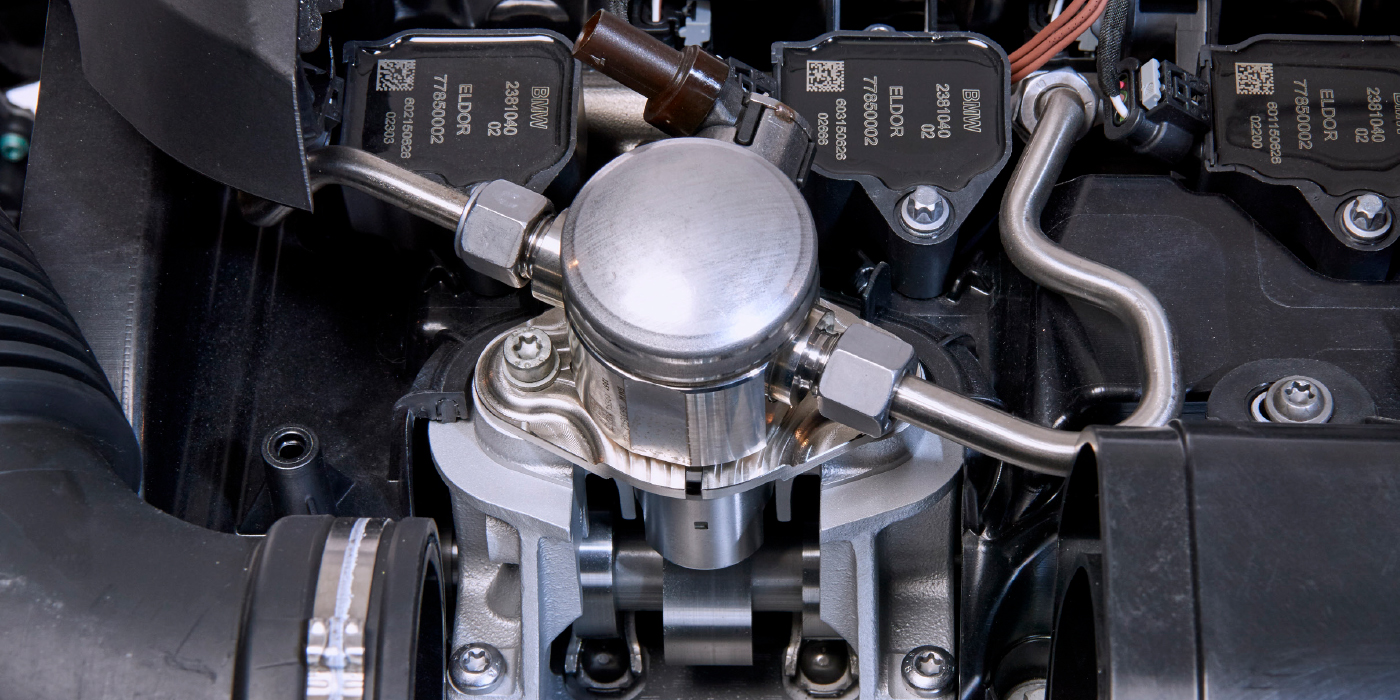
Because gasoline direct injection was popularly introduced during the 1990s, the configuration of any GDI system will vary according to age and application. Nevertheless, as an overview, the heart of the GDI system is a low-resistance conventional magnetic solenoid injector or a piezoelectric fuel injector, a high-pressure mechanical fuel pump, a contoured combustion chamber and a modern air/fuel ratio sensor.
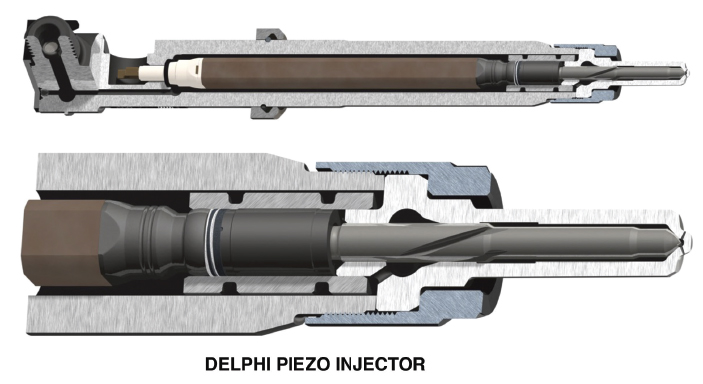
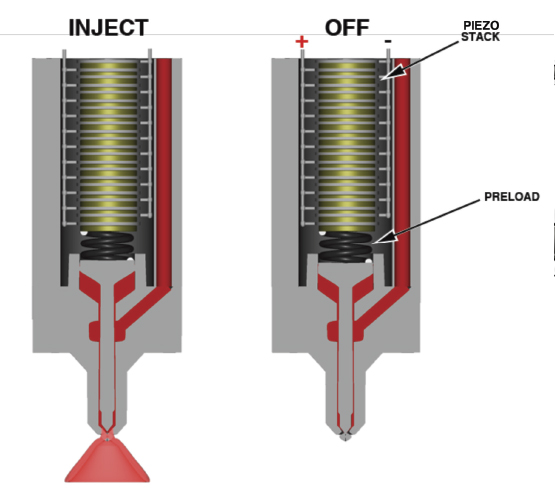
In contrast to the magnetic solenoid injector, the piezoelectric injector is composed of crystal wafers. When the wafers are electrically energized, they expand to produce the high mechanical pressures needed to open the injector pintle valve under 2,000 psi of fuel pressure. These crystal wafers are stacked in the GDI fuel injector so that they can nearly instantaneously pull the injector pintle valve open to admit fuel to the cylinder. Due to their design, operating voltages can range up to 90 volts at 15 amperes of current flow. Nozzles vary in design to ensure that the stream of fuel entering the cylinder conforms with the shape of the combustion chamber.
The high-pressure mechanical fuel pump, which is driven by one of the engine’s camshafts, is supplied by a conventional, single-line, in-tank pump. Fuel pressure on the mechanical pump is usually controlled by a pulse-modulated bypass solenoid mounted on the pump body.
Since direct fuel injection requires high fuel pressures to overcome combustion pressures created in the engine’s cylinders, a typical high-pressure fuel pump can produce in the neighborhood of 2,000 psi maximum fuel pressure, depending upon operating conditions. Fuel pressures are monitored by a high-pressure sensor located in the fuel rail and a low-pressure sensor located in the fuel supply line.
Modified combustion chamber design is another major feature of GDI systems. Keep in mind that the injector can be positioned in the center or to the side of the combustion chamber, or against the cylinder wall. Center-mounted injectors can use a cup-like recess in the piston to shape and contain the incoming fuel charge.
Similarly, side-mounted injectors can use channels and recesses in the piston head to help shape the incoming fuel charge. And, since the stratified or “lean-burn” mode