Automakers have installed saddle-style tanks on several car models for more than a decade. This style of tank uses two wells, one on either side of a driveshaft or exhaust system. This position optimizes luggage compartment capacity, fuel volume and crash safety. The behavior of the fuel wells, pumps and sending units are often misdiagnosed, leading to fuel pumps being replaced unnecessarily.
Automakers have installed saddle-style tanks on several car models for more than a decade. This style of tank uses two wells, one on either side of a driveshaft or exhaust system. This position optimizes luggage compartment capacity, fuel volume and crash safety. The behavior of the fuel wells, pumps and sending units are often misdiagnosed, leading to fuel pumps being replaced unnecessarily.
Basics
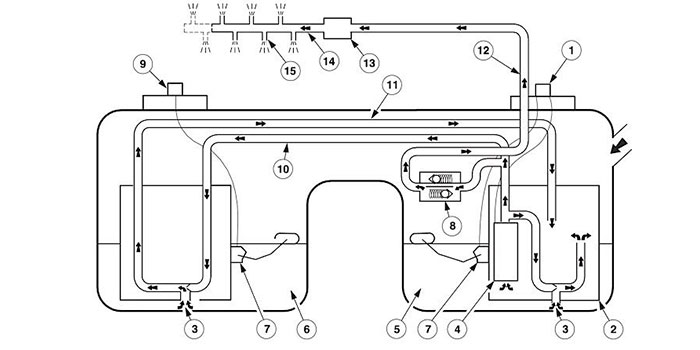
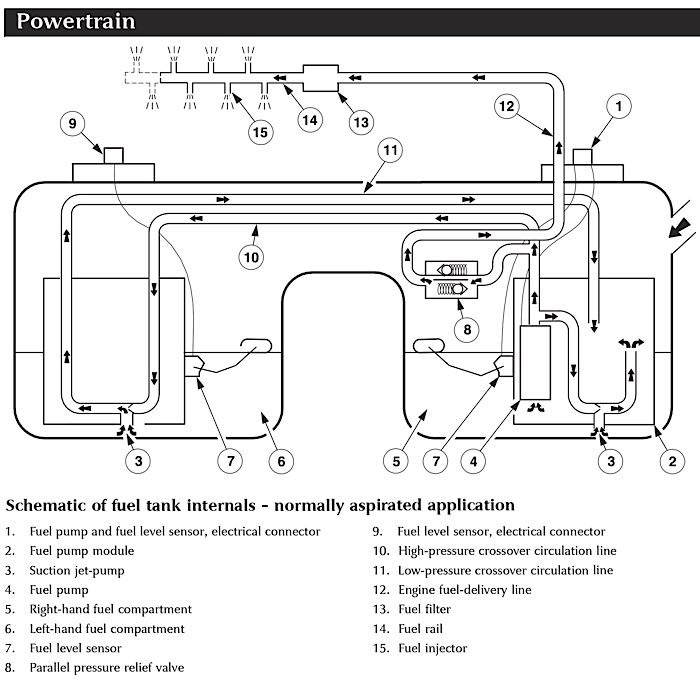
From the top, a saddle-style tank looks like one fuel tank. From the bottom, you will see two tanks. On most applications there will be a primary side that will have the pump that provides pressure to the fuel rail. This is typically the side that the fuel inlet fills first. The primary side usually uses a fuel pump module that connects to the vehicle over a serial data bus. The secondary tank contains a transfer pump, sometimes called a jet pump.
Almost all modern saddle-style tanks use a returnless fuel system that regulates the pressure to the fuel rail inside the tank. Older systems with a return line may use a suction jet that uses a venturi effect created by the returning fuel to suck fuel into the primary fuel well.
Both the primary and secondary wells contain fuel-level sender units. These are used to determine the fuel level in the tanks for fuel distribution, instrument panel readings and EVAP testing.
Fueling
During fueling, the primary side of the tank fills up first. Fuel then moves through a connecting passage to fill the secondary side. The transfer pump may be active on some systems during fueling.
If you are testing the operation of the transfer or secondary fuel pump, you might want to use a fuel caddy to drain the fuel, then pump it into the secondary tank to see if the pump sends it into the primary tank. This functional test might indicate if the pump and senders are working.
Running Mode
On most modern systems, the strategy is to keep as much fuel as possible in the primary tank so the primary pump is submerged and cooled by the fuel. The system will pump fuel from the secondary to the primary as the fuel is burned. When the secondary side of the tank is empty, the fuel pump module draws fuel from the primary side of the tank only. On some vehicles, the system will balance the fuel between the tanks to optimize weight distribution until the fuel reaches a specific level.
Typically, the operating criteria will be in the “operation and theory” part of the service information. Looking at this section is critical to diagnosing some systems.
Fuel-Level Calculations
The two fuel-level senders are critical to making saddle-style fuel tanks work. The fuel level sent to the driver is a reflection of the two sender inputs. The fuel pump module and the PCM also use the senders to determine if the system is operating properly.
In some cases, a fault at the secondary side of the tank will cause the gauge to default to the primary side sending unit reading. This results in a maximum reading of half-tank. This reading will stay the same until the fuel level on the secondary side is empty and fuel on the primary side begins to drop. A fault with the primary-side sender will cause the gauge to read empty.
Most fuel pump modules are able to identify problems with the secondary or jet pump from the behavior of the fuel-level senders. The module sets these codes based on readings from the fuel tank sender units. The code will set when the PCM detects that the secondary side of the tank still has fuel stored and the primary-side fuel level begins to drop.
In some cases, the fuel level will still read quarter-tank or more when there is no fuel pressure. The primary pump will function and the circuit to the pump will be intact with no voltage drops. If the pump is replaced, the condition will return.
Ground connections and wiring harness issues are common problems for saddle-style tanks. If you have excessive voltage drops or inconsistent fuel-level readings, check the connections at the body and chassis grounds for excessive resistance. The top of the tank will often collect road salt and deicing brines that can cause shorts to ground.
Article courtesy Underhood Service.