TPMS relearns for the 2011 Toyota RAV4 are fairly straightforward and simple.
The RAV4 doesn’t have a reset button underneath the dash or within the glove box, meaning technicians don’t have to worry about getting a TPMS relearn malfunction due to the vehicle’s ECU closed loop. This also means that in order to successfully service the RAV4’s TPMS, a shop needs a dedicated TPMS scan tool.

Photo 1: Using a dedicated TPMS scan tool allows technicians to quickly capture sensor data including tire pressure, sensor battery life and sensor IDs. This information can be shared with the customer and/or used when performing a relearn.
The scan tool will also need to connect through the OBDII port to complete a relearn procedure and to replace a TPMS sensor that has a different ID number.
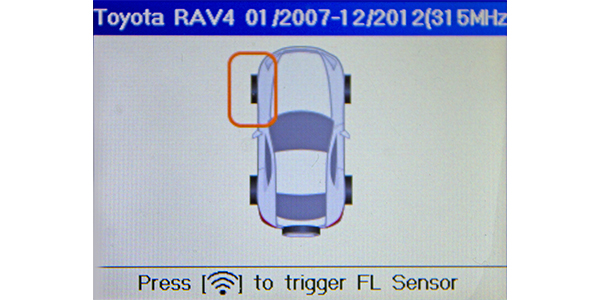
Photo 2: Make sure the vehicle’s ignition is in the off position.
After inflating all tires to the psi listed on the vehicle’s door placard, follow all the prompts on your TPMS scan tool to collect sensor IDs. Don’t forget to collect the full size spare’s information as well.

Photo 3: Plug into the OBDII port located under the driver’s side instrument panel. You will be prompted to then turn on the ignition of the vehicle, without starting the engine. Following the scan tool prompts, continue until a successful relearn is performed.
Once all the IDs are relearned, the TPMS light will go off in the display panel.

Photo 4: Direct TPMS uses radio signals to send sensor data to a vehicle’s module. The majority of sensors are activated with a low-frequency signal, and this can be prone to interference.
Anything transmitting in a similar frequency range, such as an electric motor, appliances and cell phones, can interfere with sensor communication. Additionally, anything that may block a radio signal, such as metal, may also cause interference with a signal.
It is also a good idea to keep TPMS sensors away from each other during a relearn. If sensors are too close together, a different sensor may be triggered and relearned instead of the one that is needed.

Photo 5: While sensor kits may seem so tiny and insignificant, not replacing the kits could cause big problems with tire pressure and vehicle TPMS if not properly serviced.
It’s critical to never reuse a valve stem. Valve stems are subjected to heat from both the brakes and road and can degrade over time. Always use the valve core included in the kit. Replacing the valve stem core will prevent future leaks.
If a nut is reused, the anodized aluminum surface (which prevents against galvanic corrosion and material deterioration) could be scratched away. This could cause corrosion between the sensor, wheel and stem making the nut impossible to torque to the correct specifications or remove due to corrosion on the threads.
Reusing seals and grommets can also cause problems. On the sensor, the two grommets help seal the nut to the wheel. As soon as the nut is torqued, the grommets conform to the shape of the wheel. This is the previous shaping and can’t be fixed, and reusing these pieces may cause a slow leak.
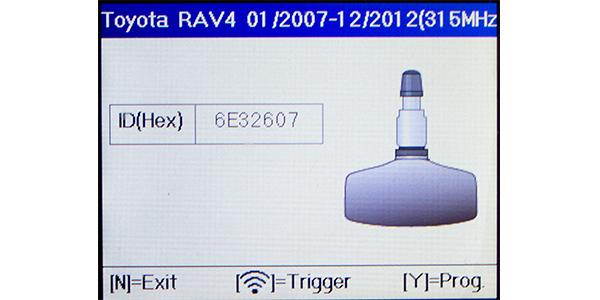
Photo 6: The RAV4 utilizes direct TPMS.
Article courtesy Underhood Service.