The first electric fuel pump circuits were very simple. The pump circuit usually involved a relay and fuse. The control side to the relay was typically wired to an ignition circuit or key switch. The control of the fuel pressure was performed with an analog regulator that could keep a static pressure and adjust for loads with a vacuum signal.
This forced the fuel pump to operate at full battery voltage the whole time no matter the load on the engine. This is not good for the life of the pump. In the early 1990s, vehicles had circuits that used resistors controlled by the engine control computer to slow down the pump and extend its life. These systems operated like a blower fan motor controller.
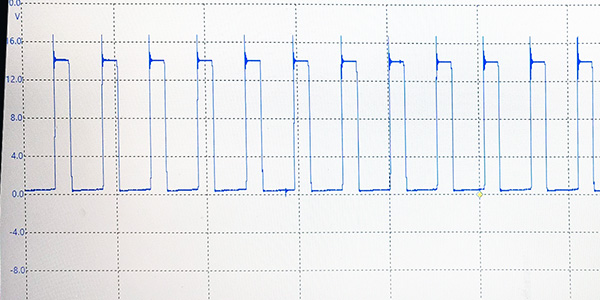
The major shift was when fuel pumps became controlled with pulse-width moduled voltage. The fuel pump was now driven by a signal that changed in duty cycle to control the speed of the motor and pressure delivered to the fuel rail. The driver for these fuel pump circuits was part of the engine control module. Soon after, manufacturers moved the driver for the fuel pump to modules in the rear of the vehicle. Some manufacturers moved the control of the pump to a rear electronic module; some moved it to a dedicated fuel tank module that also performed EVAP control.
As the control for the fuel pump moved to modules, codes for fuel pumps became more common. Some of the most common codes you will see are codes for the fuel pump circuits. These typically indicate the circuit is open or the voltage is too high or low which indicates a short or high resistance in the circuit. Some of these codes are generic, but if the module is separate from the engine control module, you could be dealing with manufacturer-specific codes.
The module that drives the fuel pump is typically looking for data PIDs from the engine. The data PID for fuel pressure can be critical in a diagnosis of a fuel pump. It can also save you from hauling out the fuel pressure gauge and the assorted fitting to make a connection. Also, some vehicles have eliminated the test port on the fuel rail. But, how do you know the fuel pressure sensor is bad?
The fuel pressure sensor usually has three wires and operates on five volts. As the fuel pressure increases, the resistance changes. The sensor monitors fuel system pressures and the performance of the pump. If the sensor is not getting a clean five volts, the voltage on the signal side will change. On some systems, this could cause the pressure to read lower than normal and creates some fuel pump performance codes.
Observing the fuel pressure PID during a test drive can give you insights into the health of the pump. If the pressure drops dramatically when accelerating, it could be a sign the pump is failing. The pressure should not change much during differing engine loads and speeds. This is because the pump is responsible for providing the correct volume while the pressure remains the same. Fuel pressure for most vehicles should stay in a 5-10 psi range. But, make sure you look at the service information for the specifications.
Other data PID used to regulate the fuel pump includes the engine position sensors. Additional data used to control the pump could be the engine load and fuel requirements. The goal of these sensors is to provide the correct amount of fuel pressure at the fuel injector so when the fuel injector opens, it shoots an accurate amount of fuel into the cylinder with a proper spray pattern.
Sensing if there is a problem with the fuel pressure caused by a pump that is not producing the correct pressure might be able to be seen in several data PIDs like fuel pressure and fuel trims. Driveability symptoms of a weak fuel pump might be a loss of power.
Some vehicles will record the fuel pressure as part of the freeze frame if a code is stored. This can help you track down an intermittent fuel pump problem.
Since the fuel pump module needs information for various sensors, it usually communicates on a serial data bus. If modules are not communicating, the fuel pump can’t be adequately controlled. The key to investigating these problems is to communicate with different modules to see what data PIDs are present and which ones are missing.
Article courtesy Underhood Service.