No road is entirely flat. Even a small tar strip or dip causes movement in the suspension. This movement is controlled by the spring and dampener. No matter the type of movement, the spring is compressed and then releases the energy into the body, dampener or road.
During this cycle, the steel of the spring will compress, and just a little bit of life is taken out of it. It’s not the amount of travel that matters, but the frequency of the cycles. As a suspension exceeds 80,000 miles, the number of cycles could be in the trillions. This is why springs wear out and break.

A spring’s design is tuned to many factors. Engineers will use terms like frequency and amplitude to describe spring construction. For the layman, these terms translate to how fast and how far the spring has to travel. Frequency and amplitude are tuned for ride quality, center of gravity and the sprung weight of the vehicle.
One area of the spring might be great for controlling body lean, but it could be too hard to give a comfortable ride. To increase the versatility of the spring, engineers can tune the coils so it is progressive and change the spring rate when they are compressed or are put under certain forces.
Changing the spring rate of a coil spring is not easy. Engineers can change the spacing and pitch of the coil to generate different spring rates. They can also change the geometry of the spring by making it a barrel shape that affects how loads are absorbed. Also, how the spring is formed and treated can influence the spring rate. Progressive spring designs have one disadvantage — they can fatigue in specific areas. When this happens, the spring can break.

Why Springs Need Replacement
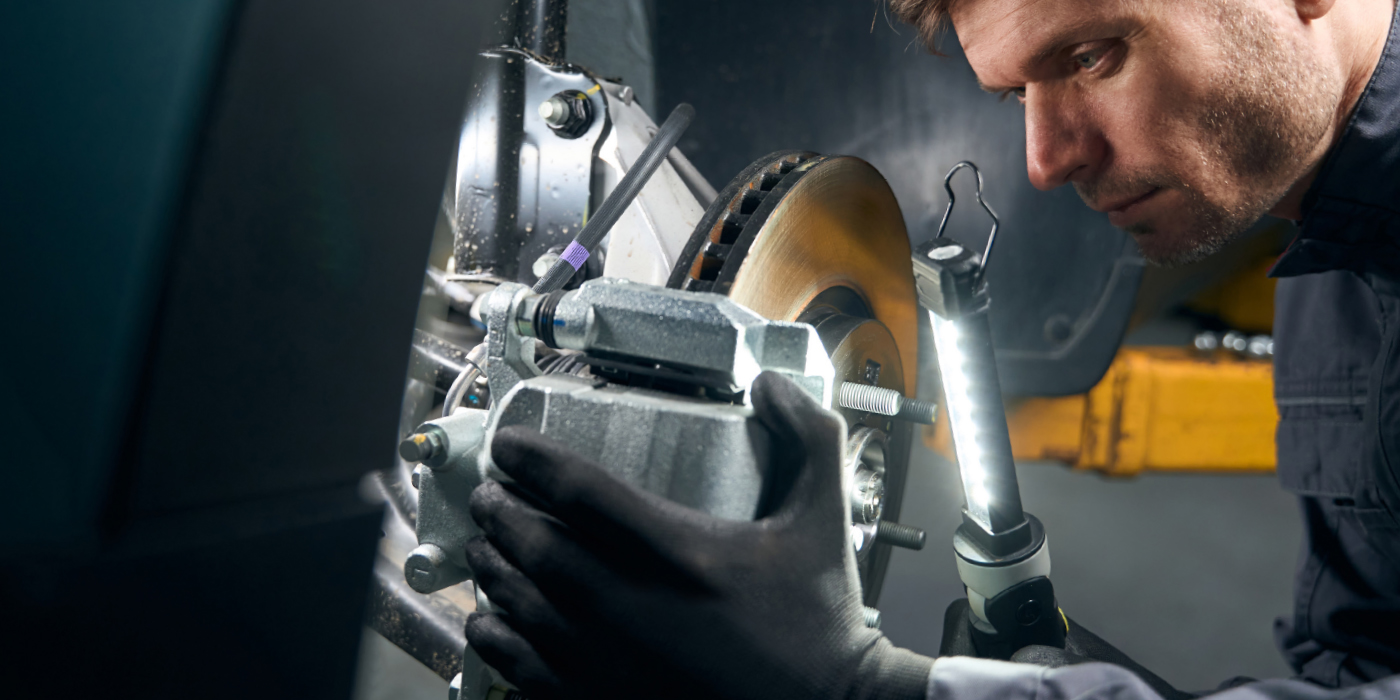
If you were rebuilding an engine with new heads and camshafts, would you reuse the old valve springs? Probably not, because that would impact performance. Likewise, on some high-mileage vehicles, when the struts are replaced, the performance of the springs no longer matches that of the new strut. When a new strut is reassembled with the old and tired spring and strut plate, the results can be less than desirable.
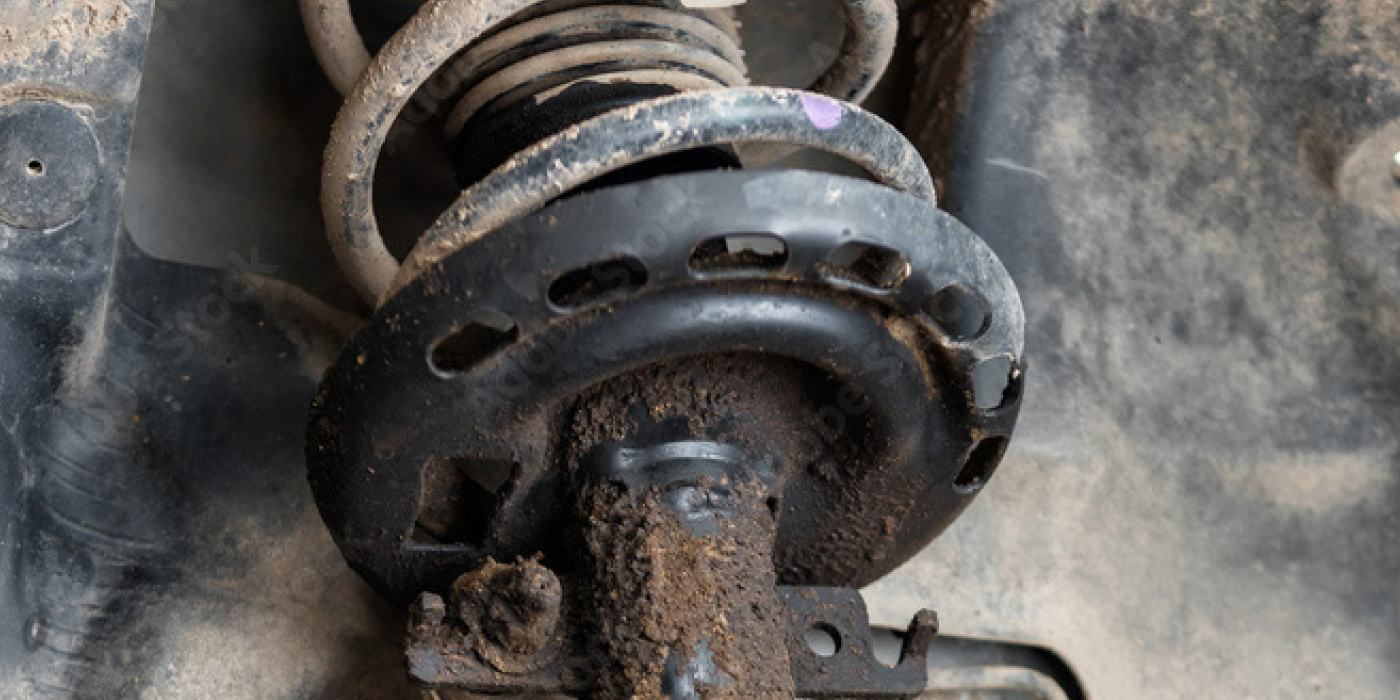
Tire wear, steering and handling can also be affected by ride height and the health of the spring. If the chassis is sagging on one side, or in the front or back, weak springs are the likely culprit. Weak springs can affect both camber and caster, which may result in a steering pull, a change in steering effort or return and/or uneven tire wear.
Look up the ride height specifications and measure ride height in the front and rear and on both sides of the vehicle. If ride height is less than specifications or the measurement exceed tolerances, the problem is most likely one or more weak springs that should be replaced. In some cases, the manufacturer will also recommend a test drive to inspect the condition of the springs. Springs should usually be replaced in pairs to maintain the same ride height side to side. In most cases, all four springs should be replaced at the same time.

Weak springs are also more likely to fail when a new strut or shock is installed. The springs on many late-model vehicles are thinner to reduce weight and have an outer plastic coating to protect the metal from corrosion. If this outer coating is cracked or damaged, corrosion can form a hot spot that eats into the spring, weakens it and eventually causes the spring to break.
Article courtesy Brake & Front End.













