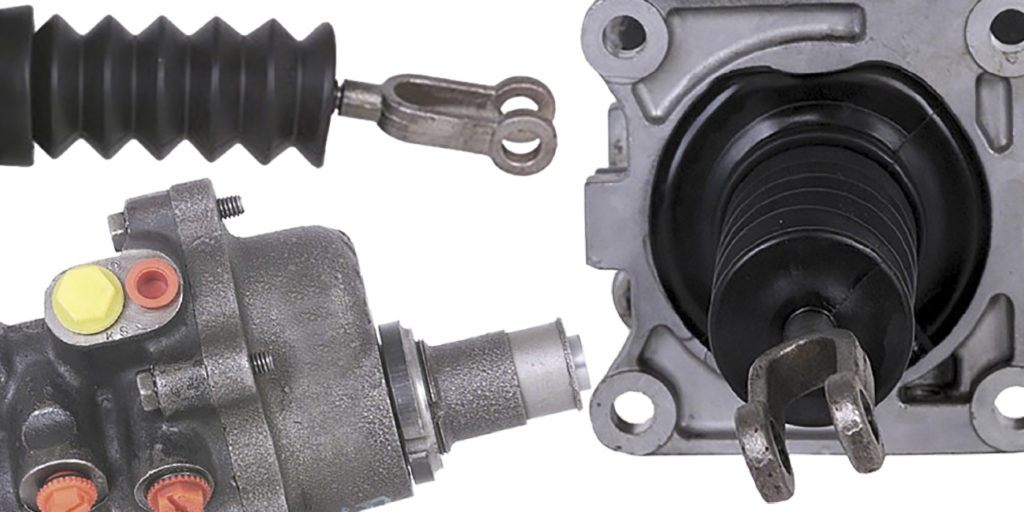
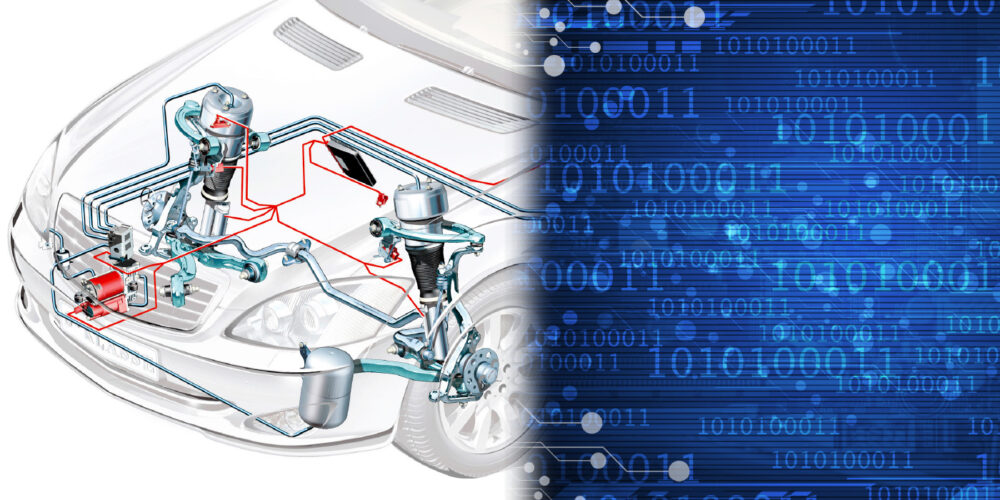
One of the most misunderstood brake systems is hydroboost. This system uses the pressure of the power steering pump to power the brake booster. The booster is essentially a power steering unit that supplements the driver’s input.
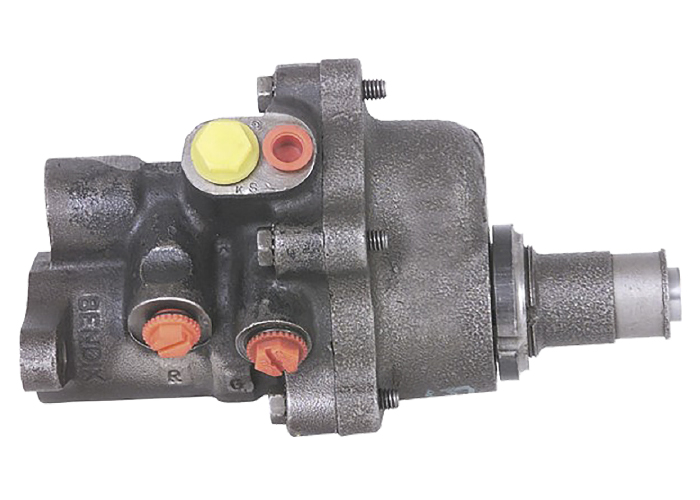
When hydroboost was first introduced in the 1970s, the government was rolling out new safety and fuel efficiency mandates, so new technology was created to solve a few issues.
For one, this can produce more boost than a vacuum booster. Second, the units are compact enough to fit in spaces a vacuum booster can’t, like on vans. Lastly, they would aid diesel vehicles that can’t produce enough engine vacuum.
Hydroboost vehicles are not hard to work on and typically don’t require special tools, but they require service information and a working knowledge of the system.


1. Listen
Properly operating hydroboost units will produce certain noises not heard in vacuum booster systems. These noises occur when the brake pedal is manipulated in a manner not associated with everyday driving habits. The general categories of normal operating noises are hissing and clunk/clatter noises.
2. Basic Function Test
To check if a hydroboost system is functioning, perform this test.
1. With the engine off, pump the brake pedal until it is hard.
2. Start the engine.
3. The proper operation should result in the brake pedal sinking down and then pushing back up against your foot. The sinking of the pedal when the engine was started is a result of the power chamber being pressurized. Once the power steering system is at full pressure, the pedal pushes back against your foot pressure.
This test will only verify if the pump, hydroboost unit and reserve are working. This test will not diagnose performance problems of certain customer complaints.
3. Check The Vehicle Service Information For Correct Test
The basic function test can only tell you if the system is functioning – it will not tell you how well the system is functioning. Many OE test procedures have specific rpm ranges and steering wheel movements to determine the health of the system. Look them up.
4. Hoses Are Safety Items
Power steering hoses are just as important as brake hose. Inspect all power steering hoses, which includes hoses that connect only power steering gear to the pump. If leaking or soft, spongy hose is found anywhere in the system, replace all hoses. If any hose is bad, the others are likely to be ready to fail.
Not all hose defects can be detected from outward inspection because they usually fail from the inside out. Deteriorated hoses produce debris, which will damage all parts of the system, including the hydroboost unit.
5. Flush The System
The spool valve fits into a precisely machined bore that is part of the hydroboost housing. The fit between the spool valve and the bore is such that it creates a seal while at the same time allowing enough fluid between the lands and bore to provide lubrication. The tolerances of the moving parts inside the hydroboost are so precise that just a small amount of contaminants can cause a malfunction. This is especially true of the spool valve. The tolerances necessary to form a metal-to-metal seal are quite small and any contaminants or tarnish buildup can prevent smooth operation of the spool valve. A properly functioning spool valve is critical because it controls the flow of fluid into and out of the power chamber.
Any vehicle equipped with a hydroboost power assist will benefit from a periodic power steering flush, but there is an additional step you have to perform to ensure the hydroboost power chamber and internal parts are flushed. When performing the flush, apply and release the brake pedal slowly to allow the new fluid into the hydroboost. If you skip this step, you will have a large quantity of old fluid in the hydroboost that will mix with the new fluid once the brake is applied and released a couple of times.
6. Look For Leaks
Any leak on the hydroboost unit is grounds for replacement. Look for leaks on the end caps, housings and firewall. Leaks will cause a sinking or long pedal condition.
7. Bleeding
Hydroboost brake systems are self-bleeding if there is no other problem in the system. Use this initial bleeding procedure whenever replacing or servicing any component in a hydroboost system. Normal driving conditions will remove air that remains trapped within the system when components are properly installed and there are no flow restrictions in the system. Always refer to the vehicle service manual for specific installation and testing procedures.
8. Check The Cooler
Like the power steering gear, the hydroboost unit does not like to be overheated. Some off-road maneuvers or large tires can cause the fluid temperature to skyrocket. This can damage the seals and spool valve. If your customer has a lifted truck with large tires, recommend a power steering cooler to save the brakes.
9. Adjustments To The Pedal And Master
Cylinder
Most hydroboost replacements fall off the rails during an adjustment to the rods that attach to the brake pedal and master cylinder. The input and output rods must be the correct length for the spool valve and master to operate properly. Older systems are adjustable and require measuring the rods and flange. Newer systems may not have any adjustments.
10. Check The Belt
Check the tension and condition of the drive belt and tensioner as part of any brake inspection. A belt that is worn or a tensioner that is weak can cause performance issues under high pump load. This can include a low pedal and noise.
Article courtesy BRAKE & FRONT END.