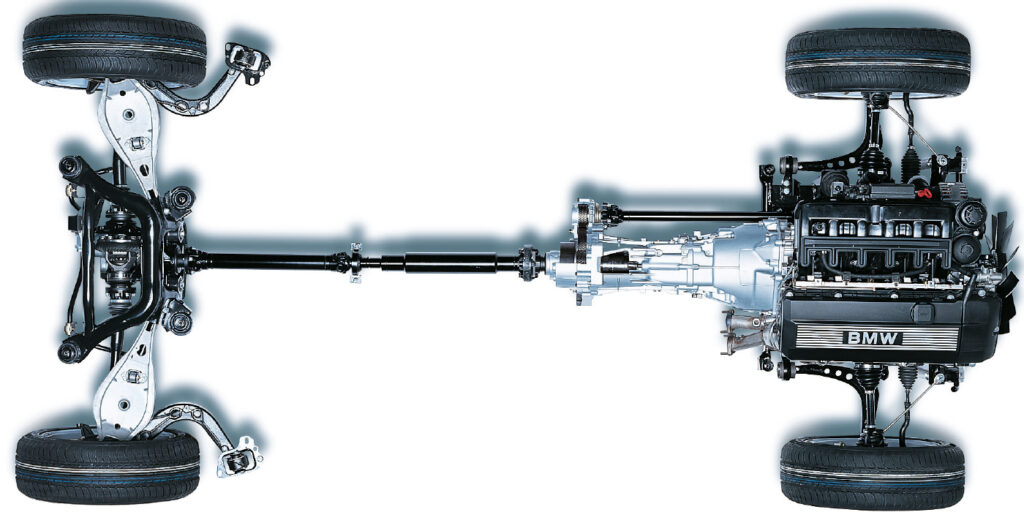
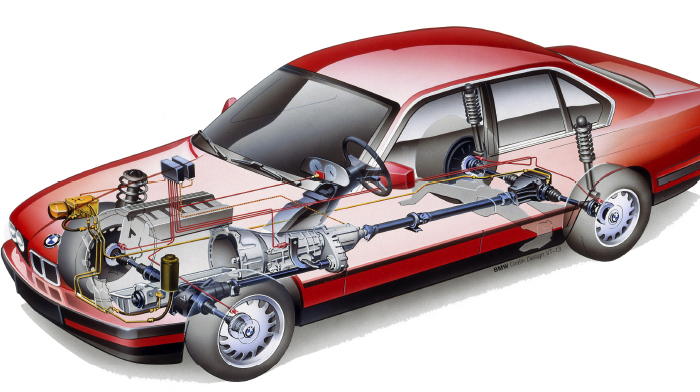
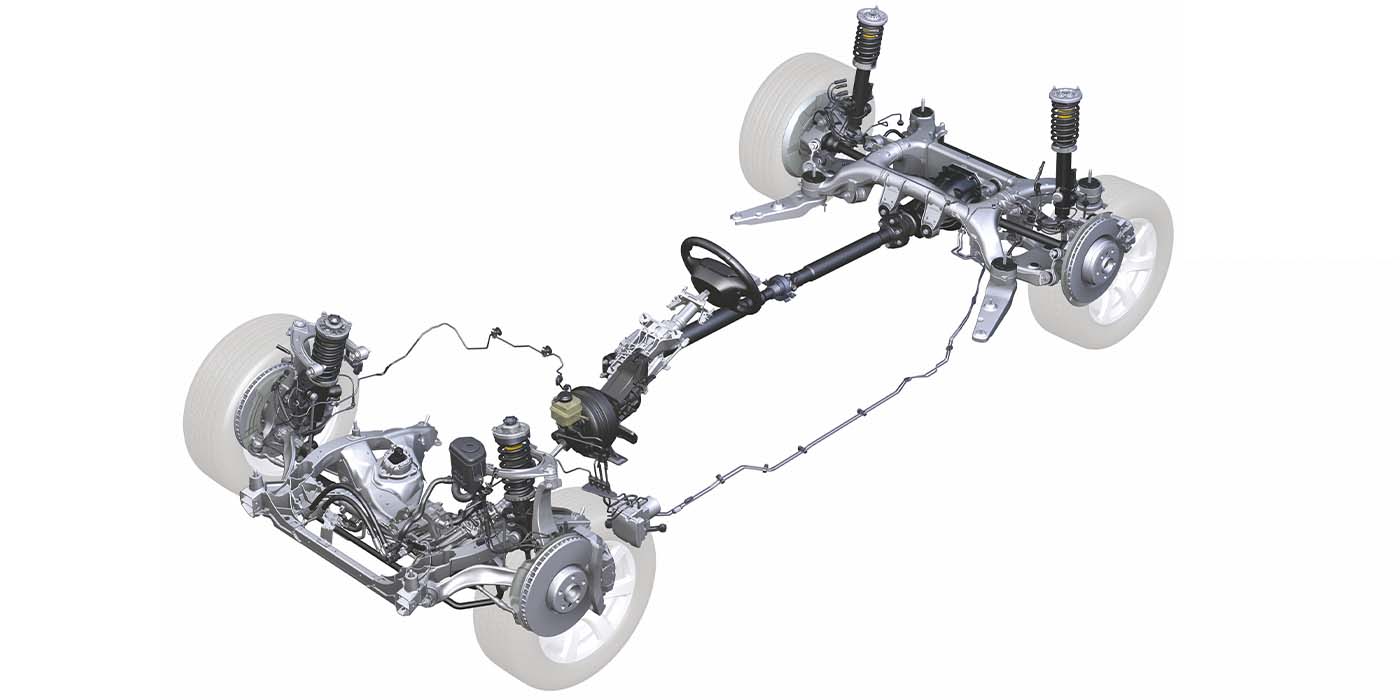
Part of BMW’s DNA is a longitudinally mounted engine and transmission connected to a rear differential with a driveshaft. Over the past 50 years, the designs of these driveshafts have changed with the different chassis and platforms. If you look at the different models you can see several types of joints, support bearings and flex discs. The only consistency is that one day the shaft will fail in a manner that will cause the customer to notice noise and maybe vibration.
Here are the top questions from technicians:
WHY ARE SOME DRIVESHAFTS ONE PIECE AND OTHERS ARE TWO PIECES?
It comes down to harmonics and horsepower. A large single piece driveshaft has a natural frequency within the range of human hearing. A two-piece driveshaft breaks up that harmonic. On an M3 or M4 model, the harmonics might not matter as much as the stresses on the drivetrain.
WHY DO CENTER SUPPORT BEARINGS FAIL prematurely?
Premature failure of the center bearing could be the result of too much driveshaft angle. This can be caused by weak motor, transmission or rear differential mounts. The other type of failure is environmental. A water or heat shield could be missing and expose the center support bearing, causing it to fail too soon. Also, high mileage and bearing wear can contribute to premature wear.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF A FAILED JOINT?
There are different things to look for when you suspect universal joint problems:
- The cling and crunch sound when going from drive to reverse with the brake on;
- Rust-colored dust around the universal joint itself;
- With driveshaft removed, any binding in the movement of the universal joint; and
- Vibration on takeoff and vibration on torque.
WHAT IS PHASING?
Phasing is the proper alignment of the inboard yokes. The first thing to do after the vehicle has been hoisted and the driveshaft has been removed is to mark the yokes for correct phasing. If you are working with a split shaft, make sure to mark the shaft before splitting it.
HOW SHOULD A DRIVESHAFT BE SECURED IN A VISE?
Make sure to clamp around the yoke and not on the hollow tube itself. This eliminates the chance of the hollow tube being damaged if clamped too hard. The best way to remove an old universal joint is to use the proper tools. If the shaft is dented it should be replaced because the outer shaft carries the loads.
WHAT CONDITIONS SHOULD BE REPLICATED FOR DRIVETRAIN NOISE ON 4WD VEHICLES?
Driveline noises caused by loading in 4WD vehicles may be mistaken for transfer case or front axle noise because they can sound very similar. 4WD noise caused by loading may exhibit the following conditions:
- The noise will be greatest on a clear, dry road and decrease
on a low-traction surface. Front axle or transfer case noise
caused by a bearing, ring and pinion, or planetary gearing
will be the same on all surfaces. - The noise will increase while making a tight turn. Most
front axle or transfer case noises won’t increase. - The noise can be changed from a deceleration condition
to acceleration (or acceleration to deceleration) by raising
or lowering tire pressure at one end of the vehicle; or - One or more of the tires may show small, short scratches
around the circumference of the tire tread. These
scratches are caused by the tire slipping, or “scuffing,” on
the road surface.
WHY DO SOME DRIVESHAFTS USE FLEX DISCS?
The flex disc or guibo is designed to absorb vibration and reduce drivetrain shock loads. The guibo is made of rubber on most BMW applications, but later applications use an aluminum carrier with round bushings. The symptoms of a worn guibo or flex disc are vibration and clunking when shifting