What is the difference between a power supply and a battery charger? The answer is a lot. A battery charger is designed to change the state of charge of the battery by applying current. A power supply applies a current to the vehicle’s electrical system and keeps the voltage level consistent, no matter the loads on the system.
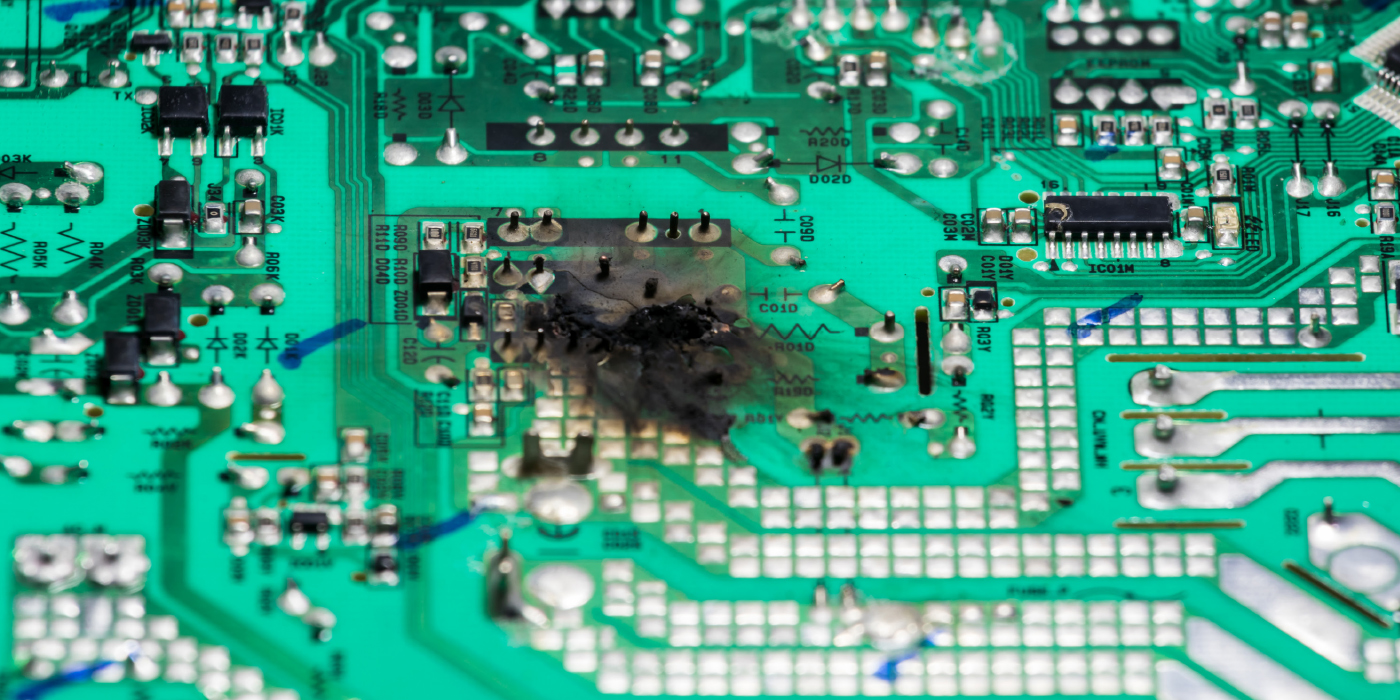
The most challenging part of reflashing a steering rack, module or actuator can be keeping the overall electrical system voltages within specifications during the entire process. If the system voltage drops below a range where the communication between modules can occur, it is like pulling the plug on a desktop during an update. You could “brick” a module on the vehicle.
Reflashing voltages can vary from 12 to 15 volts depending on the OEM and model. If the battery voltage drops below a set voltage, the reflashing process will stop and possibly damage the module. Some manufacturers call for a consistent 13.1 volts, but Honda says that a battery jump pack can be used. Others like some BMW models may require 15.1 volts to be able to start the process.
The real news is regarding the amperage required for some updates. With electric power steering, more powerful ABS systems and more modules, the system may need 80 to 100 amps during the reflashing process that might take hours. Trusting that a “home-brewed” solution with older chargers and batteries will keep the power in the zone could cost you a lot more than the cost of a purpose-made battery voltage maintainer. But, a reflashing battery supply can also provide a margin of error if a door is opened in the middle of a procedure.
The other consideration is the amount of current required during a reprogramming procedure for an extended period. BMW recommends that a battery maintainer be able to deliver at least 70 amps for short periods. Sure, some battery chargers can crank out 70 amps, but how a battery charger delivers the current can fry a battery.
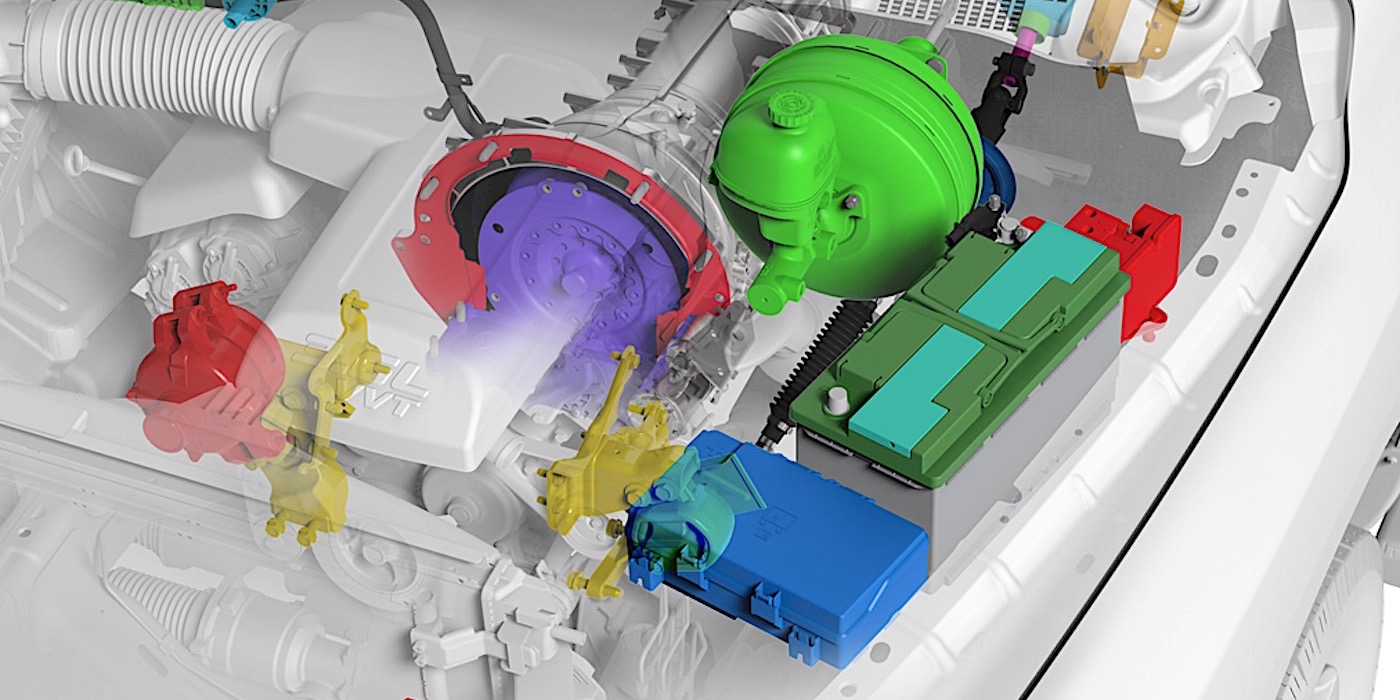
Reflash procedures are not getting any faster. Some steering system reprogram procedures can involve three modules that might be found on the rack, in the body and in integrated security gateways. Also, the reflash process does more than install the latest software. Many components like steering racks also perform tests to calibrate the sensor in the new unit and the other sensor on the vehicle.
Your old battery charger should not be used because these turn the power off and on. There are battery maintainers made specifically for reflashing that can deliver the correct voltage and amps during a procedure. Check the OEM’s website for information on the equipment about maintaining the battery. It is best to invest in a battery maintainer made for reflashing before starting to reflash process.
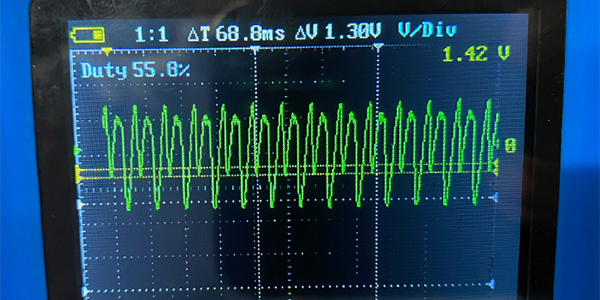
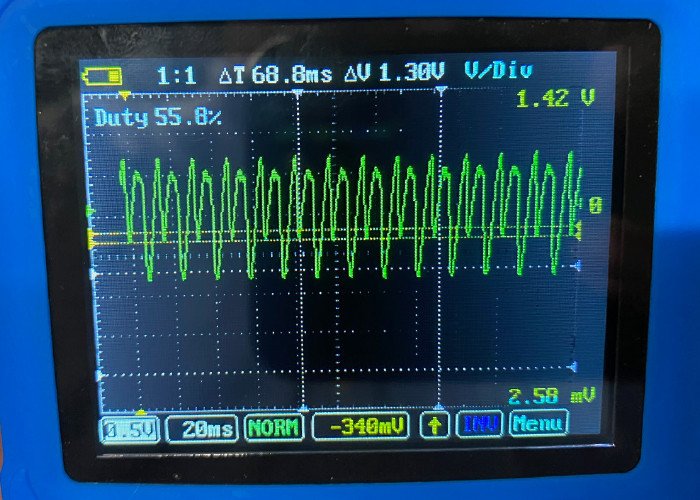
Both types of chargers have the same problem: the power is not clean DC. Due to the type of transformers inside, AC power contaminates the DC power. Having a little AC in the power feed is okay when you are charging a battery. But during a reprogramming session, it can cause problems with the data being transferred from the OEM’s servers.
If you look at the AC power on a scope, the power cycles between positive and negative peaks. Some call it a ripple. If you cover the negative peaks and just leave the positive peaks, the rapid switching of power looks a lot like the binary communication of ones and zeros. If you have this stray AC voltage when a module is being programmed with a J2534 device, those extra voltage peaks can garble the code.
WHY YOU CAN’T USE A JUMP PACK
If you have a jump pack or box at your shop, it might work for some vehicles. Battery or jump packs don’t have AC voltage problems and, in theory, can keep up with short high- current demands. For some minor reprogramming procedures, Honda advises the use of the battery jumper pack to maintain the system voltage above 12 volts. But, not all jumper packs are the same.
Newer jumper packs are not designed to output a constant 12 volts. Some are designed to deliver the maximum current output when it senses the starter is engaged on a dead battery.
The biggest issue with battery packs is that you can’t control how long you can keep the system voltage at a set level for an undefined period for a reflash. Also, some OEM procedures require more than 13 volts. Some vehicles might even require a higher voltage to start the reflashing procedure.
WHY ARE REFLASH OR REPROGRAMMING POWER SUPPLIES SO EXPENSIVE?
A reflash power supply is not designed to charge a battery or jumpstart the vehicle. A reflash power supply is designed to keep the system voltage in a specific range during the entire procedure. It is computer-controlled and regulated. The power inverter takes 120 volts AC to clean AC voltage that can be set to a specific voltage, depending on the vehicle. Most of all, a reflashing power supply can keep the system voltage consistent indefinitely.
When reflashing and reprogramming became an essential service more than 20 years ago, the reflashing power supply was a dealership tool. The early power supplies were 30 to 50 amps. As the number of modules increase with every new model year, the power requirements for reflash power supplies have also increased. Some late-model vehicles may require 70 to 100 amps from the power supply during the reprogramming procedure. The reason for the increase in current requirements is because some components are actuated as part of the reprogramming and possible recalibration procedure.
You will not be able to perform flash reprogramming straight out of the box. It takes time to set up the computer and register at the OEM websites. So, on a slow day, take some time to experiment on shop vehicles. There is nothing worse than having to wait for a verification email from an OEM just to start up the subscription. Learn before you burn or brick.