When servicing catalytic converters, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how they operate.
To begin, an internal combustion engine creates heat energy by igniting a mixture of gasoline and atmospheric oxygen with a high-voltage spark. Unfortunately, a residual quantity of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) are left over after combustion. Consequently, a catalytic converter uses precious metals like platinum as a catalyst to convert harmful pollutants like HC, CO and NOx into harmless gases like oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Since a catalyst will accelerate a chemical reaction without being consumed by the process itself, the catalytic converter will theoretically last forever. In reality, catalytic converters eventually succumb to heat stress and contaminants from coolant and engine oil additives.
Converter Types
“Direct-fit” catalytic converters are of three basic types: two-way, three-way and three-way plus oxidation converters. Two-way “oxidation” converters were used up to 1980 and are designed to eliminate HC and CO. Three-way converters are designed to eliminate NOx as well as HC and CO. A three-way plus or “dual-bed” converter allows atmospheric air to be injected between the three-way catalyst and an extra oxidation bed to further clean the engine exhaust.
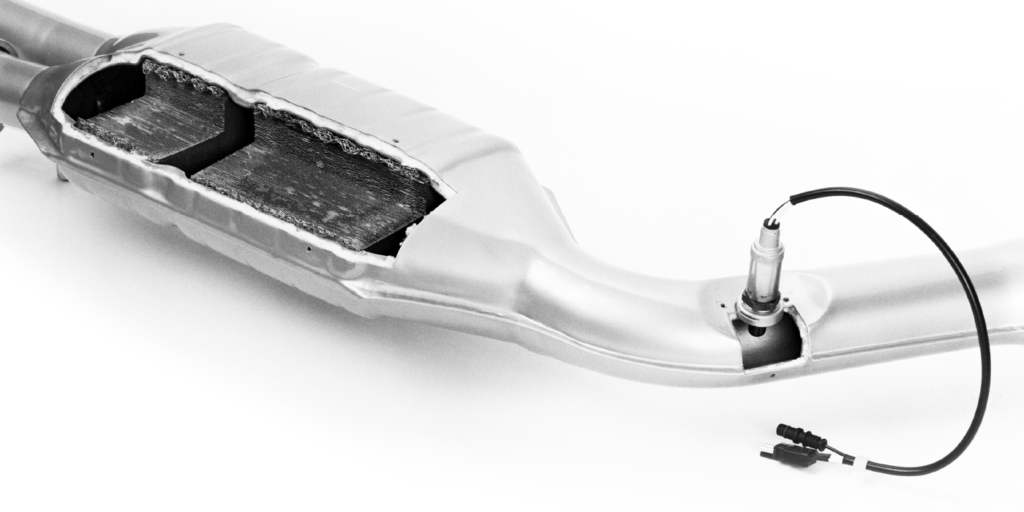
The precious metals used as catalysts are distributed in molecular form over a rough-surfaced ceramic wash coat covering the metallic honeycomb substrate. The effectiveness of the converter is basically determined by the amount of precious metals present on the honeycomb substrate. Consequently, it’s very important for suppliers and technicians alike to meet EPA requirements by selecting the correct catalytic converter for the application.
The Catalyst Monitor
The catalyst monitor or self-test runs only once after the engine is started and driven. Basically, the engine control module (ECM) uses a mathematical algorithm programmed into the ECM software to compare the electrical activity of the upstream oxygen sensor (before the converter) with that of the downstream oxygen sensor. When the electrical activity of the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors doesn’t meet programmed parameters, a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0420 and/or P0430 is stored in the ECM’s diagnostic memory and the orange “Check Engine” warning light is illuminated.
Because the catalyst monitor is mathematically-based, attempting to diagnose a converter by comparing inlet and outlet temperatures or by using an exhaust gas analyzer will not yield valid test results. When a P420/430 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is present, the professional technician should check for related ECM calibration update bulletins before replacing a catalytic converter. In many cases, reprogramming the PCM might solve a stubborn P420/430 DTC issue.
Typical Causes Of Catalyst Failure
An ignition system misfire is the most common cause of catastrophic converter failure. When a misfire occurs, the catalytic converter overheats because combustion takes place in the converter rather than the engine. When the converter exceeds an operating temperature of about 1,300 degrees F, the converter substrate begins to melt and cause exhaust restriction. Common failures also include a catalyst suffering from an external impact or being contaminated by coolant from leaking cylinder head gaskets.
When To Sell Catalytic Converters
The auto manufacturer’s original equipment (OE) catalytic converters are initially covered by an EPA-mandated 8-year, 80,000-mile warranty. A new aftermarket catalytic converter can be installed only if the original is missing, fails a state or local emissions inspection program or is plugged, leaking, or has sustained physical damage. Most vehicles require catalytic converter replacements when an illuminated CEL indicates a converter failure or if the engine itself has failed an exhaust emissions test. To pass an exhaust emissions test, the converter must meet the exact configuration and capacity as specified by the OEM. Due to adopting more stringent emissions standards, many other states are now requiring catalytic converters that meet California specifications. When selling any catalytic converter, remember to fill out the paperwork as required by state and local agencies.
Article courtesy Underhood Service.