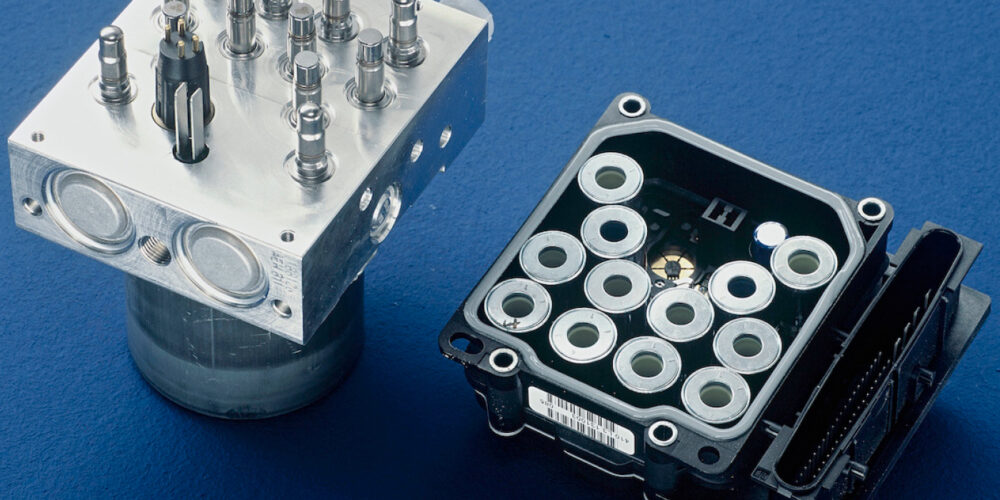
The anti-lock braking system (ABS) module is usually mounted to a hydraulic control unit (HCU). Inside the HCU can be eight or more electric solenoids that control the flow of brake fluid.
Most designs are non-integral to the braking system. This means that if there is an issue with the ABS module, the brakes will still operate using the pressure generated by the master cylinder. But, non-integral does not guarantee that there could be mechanical issues with the valves inside the HCU that could cause issues with braking and pedal feel.
A basic ABS four-channel system will have eight solenoids (four isolation and four dump) or two for each wheel. Some systems will have more solenoids or valves to isolate the master cylinder from the HCU. Basic stability control systems will typically have 12 or more valves. If a system has electronic brake distribution or automatic emergency braking, it can have 16 valves.
The valves in the HCU are designed to do very specific tasks. The first task is to isolate a hydraulic circuit so the application of the brake pads can be controlled. To control the application of the brake pads, there are typically two valves that allow dump or hold the hydraulic pressure. More sophisticated HCUs that manage stability control, will have additional valves that will allow the pressure pump to apply the brakes independent of the master cylinder.
When the master cylinder applies pressure, it goes directly to the wheel because the outlet/dump solenoid is closed. This is a normal braking event. The unit is in a “passive” state.
If the system senses a wheel is locked, the inlet/isolation solenoid is closed to prevent any more pressure from the master from reaching the wheel. The wheel might start to turn.
If the wheel does not start to turn, the outlet/dump valve will open. This will release or bleed off the hydraulic pressure that is holding the wheel. The wheel will now rotate.
Since pressure from the master cylinder has been bled off, the pump in the HCU will spool up and apply pressure. The outlet valve is closed and the inlet valve is opened. The pump applies pressure to the wheel.
If the wheel is still outside the wheel slip parameters, the cycle will start over. This happens very quickly. The operation of the solenoids and pump will cause a “kickback” or pulsation in the pedal.
HCU Mechanical Problems
Mechanical issues with the HCU are rare, but they can happen. Valve seats and pintles can become stuck or not seat properly due to debris, corrosion or contaminated brake fluid.
If the inlet/isolation valve is stuck open, it will not affect normal braking in any way. It will only hurt the ABS system. This could lead to a pulling condition during ABS activation.
If an outlet/dump valve is stuck open in one circuit, this could cause a pull condition during normal braking. This is due to the loss of brake pressure at a wheel. Typically, this is not discovered until brake hoses, calipers and other parts have been replaced.
Sometimes a stuck or defective solenoid or pump will set a code. A solenoid has a resistance between 2 and 8 ohms. On some units, it is impossible to access the individual solenoids. Testing the unit with a scan tool with bidirectional control might be the best way to confirm the condition of the HCU.