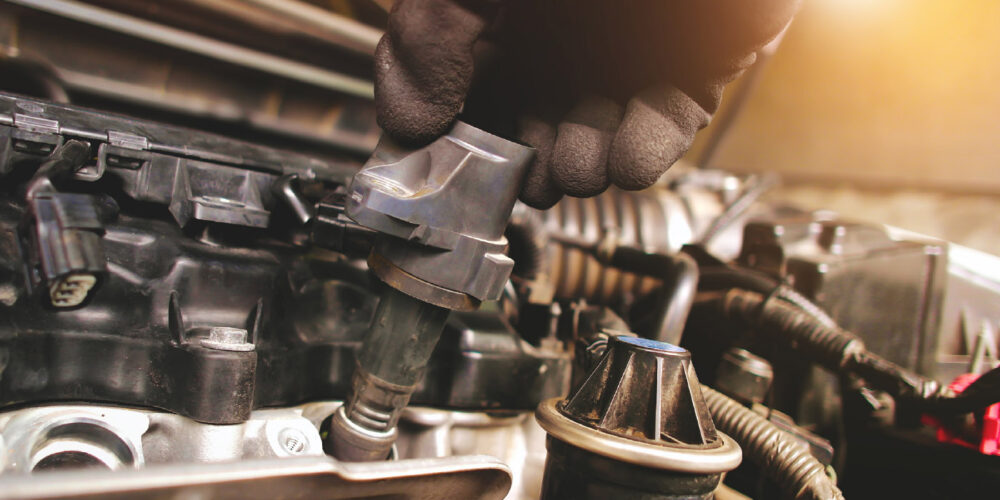
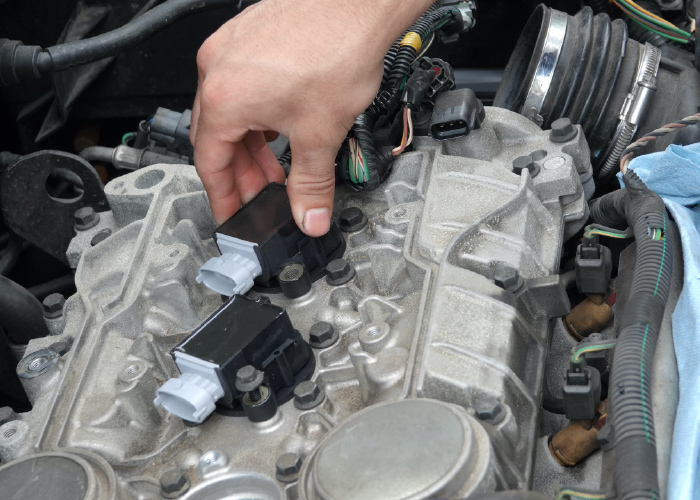
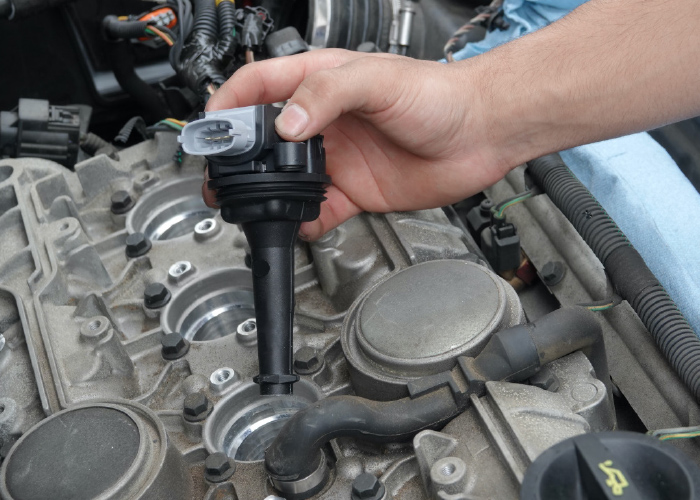
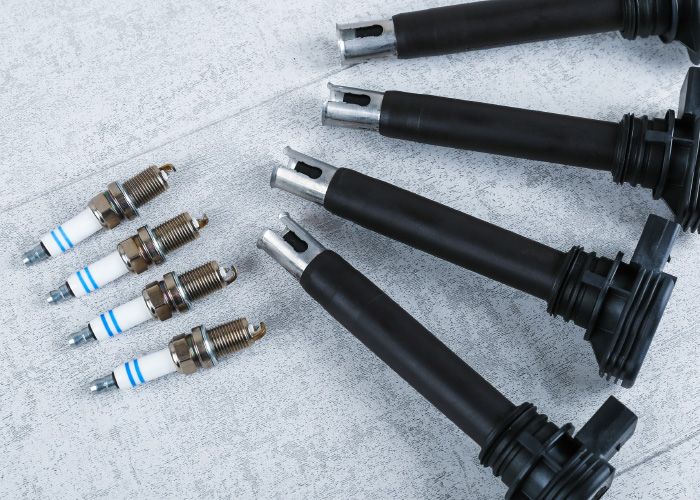
In a perfect world, a flashing check engine light for DTCs P0301 through P0312 would always be solved by installing a new ignition coil. If this were true, technicians would not need countless hours of training. However, the reality is that a misfire can be more than a missing spark from an ignition coil. Also, replacing a single coil might not be the best approach to curing an engine of a chronic misfire.
The Nature of Misfires
Misfires below the vehicle’s threshold often pass unnoticed, but a constant misfire is hard to overlook by you or the engine management system. These misfires would set a DTC inside the engine computer. Misfires that turn on the check engine light and log a cylinder-specific fault code are the easiest to diagnose, while random misfire codes can be more troublesome. The OBDII system can identify the cylinder(s) not contributing their regular dose of power and set a corresponding DTC. A P0303 DTC, for example, would indicate a misfire on cylinder number 3. If the ODBII system cannot identify a specific cylinder, a P0300 random cylinder misfire DTC will be set. But neither means that the ignition coil or any other specific part is at fault. It simply means that more testing is necessary.
Coil Failures
Ignition coils can vary greatly in size and shape but share three common parts. These are the primary windings, secondary windings and non-conductive or dielectric insulation material that separate the two windings. The insulation material is typically a dielectric resin that is applied in a vacuum, so air bubbles are not formed. Air bubbles can create a path for electricity inside a coil and lead to premature failure.
Coils fail for various reasons, including heat, vibration or issues on the secondary side of the ignition system. Coils are commonly found bolted to the cylinder head, either on top or inside a cylinder-specific well. Excessive heat and vibration can cause the insulating material to break down and create internal coil failure.
Worn secondary ignition components such as spark plugs or wires can cause a coil to work harder, require more voltage, and significantly reduce the coil’s operating life.
When a coil fails, it is possible the electricity created is unable to reach its destination, the spark plug. When this happens, the electricity produced inside of the secondary windings looks for the path of least resistance to ground. This path is commonly found through the boot or body of the coil.
Carbon tracking happens when oil, dirt or moisture is electrostatically attached to the boot or insulator, creating a path to ground. When carbon tracking is found, the coil and corresponding plug should be replaced. It is also possible that a failed ignition coil can cause damage to the engine computer or ignition control module.
Most gasoline engines have at least four cylinders. Depending on the configuration of the ignition system, you will have at least two coils (wasted-spark system), and most will have four coils or more. All the coils are exposed to the same conditions under the hood, including heat and vibration. Also, all the coils operate under similar conditions regarding the engine’s health and spark plugs. When it comes to replacing ignition coils, it might benefit the customer to recommend the replacement of all the coils at the same time in the event of a coil failure.
Non-Coil Misfires
Commonly an engine computer detects a misfire by measuring the changes in crankshaft speed. This change in speed can be caused by a combustion event that is happening early, late or not at all.
Worn spark plugs are one of the leading causes of misfires on a high-mileage engine. Over time, a large amount of voltage needed to create a spark erodes the electrodes, increasing the gap. This change in the spark plug’s gap increases the voltage required to generate a spark. Eventually, the ignition system reaches a point where it fails to jump that gap, and the spark plug does not fire.
The air/fuel ratio also can cause a misfire. The state of the fuel and air charge (too rich or too lean) inside the cylinder changes how the spark forms and how much voltage is required to jump the spark plug gap and create a spark.
A lean misfire occurs when the predetermined air/fuel ratio is more air than fuel, or, in extreme cases, all air and no fuel. This can be caused by a fuel injector not spraying, a faulty EGR system or anything that is forcing more air into the cylinder than the engine computer had planned for. A rich misfire is less common than a lean misfire. The most common rich misfire is caused by a leaking or stuck open fuel injector. Rich or lean misfires can also be caused by a failed oxygen sensor. The engine computer monitors the oxygen sensor to report back the efficiency of the combustion event. A skewed or dead oxygen sensor can cause the engine computer to incorrectly add or subtract fuel.
Replacing a single ignition coil before diagnosing what is causing the misfire may seem like a tempting diagnostic shortcut. But, it can set you back in your diagnostic process. So, the next time you get a vehicle in your shop with a misfire, don’t just assume it’s a bad coil. Test, don’t guess.