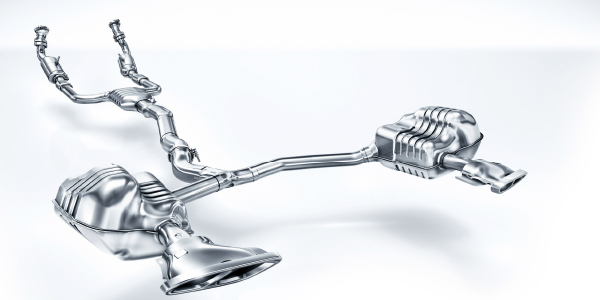
The catalyst efficiency monitor verifies that the catalytic converter is operating at a high enough efficiency rating to keep exhaust emissions within predetermined values. The PCM compares the signals from the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors to determine the state of the converter. These “tests” are called the readiness monitors.
Continuous and Non-Continuous Readiness Tests
A monitor is a section or segment of an operation that the vehicle normally performs, or one that needs to be done to verify a certain aspect or condition of the vehicle. There are two basic types of readiness monitors: continuous and non-continuous. Continuous monitors are constantly tested and evaluated while the engine is running. The non-continuous monitors need to have certain conditions met before a test can be completed.
Some operations such as a misfire or fuel system issues can be either continuous, non-continuous or both, and can be checked during both types of monitors. Non-continuous monitors will differ between gas and diesel engines as well.
A newer vehicle can report its emissions monitor status during its current driving cycle. These monitors start from the beginning whenever the monitoring cycle meets the criteria to run a readiness test. Older cars might not support this feature. Because the monitors are a self-check routine that the driver does not have to initiate, the best way to get them ready to perform a self-test is to drive the vehicle. However, driving alone won’t meet all the needed conditions. There are a few specific requirements that vary from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Make sure that the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light) is not commanded on. If there are any efficiency or related codes stored or even a pending diagnostic trouble code, they can prevent a monitor from ever running or completing.
Lastly, you have to complete a “drive cycle.” The drive cycle is to let the car run its on-board diagnostics. This allows the readiness monitors to go through their preset diagnostic routine.
What is Efficiency?
The converter has an efficiency rating that is computed by the vehicle’s manufacturer. The efficiency of the converter is tied to the fuel trim of the engine. The fuel trim is monitored by the oxygen sensors and is constantly adjusted by the PCM. This helps to keep the converter at the correct temperature for the most efficient operation. One of the things the converter does is store a certain amount of oxygen in it. If an engine is running too rich, it cannot store oxygen. If it is running too lean, the oxygen levels may prevent the converter from reaching its optimum heat range.
A rich condition means less oxygen; a lean condition means excessive oxygen. A rich condition would mean the PCM wants to lean out the fuel mixture. Meanwhile, a lean condition would mean the PCM wants to try and increase
the fuel mixture.
The stoichiometric value of the fuel-to-air mixture is 14.7 to 1 (by weight). For the converter to operate correctly, the stoichiometric value needs to be reached so that the catalyst can react with the oxygen and reach the proper operating temperature. The catalytic converter begins to function at 400 to 600 degrees F. The normal operating temperature can range up to 1,200 to 1,600 degrees.
Converter efficiency can be checked with a scan tool as well as watching the O2 sensors switching between rich and lean. Lab scopes can also be used to monitor the switching. Once the efficiency drops below a specified level and other criteria are met, an efficiency code will be set.
Most converters start out at about 99 percent efficiency when new, and quickly taper off to about 95 percent. As long as the efficiency doesn’t drop off more than a few more percentage points, the converter will do a great job of cleaning up the exhaust. But, if efficiency drops below 92 percent, it will usually turn on the MIL lamp.
Newer vehicles have to meet an even tougher Low Emission Vehicle (LEV) requirement. Now, there’s even less room for leeway. A drop in converter efficiency of only 3 percent can cause emissions to exceed federal limits. The LEV standard allows only 0.225 grams per mile of hydrocarbons.
Some OEMs have updated calibrations for the catalyst monitors. The new calibration can then be re-flashed into the PCM. But, if the vehicle already has a damaged converter, the re-flash will do nothing at all for it. But, if the converter is near the threshold limit, the re-flash may extend the life of the converter and prevent the light from coming on for another 10,000 or even up to 80,000 miles.
Causes of Converter Efficiency Loss
Faulty O2 sensors can lead to converter efficiency failure, too. One of the things a lot of technicians neglect to check is probably the easiest thing to check — the O2 sensor connections. The connector not only is the supply for the voltage and grounds, but the source of the needed air supply to the zirconium sensor. If the connector is full of oil or debris, no air can pass down the wire leads to the sensor internally. The old one-wire O2 sensors had a perforated area on the outside and didn’t use the wire leads as the oxygen supply.
Years ago, I had a car that came in with silicone sealant completely encompassing the connectors. A code was present, but the damage was already done. All four O2 sensors had to be replaced. The converter efficiency was in question, but after running the monitors several times, the code never came back.
Obviously, tune-up related items have to be considered into the efficiency of the converter. Anything from PCV valve condition, broken exhaust hangers that damage the converter’s inner structure, to EGR valve and related EGR problems can affect the efficiency. Exhaust leaks ahead of the O2 sensors can greatly affect the efficiency, too. Installing the wrong O2 sensors in the wrong position can also be a problem. Just for the record, B1 sensors are on the No. 1 cylinder side of the engine while B2 sensors are on the opposite side. It wouldn’t be the first time I’ve seen the rear O2 sensor in the front or a vehicle with a B1 sensor code and somebody changed the B2 sensor. Keep in mind a lot of vehicles now have multiple catalytic converters and more care has to be taken to ensure you’re changing the correct one.
As you can see, the efficiency of today’s cars is not based on just one part, but on the overall condition of all the components involved. Preventive maintenance can help lengthen the life of a catalytic converter as well as paying attention to the service light when a code for converter efficiency pops up. Keep in mind the efficiency of the converter is determined by what is going on in the combustion chamber and what the PCM is being told by the O2 sensors.
For the most part, an efficiency code is the result of something that has already occurred and not necessarily a catalytic converter failure. Diagnose and repair the cause, not just the results.
Article courtesy Underhood Service.