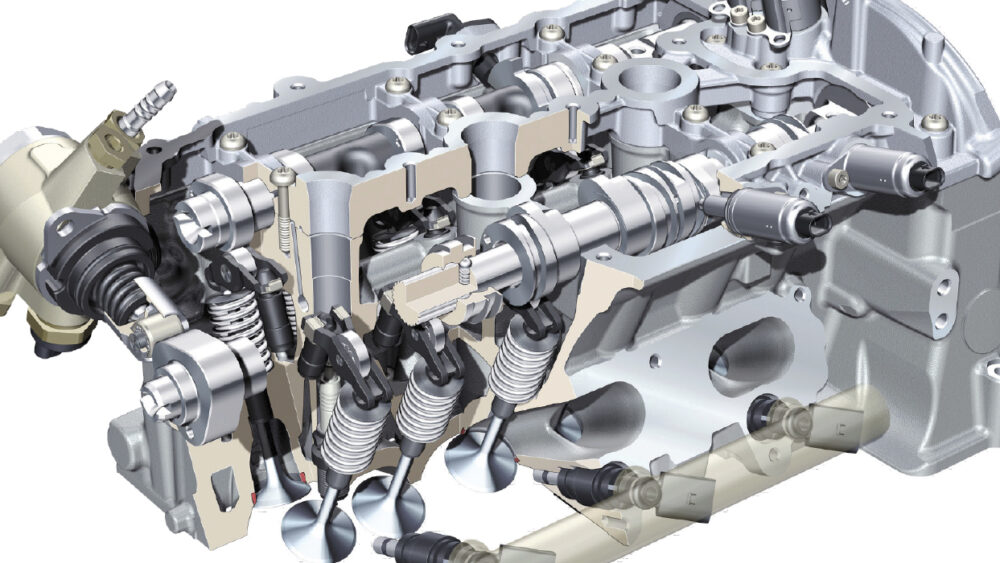
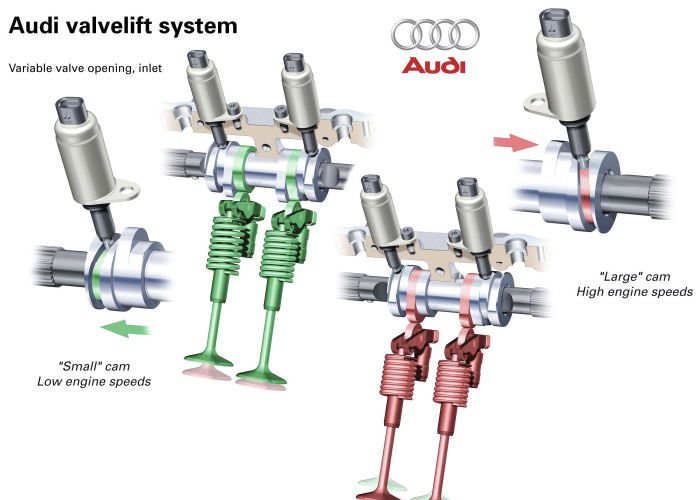
The Audi Valve Lift System (AVS) was first introduced in 2008 on the 2.0 TFSI engine and V6 turbocharged engines. The system changes the amount of lift of the intake and exhaust valves. The camshaft has two lobes that are controlled by an electric solenoid. The system can do a neat trick with the valves. The throttle body can be 100 percent open and the air ingested into the engine is controlled by the valves. The advantage is that the obstruction of the throttle butterfly is minimized. Also, the air entering the engine is less turbulent
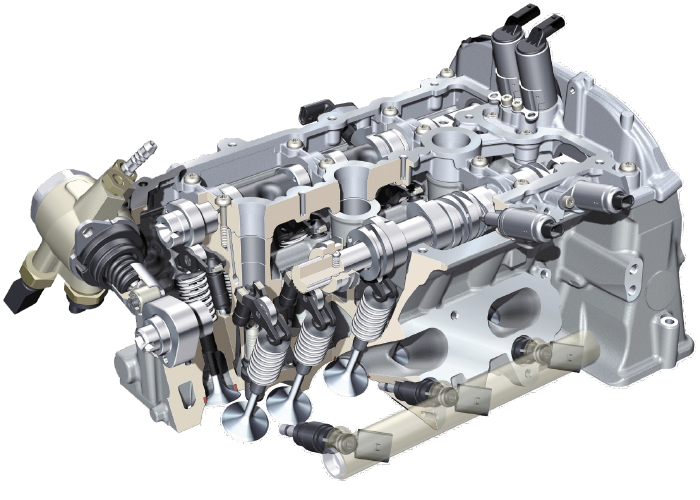
In the latest-generation 2.0 TFSI, the AVS varies the lift of the exhaust valves. It reduces flushing losses in the combustion chamber and also ensures that the optimal flow of the exhaust gas is directed to the turbocharger. Both versions have a simple, compact and lightweight system design making use of so-called cam pieces – sliding electromagnetic sleeves on the camshaft.
The Audi Valvelift System (AVS) regulates the lift of the valves in two stages, depending on load and engine speed. The system increases torque while also reducing fuel consumption. Two versions of the AVS system are in the field. In the V6 engines in which AVS is used, it acts on the intake valves, largely regulating the amount of intake air. The other version can be found on the 2.0 TFSI engine.
This article appears courtesy of ImportCar.