On older vehicles, the alternator and engine were never really connected. The alternator was internally or externally self-regulated to a voltage, but that was it. Under certain conditions, the idle would drop when loads increased.

Under some conditions, this wasn’t ideal for performance and emissions. Also, as electrical loads increased for systems like heated seats, electric power steering and infotainment systems, the need for better power management was required.
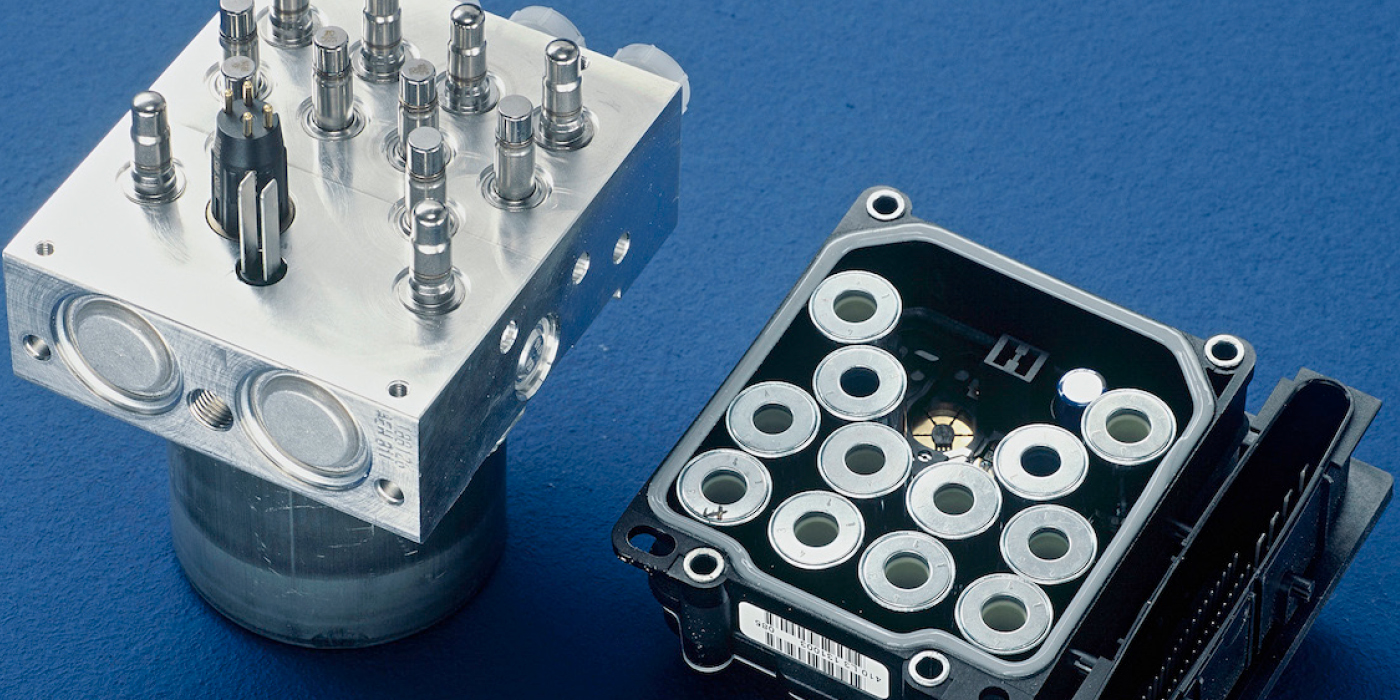
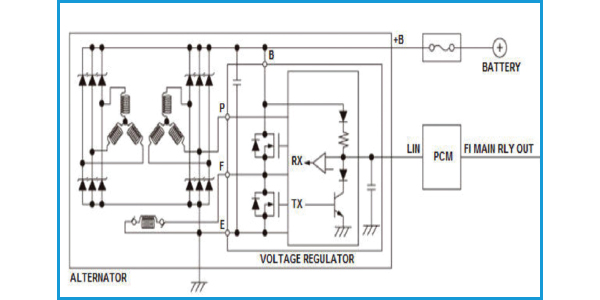
Honda’s solution was to use a dedicated local interconnect network (LIN) line that connects the alternator and the powertrain control module (PCM). The LIN line uses a master/slave protocol to send and receive data to the different components on the line.
The alternator is the slave. The alternator receives data from the PCM and provides feedback, which allows the PCM to operate the engine electrical system efficiently and with little change in engine performance. If there are problems with the LIN line, code P16E2 will be set.
The alternator has a continuous monitor that is running when the engine starts and reaches 500 rpm. Once the engine starts, the alternator has three seconds to communicate with the PCM. Also, the voltage can’t drop below 10.0-volts, or a code will be set.
The PCM sets a target generating voltage in the range of 12.5- to 14.5-volts using the LIN line. If the output voltage does not match the commanded voltage for the engine speed, it sets a code that the voltage is too high or too low. DTC P0562 is for the charging system voltage that is too low. DTC P1549 is for the charging system voltage being too high. If there is no voltage coming from the alternator, code P056A will be set for “No Charging Malfunction.” Both of these codes are cleared after one key cycle.
If the sensor detects the alternator is overheating and has exceeded 320 degrees F, it will set code P16E4.
Most late-model Honda alternators have a Overrunning Alternator Decoupler (OAD). This type of pulley also has a one-way overrunning clutch inside the hub, as well as an internal torsion spring to dampen vibrations in the belt drive system further. The spring acts as a shock absorber to cushion the hub. This reduces noise at idle and low engine speeds, and helps dampen harmonic vibrations at higher speeds. If the clutch or spring inside the pulley has failed, the pulley may fail to drive the alternator, or it may create vibrations and noise.
Battery Management
On most 2008 and newer Honda models, there is a battery sensor attached to the negative battery terminal. The sensor measures internal resistance, temperature and current. The sensor sends a signal to the PCM through the gauge control module.
Article courtesy ImportCar.