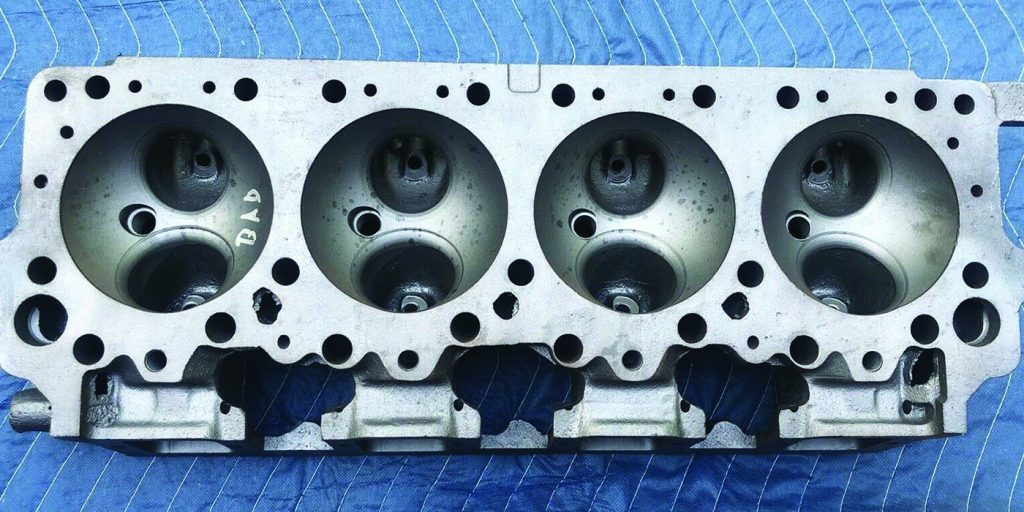
A hemispherical combustion chamber or “hemi head” allows for larger valves, better spark plug placement and optimized flow by placing the valves on the side of a dome. Hemi heads have been used by many manufacturers from Desoto to Porsche. With the correct engineering, the hemispherical cylinder head can produce a ton of power, but they do have limits.
The first limiting factor in the design is limited to just two valves per cylinder. Yes, these are large valves. But, the mass of valves can limit the redline of the engine.
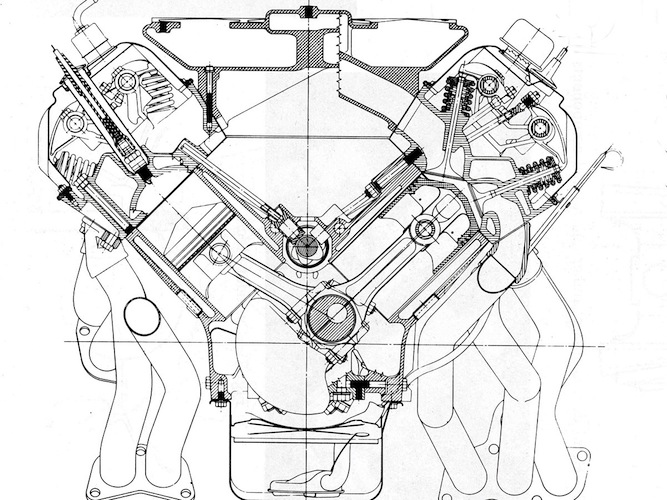
The second limiting factor is the complexity of the valvetrain. With cam-in-block designs, the valvetrain requires broad heads with the pushrods passing through the block at odd angles giving it very complex geometry. Even if the engine used a single overhead camshaft, rockers are required. Some engines used double camshaft designs, but this resulted in an even wider head and more power losses to drive the valvetrain.
The most famous hemispherical engines are the Desoto Fireball V8 and Chrysler Hemi. The first generation lasted from 1951 to 1957 and war revived in 1964 and went out of production in 1971. While some people say emissions and fuel economy standards killed the hemi engine, the reality for Chrysler is that it was too expensive to manufacture.
But what about the “modern” Hemi in many of today’s Dodge engines? To many experts, the engineering of the Gen III Chrysler engines just doesn’t fit the “hemispherical” design of the originals, but the engine still has plenty of power – and fans