Today’s vehicles with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are equipped with features that enhance safety and provide convenience to drivers. ADAS includes a range of technologies, such as lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, automatic emergency braking and blind-spot detection. However, for these systems to function accurately, ADAS calibration is crucial.
ADAS Calibration for Customer Safety
ADAS calibration ensures that the various components of the system are working harmoniously to provide accurate information and assist the driver effectively. It involves recalibrating the sensors, cameras, and other ADAS components to ensure they are aligned correctly. Failure to calibrate these systems can result in inaccurate readings and potentially unsafe driving conditions.
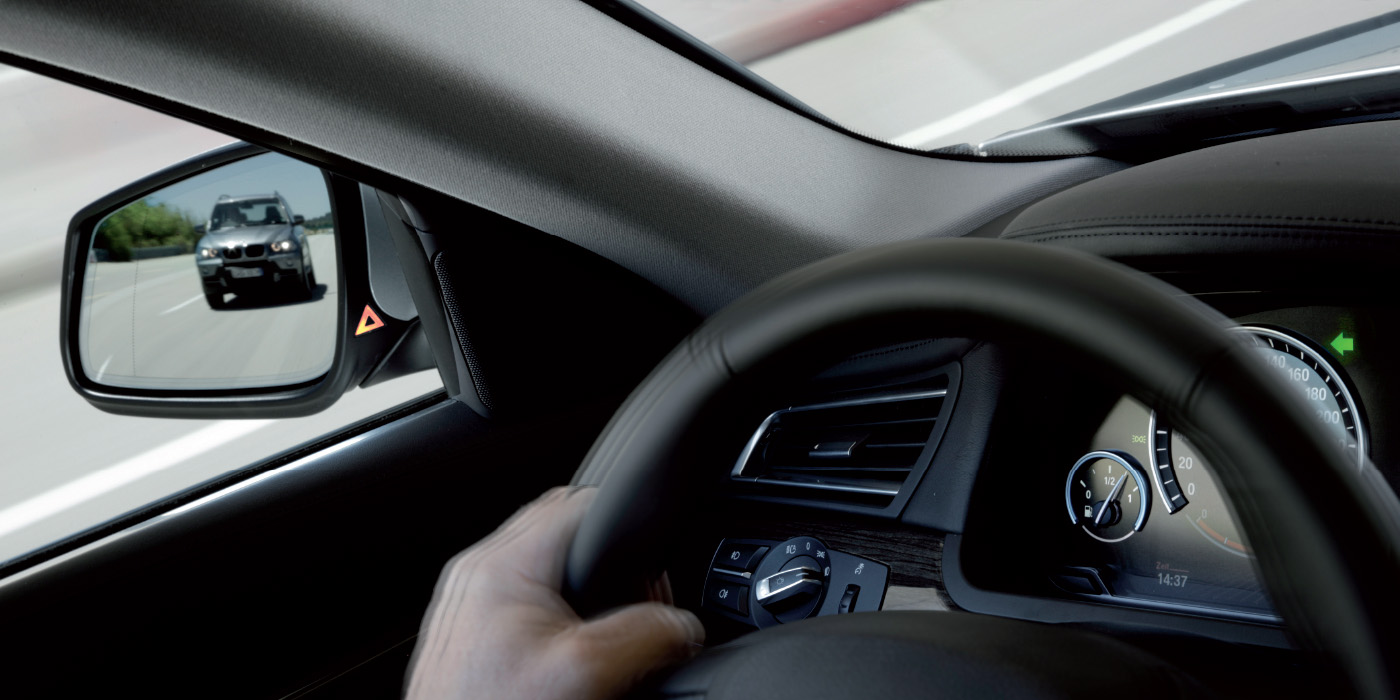
Proper calibration guarantees that the ADAS system will accurately detect and respond to potential hazards on the road. It ensures that the vehicle’s safety features, such as collision avoidance and lane keeping, are functioning optimally.
Static Calibration
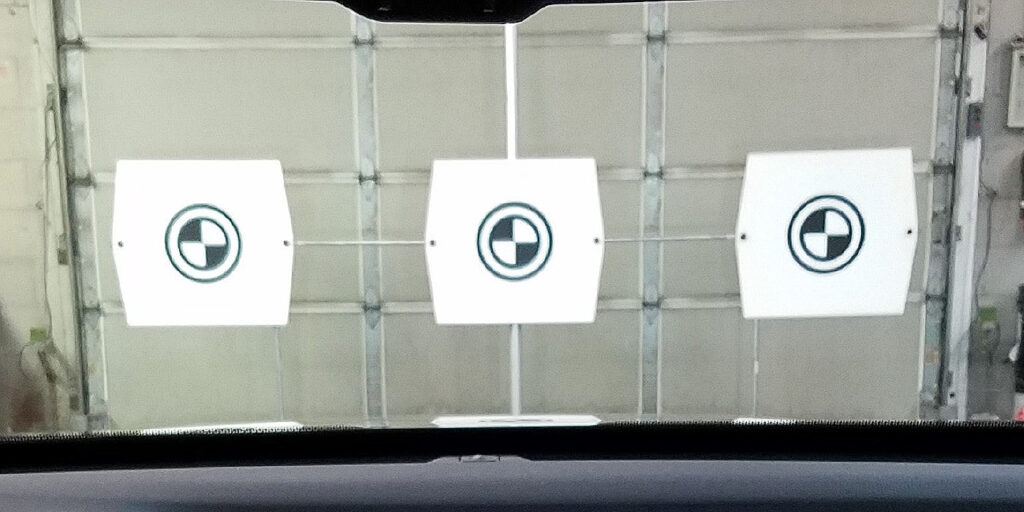
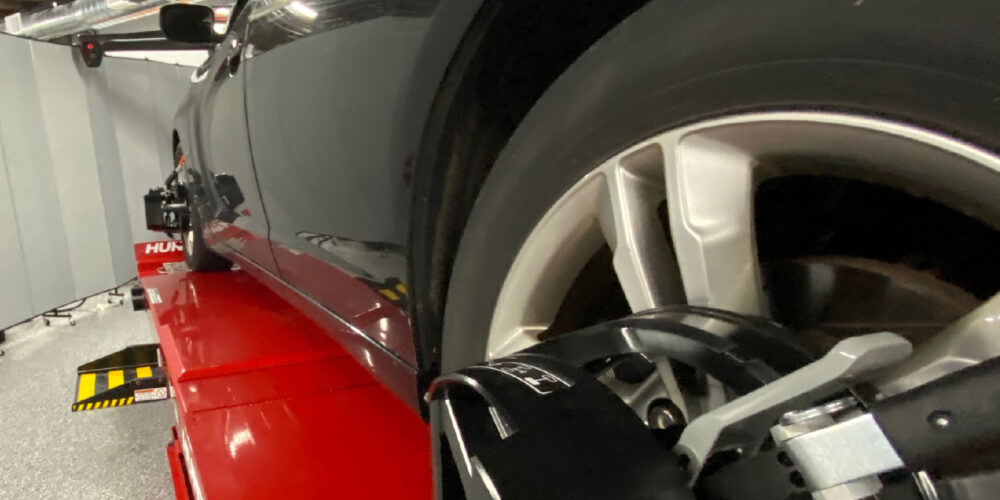
Static calibration is the process of aligning and calibrating the cameras and sensors of the ADAS system using a calibration target and specialized equipment. This calibration is typically performed in a controlled environment where the conditions can be precisely controlled. Static calibration is necessary because it establishes a baseline for the ADAS system, ensuring accurate readings and reliable performance.
During static calibration, the vehicle is positioned precisely in front of the calibration target, and the sensors and cameras are adjusted to match the target’s reference points. This process ensures that the ADAS system can accurately detect objects, lane markings and distances. Static calibration is essential for systems such as lane departure warning and blind-spot detection, as they rely heavily on precise camera alignment and accurate sensor readings.
Dynamic Calibration
While static calibration focuses on aligning the cameras and sensors in a controlled environment, dynamic calibration is performed on the road during a test drive. Dynamic calibration allows the ADAS system to adapt to real-world conditions and fine-tune its performance based on the vehicle’s actual driving behavior.
During dynamic calibration, the ADAS system collects data from the vehicle’s sensors and compares it with the expected readings. This process helps the system adjust its parameters to account for variations in road conditions, vehicle load and other environmental factors. Dynamic calibration is particularly important for systems like adaptive cruise control and automatic emergency braking, as they rely on real-time data to make accurate decisions.
Equipment Needed for ADAS Calibration
To perform ADAS calibration effectively, you need the right equipment. Here are the essential tools and devices required for successful calibration:
Calibration Targets: These are precision targets used during static calibration to align the cameras and sensors accurately. Calibration targets come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the specific ADAS system being calibrated.
Diagnostic Scan Tools: Diagnostic scan tools are used to communicate with the vehicle’s onboard computer system and access the ADAS calibration menus. These tools allow technicians to perform system checks, perform vehicle pre and post scans, diagnose errors and initiate the calibration process.
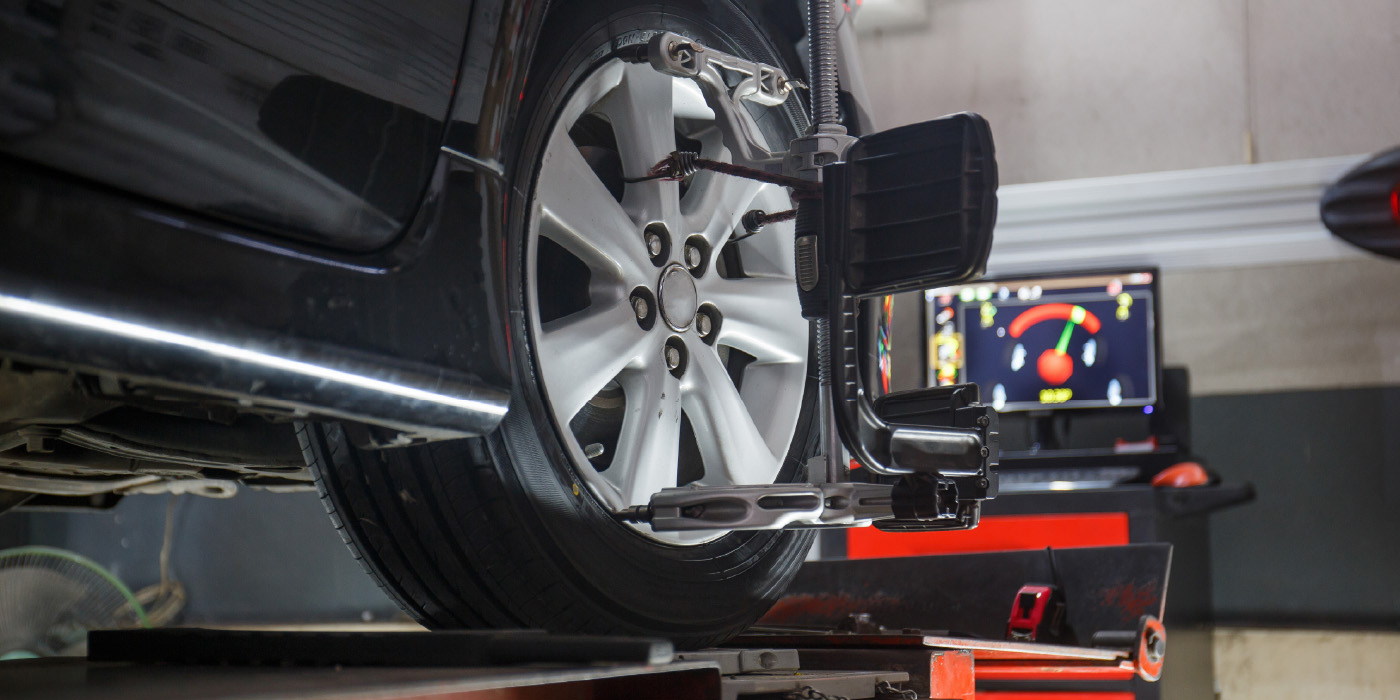
Alignment Systems: Alignment systems are used to position the vehicle accurately during static calibration. These systems ensure that the vehicle is aligned correctly in relation to the calibration target, allowing for precise calibration of the ADAS components.
ADAS Calibration Software: Specialized software is required to perform ADAS calibration accurately. This software provides step-by-step instructions, calibration data and diagnostic capabilities to ensure a smooth and efficient calibration process.
Investing in high-quality ADAS calibration equipment is crucial for accurate and reliable calibration. By utilizing the proper tools, you can guarantee the safety of your customers’ vehicle and provide them with a superior driving experience.