The Ford Mustang Mach-E is Ford’s first all-electric vehicle that is between a sedan and a crossover. It does not use the Mustang platform. Instead, it uses the GE1 platform, which is a heavily modified version of the C2 platform used for the fourth-generation Focus, Escape and Bronco Sport. The Mach-E can be just RWD or AWD. Battery pack options are available to extend the vehicles’ range.
Like internal combustion Ford vehicles, the maintenance schedule is built around 6- and 12-month inspections of components and fluids. So despite what you may imagine, there are some maintenance and repair opportunities for the Mach-E.
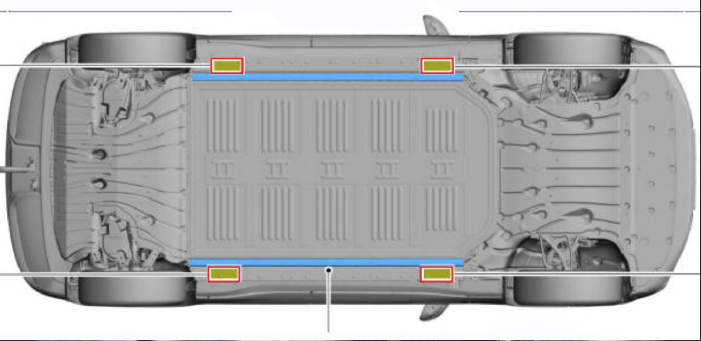
Lifting the Mach-E
The Mach-E can be lifted just like any vehicle, but there are several precautions. On the underside of the car are four lifting points. Do not use the high-voltage battery guardrail as jacking and lifting points. Position the hoist lift arms as shown in Figure 1. You also can identify the correct jacking points by locating the triangle stamped into the uni-body sheet metal or vehicle frame, or molded into the body rocker molding.
Ford recommends when jacking or lifting the vehicle, block all wheels remaining on the ground. Set the parking brake if the rear wheels will stay on the ground. These actions help prevent unintended vehicle movement. Ford also recommends placing blocks underneath the lifting points. When raising a vehicle on a two-column hoist, use care when positioning the car so that the hoisting forks do not interfere
with suspension components, the axle or
the rear cover.
Coolant System Service
One of the potential service opportunities for all EVs is the cooling system. The cooling system for the high-voltage system cycles coolant through the motors, battery pack and inverter. Also, the excess heat is used to heat the cabin. The coolant has a service interval of 10 years or 200,000 miles. But, most Mach-Es will require repair for the cooling system before the interval is reached.
Ford recommends using coolants that meet Ford’s WSS-M97B57-A2 and ASTM D 3306. The stock coolant has a yellow color. The system will hold two gallons of coolant or more, depending upon whether it has dual motors or larger batteries. Ford recommends that the coolant concentration should not exceed 60% or damage can occur to the motors.
Ford recommends filling the system using vacuum-filling tools. To perform the final bleed, you will need a scan tool. The scan tool should be able to put the cooling system into fill mode. This mode runs the coolant pumps to move air to the expansion tank so it can escape.
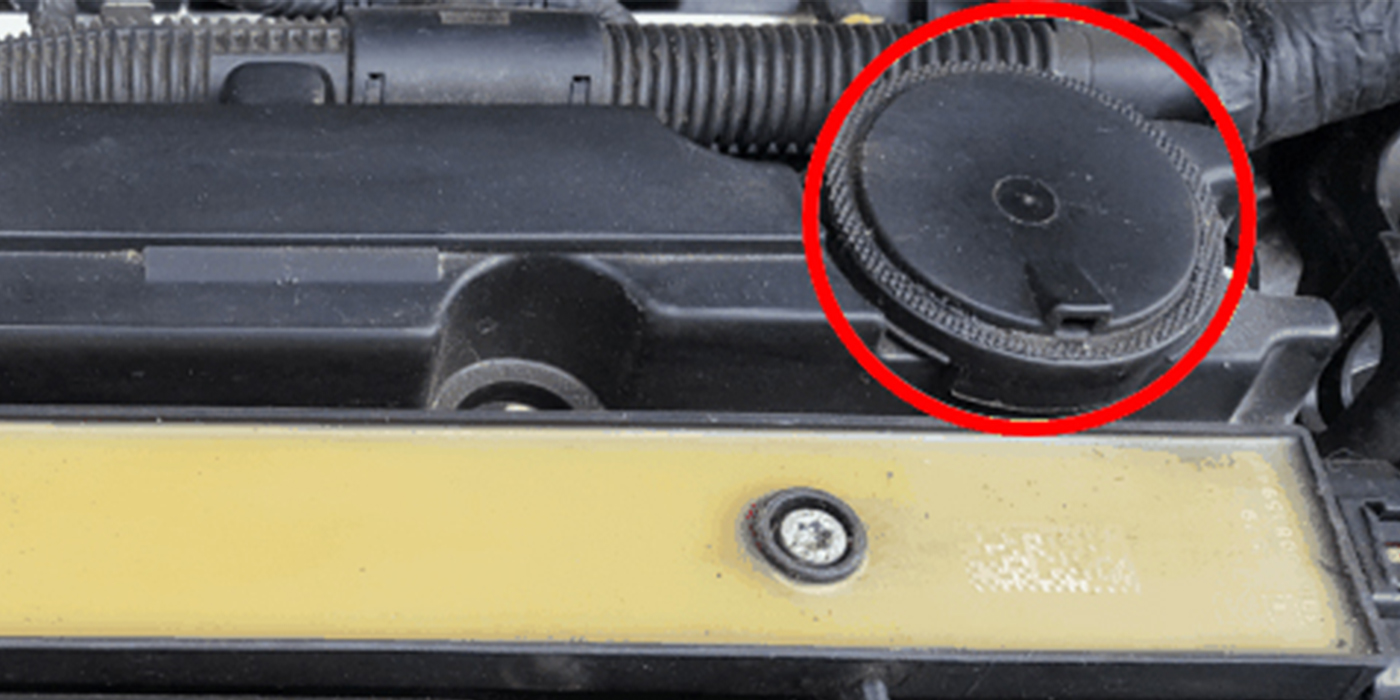
Before running the service fill mode procedure, ensure the coolant fill levels in the motor electronics cooling system and the high-voltage battery cooling system are between the MIN and MAX marks on the coolant expansion tanks.
Watch for air bubbles in the coolant expansion tank for the high-voltage battery. Add coolant to the coolant expansion tank if the level falls below the MIN mark. Bleeding is complete when bubbling stops. The process can take an hour.
Brakes
Just like every internal-combustion powered vehicle, the Mach-E has disc brakes all around that are controlled using hydraulics. Ford says the parking brake system should be in brake maintenance mode before service. This mode prevents the activation of the rear parking brake and electronic brake booster during service. The mode also prevents false leak codes that can occur when pushing the piston back. To engage the service mode, follow these steps:
- Set the ignition to ON.
- Release the EPB.
- Press and hold the accelerator pedal and place the EPB switch to the RELEASE (downward) position. Continue to hold the accelerator pedal and EPB switch.
- Set the ignition to OFF, then set the ignition to ON within 5 seconds. Continue to hold the accelerator pedal and the EPB switch.
- Set the ignition to OFF, then release the accelerator pedal and EPB switch.
The brake system will be deactivated, preventing brake application until the service has been completed and the service mode has been deactivated. The yellow EPB indicator will be illuminated, and maintenance mode will display on the message center.
Alignment
The suspension of the Mach-E has adjustments for camber, caster and toe, just like any other vehicle. There are no special procedures but using the brake service mode can make rolling-compensation alignments easier.
Tires
Due to the extra weight and torque generated by the electric motors, the Mach-E can wear out tires faster than an internal-combustion sedan of a similar size. It is recommended that replacement tires have a load rating of XL or greater. Check the placard on the driver’s door jamb for more information due to the different combinations of motors and wheel packages.
The TPMS system is identical to other Ford models, and procedures to replace sensors and train locations are the same.
Battery
The Mach-E is equipped with a 12-volt battery in the front compartment. The high-voltage battery has a high-voltage to low-voltage energy transfer feature that keeps the 12-volt battery charged. When the 12-volt battery’s voltage is low, the high-voltage battery transfers the energy to charge the 12-volt battery when the vehicle is off. The high-voltage battery needs to be de-energized when servicing the 12-volt battery, according to Ford.
The Battery Monitoring Sensor continuously monitors the condition and the state of charge of the 12V battery and provides the BCM with this information. The Battery Monitoring Sensor also estimates losses in the battery capacity over time. The Battery Monitoring Sensor should be reset only when the battery is replaced. It is recommended that the replacement battery has the exact same specification as the original battery. If it does not, the accuracy of the Battery Monitoring Sensor outputs will be compromised.
The Battery Monitoring Sensor is clamped directly to the negative terminal of the battery and grounds to the vehicle at the chassis ground connection point through the negative battery cable and eyelet. If you are charging or jump-starting, connect the negative clamp to the ground eyelet and not the negative terminal. Should the battery need to be isolated, it should be done by disconnecting the ground eyelet at the chassis ground. Bypassing the sensor this way can cause the battery management system to be inaccurate.