The suspension for the Toyota Camry stayed the same from 2002-2011. The basic platform is easy to service and has no major issues. But, if the toe is adjusted, you must recalibrate the steering angle sensor. To find out if the vehicle has the optional VSC system, a light will illuminate on the dash when the vehicle is started.
When you get a 2002-2011 Camry in your shop, it is important to find out if it is a four-cylinder or V6 model, and if it is a SE or LE model. Typically, this information can be found on the rear trunk panel above the bumper in chrome letters. While the suspension basics stayed the same for nine years, the camber, caster and ride height specifications change depending on the engine and trim level
Suspension
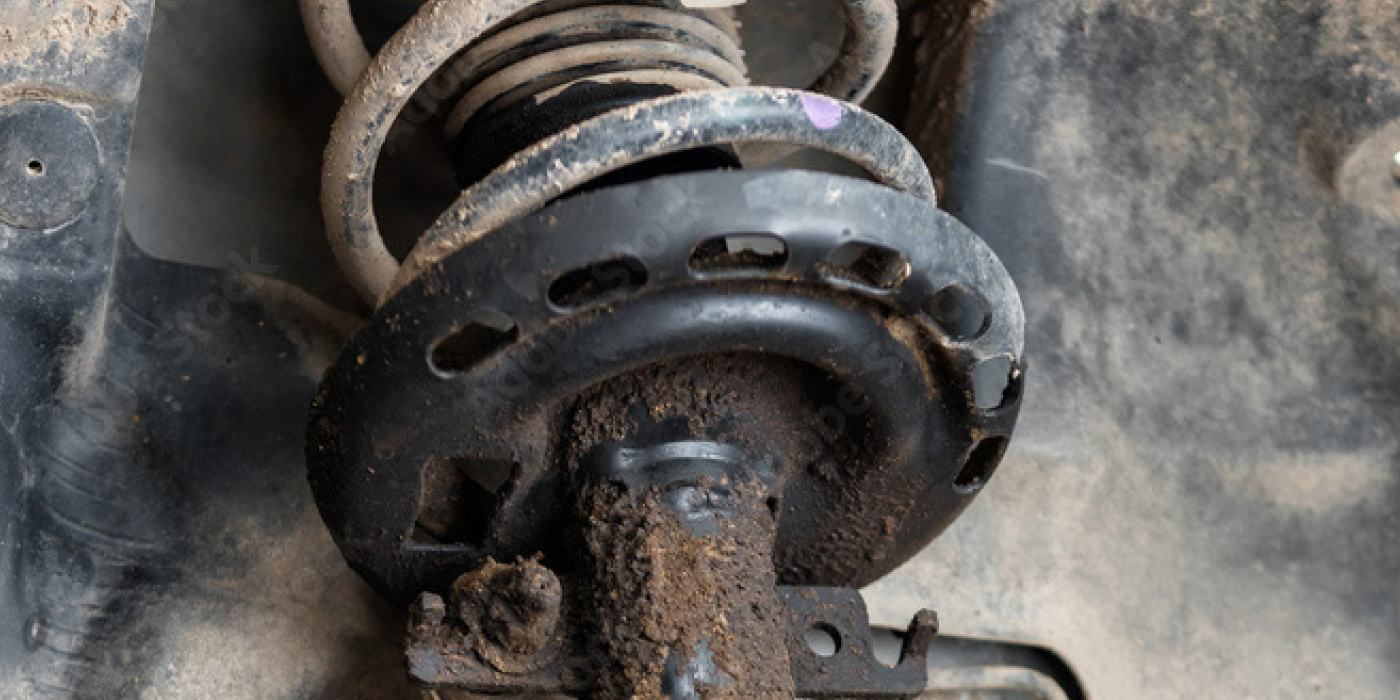
The suspension on the Camry is nothing special and has no real quirks. Toyota designed the front control arm on the Camry to absorb and deform during impacts so the body and suspension cradle will not be damaged.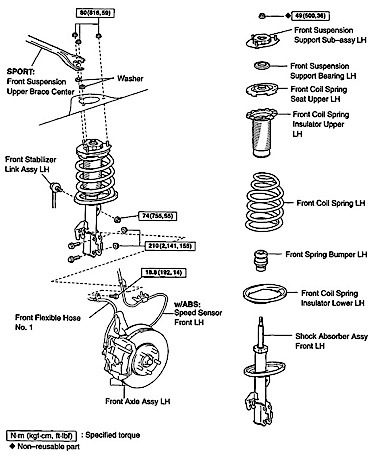
Replacement control arms are readily available for this vehicle. Pay attention to the included angle or SAI. This diagnostic angle can help you determine if the control arm or knuckle has been damaged.
The only significant TSBs listed for the suspension system concerns noise coming from the upper strut mounts in the front and rear on 2002-2006 models. The TSBs direct technicians to check the torque of the strut mount and bolts that hold the strut mount to the body.
Another area that has plagued the Camry is the steering shaft and noise. For some 2002-2003 models, TSB ST002-03 recommends using a syringe to apply dielectric grease between the intermediate shaft and grommet in the firewall if the driver reports a “low frequency” noise while turning.
Adjustments
The Camry has very few factory adjustments outside of the toe angle. Installing aftermarket cam bolts on the struts can give some adjustability, but they are not substitutes for worn bushings or broken springs.
Adjustment of front camber requires the use of cam bolts. The bolts allow both positive and negative camber changes up to approximately 1.75º. The bolts require .4 hours of labor to install per side. Front caster is non-adjustable.
Adjustment of rear camber requires the use of cam bolts. The bolts allow both positive and negative camber changes up to approximately 1.75º. The bolts require .4 hours of labor to install per side.
Electronics
Some Camry models are equipped with an optional Vehicle Stability Control (VSC) system and require a scan tool and special procedures to perform a “zero point reset” for the calibration of the yaw rate, deceleration and steering angle sensor.
The steering position sensor’s basic function is to monitor the driver’s steering inputs. This includes the angle of the steering wheel and/or the rate at which the driver is turning the wheel. The steering position sensor on the Camry is located behind the steering wheel and is a high-resolution sensor.
The VSC system relies on accurate steering input from the steering angle sensor to analyze a situation and apply appropriate measures to help direct the vehicle on the intended path.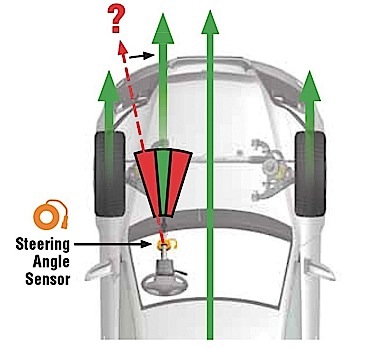
If the system is not calibrated after a toe adjustment, the system will not operate properly and may illuminate the VSC malfunction light after the driver has picked up their Camry.
A scan tool can be used or Hunter’s CodeLink tool, which is programmed to address Toyota’s requirements relative to the VSC zero-point calibration. Hunter has simplified the process with a seamless transition from the final front toe adjustment to the required reset.
After the sensor is reset, it is necessary to drive the vehicle and turn the steering wheel to the right and left at the speed of 22 mph (35 km/h) for at least five seconds to calibrate the sensors and complete the reset. If this is not performed, the VSC may set a code.
Article courtesy Brake & Front End.