Today’s heavy-duty engines have evolved to incorporate modern technology and adhere to emissions regulations—which means their components have had to evolve with them. For technicians, this means that when an engine problem comes up, it’s not so simple to determine the root cause.
Say, for instance, you think there’s an issue with a filter; first you need to determine whether that’s true by figuring out which filter is behind the issue, and then you need to take the necessary steps to fix the issue. Tomorrow’s Technician reached out to Edward Covington, director of quality at WIX Filters, to talk us through identifying and addressing these issues.
When a filter-related concern is suspected, Covington says that the first step is to “consider the indicators: engine computer codes, visible leak of filtered fluids, fluid analysis reports, poor engine performance, fluid color or condition or visible exhaust gas emissions.”
“It’s important to note that filters remove contaminants,” he adds. “As this happens, the restriction across the filter increases. This is normal, but if the contaminant load is higher than previous service intervals, filters can reach loading or termination pressure more quickly. A restricted filter may indicate a change in how the engine is operating, a change in the operating conditions, duty cycle of the equipment or vehicle, or an overdue service interval.”
The next step is to identify the specific problem and whether it’s being caused by the air, oil or fuel filter—or none of the above.
Different problems crop up with different types of filters. Covington identified the following common issues with each:
- Air filters may become clogged or restricted from higher concentrations of airborne dust. In extreme circumstances, water ingestion by an air filter heavily loaded with dust can create a mud cake, further increasing restriction. Built up snow or freezing moisture on an air filter can create higher air flow restriction until the ice is melted and subsequent water drained from the filter.
- Fuel filters can clog from microbiological growth or gelation in fuel storage tanks due to colder-than-normal fuel temperatures.
- Fuel water separator units can create a computer code to drain water. Older models without a water level sensor need regular draining, and more often, with higher concentrations of water in the service fuel. For off-road fuel storage tanks, monitoring the amount of water in the fuel is necessary to stop it from draining into the engine.
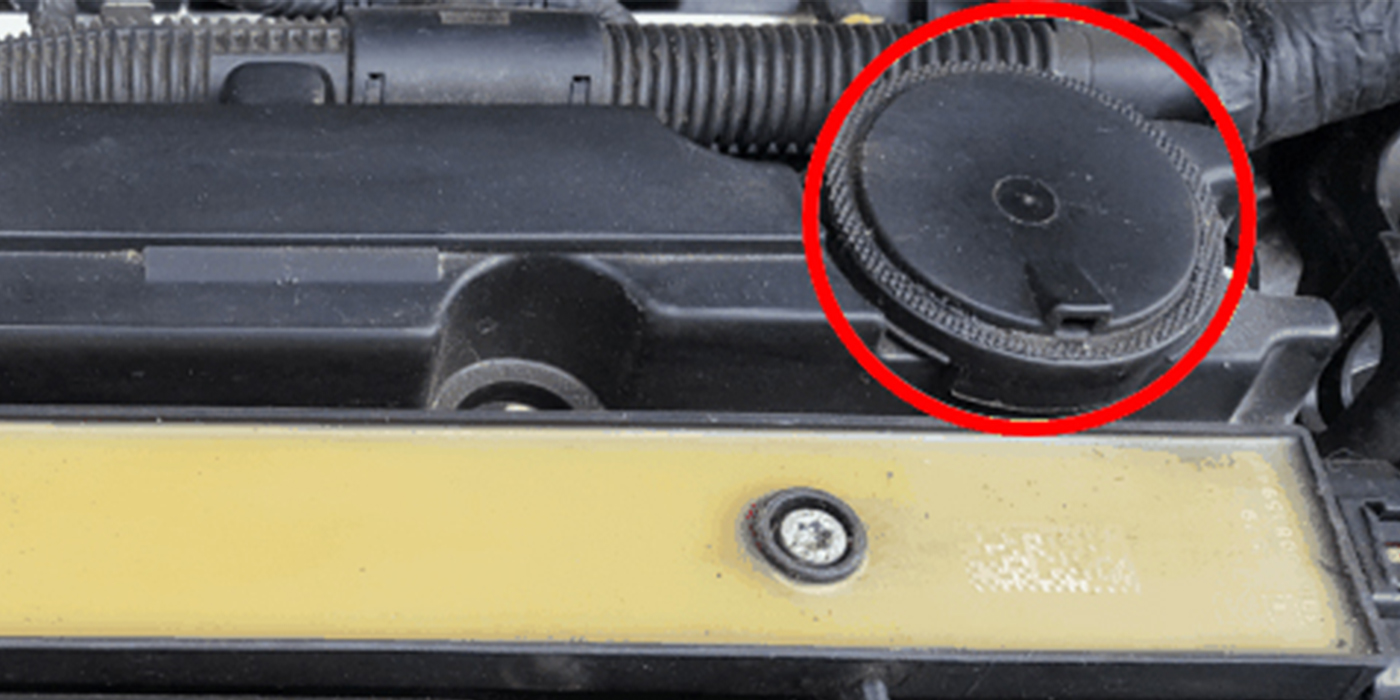
- Oil filters can prematurely plug from combustion byproducts if the engine load significantly increases, EGR system imbalances or coolant passage clogs in the oil cooler, which could result in high oil temperature during operation.
Once you determine the type of filter causing the problem, Covington notes that there are a couple of questions you will need to answer before you proceed:
- Is the filter being used recommended by the manufacturer for that specific engine and application?
- Are the correct fluids being used? For engine lubricating oil, verify base oil type, viscosity and API rating. For coolant, verify type and chemistry. For fuel, verify gasoline, diesel or bio fuel.
- Also, what is the duty cycle of the truck? Is the truck often used in harsh or severe conditions? If so, this will accelerate the service interval, which will need to be noted once the truck goes back on the road.
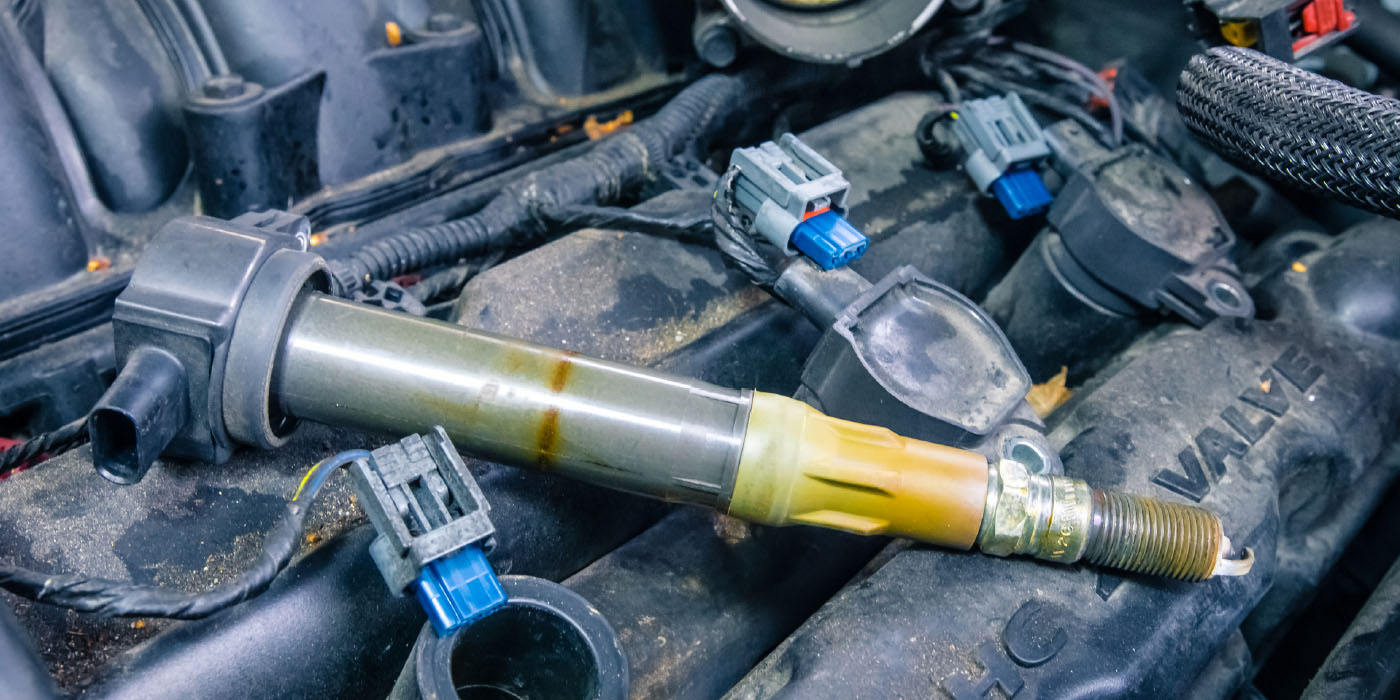
“Most lubricating oil filters require new seals or o-rings and specific installation torque values,” he notes. “Reuse of single-use seals or use of an alternate filter seal can create a leak path. Air filter differential pressure sensors need to be reset with each filter change. Engines equipped with intelligent oil life calculators need to be reset at oil and filter changes as well. These calculators rely on correct base oil, viscosity and rating, and a filter rated for the service interval and duty cycle to accurately inform when service is due.”
Lastly, for circumstances in which the filter is believed to have caused engine damage, be sure to follow the warranty submission requirements from the filter manufacturer; opening or altering the filter to self-diagnose the problem could void the warranty.