Brake rotors or discs must have the correct dimensions to work with the hub flange, caliper and knuckle. The original measurements must match the overall diameter, thickness and offset of the hat. This is the easy part of manufacturing the brake rotor.
The hard part of manufacturing a rotor is matching the internal structure, metallurgy and performance. These items can’t be tested with just one stop. Rotors must be able to withstand thousands of heat cycles without cracking or a structural failure
In 2012, an aftermarket rotor testing procedure was approved by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) titled J2928 Brake Rotor Thermal Cracking Procedure for Vehicles Below 4,540 kg GVWR. The document was a marriage of current industry tests and best practices. The goal of the document was to create a standardized test that could evaluate an aftermarket rotor’s ability to resist cracking using a dynamometer.
THE TEST
SAE J2928 test procedures subject a rotor to 150 heat cycles. A heat cycle is when a rotor is cold and brought to a high temperature. During a heat cycle, a rotor will expand and contract. This can create fatigue in a rotor that can cause cracking and structural failure.
During the 150 heat cycles, the rotor is inspected; this includes a dimension check and an inspection for damage.
The objective of the test is to thermally and mechanically stress the rotor so any deficiencies in the metallurgy or structure are exposed. J2928 also covers how to document and classify cracks.
Unlike a USDA-grade or a movie rating, SAE J2928 is just a document and recommended procedures. It is up to the industry to adopt and embrace these tests. The supply chain could benefit by comparing and evaluating rotor manufacturers as well as adding consistency and accountability — which would benefit shops directly.
THE MARKETING OF J2928
No rotor manufacturer can claim that passing the 150 heat cycles means its rotors stop sooner, make less noise or last longer. J2928 does not test for these parameters. Nor can a manufacturer make the claim that since its rotors are tested with J2928 that they meet a government standard set forth by DOT or NHTSA.
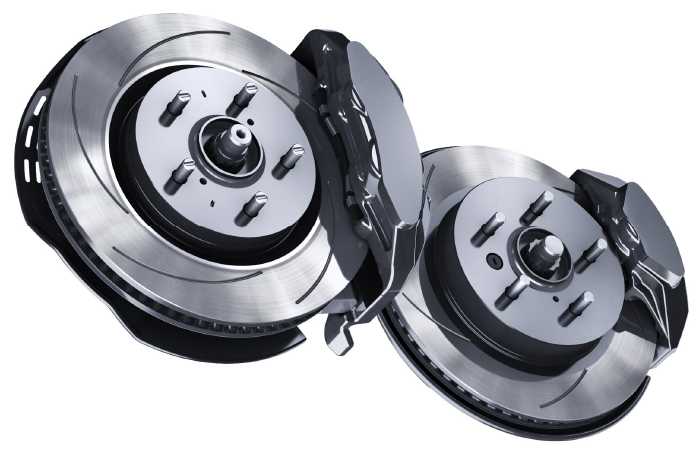

What a rotor manufacturer can claim is that its rotors were tested using SAE J2928 and assessed using industry-accepted performance criteria. Better yet, that its rotors meet industry-accepted pass/fail criteria regarding number of cycles without severe cracks.
the BOTTOM LINE
SAE J2928 is a step forward because it helps everyone in the supply chain speak the same language and it sets criteria when it comes to measuring aftermarket rotors.
SAE J2928 IS:
- An aftermarket rotor testing procedure.
- A series of 150 heat cycles performed on a dynamometer.
- A measurement of the thermal and structural adequacy of a rotor.
- A method of measuring, classifying and documenting cracks in a rotor.
- A tool for the supply chain to perform quality control on the products it sells.
- A way to compare an aftermarket rotor to an OE rotor.
- A rotor measurement for runout and thickness variation.
- A specification for a rotor to meet a percentage of the original rotor’s weight.
- A specification for a rotor to be within certain dimensional tolerances.
SAE J2928 IS NOT:
- A way to police bad rotors.
- Mandatory for all manufacturers, including OEMs.
- A measure of on-vehicle performance or stopping distances.
- A measure of noise or durability.
- A “certification” or “approval” of a rotor.
- Performed on a vehicle.
- A determination of the design of the rotors fins.