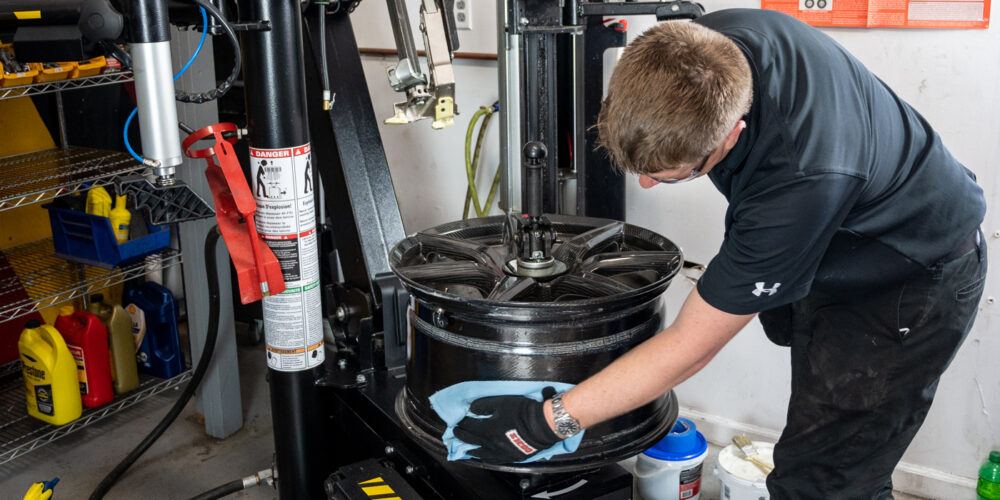
When a high-end sports car or supercar rolls into your shop, one thing is certain when servicing this type of wheel assembly: Those rims are expensive, so protect the wheel at all costs.
This is especially true with today’s composite wheels, and, in particular, carbon fiber wheels.
Carbon fiber wheels are made from a composite and injected with a resin to create their shape. They’re lighter compared to metal wheels that are made from materials like steel and aluminum. Because of this, they offer a savings of about half of the unsprung weight of a traditional alloy wheel. This reduces the wheel’s rotational mass and leads to better rolling resistance.
Because more and more carmakers are working to reduce vehicle weight for better fuel economy, carbon fiber wheels are an emerging high-end wheel trend that has started to make its way into the mainstream.
If you haven’t already, you’ll start seeing more of these wheels in your shop as sizes become more available. Because carbon fiber wheels are so delicate, cleanliness is next to godliness when mounting and demounting these types of wheel assemblies. Below are a few tips for the next time these wheels roll into your shop.
Inspection
It’s important to inspect the tire changer before putting a carbon fiber wheel on it. Make sure the tire changer, as well as its helper devices and other components, are clean. This includes the pedestal, upper and lower roller, and entire leverless duckhead, as well as the center locking mechanism (if you’re using a center-clamp tire changer).
A rim-clamp tire machine can be used, but it requires a few precautions. Use soft jaws or jaw protectors to protect the wheel.
Protection
Because of the delicacy of carbon fiber wheels, it’s recommended that the tire mounting paste, as well as the lube brush, be new or completely clean. Dust particles or debris from the tire changer can make their way into the lube, creating an abrasive paste when applied to the wheel. This abrasion could lead to scratches.
On center-clamp tire changers, use a protective cover over the centering cone to protect the wheel face. Don’t drag the locking device over the top of the wheel.
On rim-clamp machines, always use a poly duckhead and a poly cover over the tire lever.
In addition, if you have new consumables, replace them. This includes leverless duckhead protective pieces and the center cone on the lock of a center-clamp tire changer.
Care and Considerations
When possible, it’s recommended to use a center-clamp tire changer when mounting and demounting delicate wheel assemblies, such as carbon fiber wheels, since nothing touches the back of the wheel.
When lifting the wheel assembly on the tire changer’s pedestal, be sure to set it down gently to avoid scratching the backside of the wheel and line up the locator pins with the lug holes.
When you go to lock the wheel, make sure to hold the locking mechanism with two hands—one at the tip and one at the handle—to ensure it doesn’t bump the wheel.
Once the tire is demounted, clean the entire wheel with a dry cloth. Throughout the tire changing process, it’s important to use a liberal amount of lube on the tire, in the drop center, on the barrel of the wheel and on both beads.
Content provided by Coats Garage. For more information, visit coatsgarage.com.