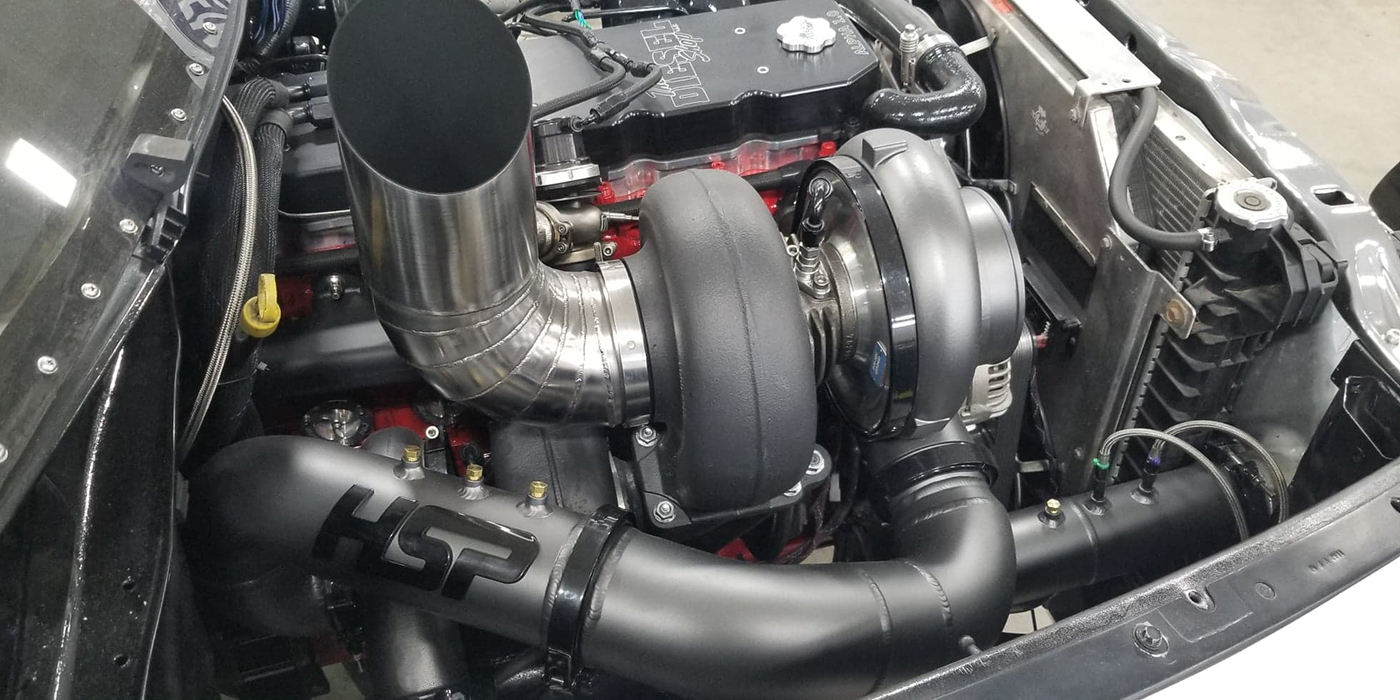
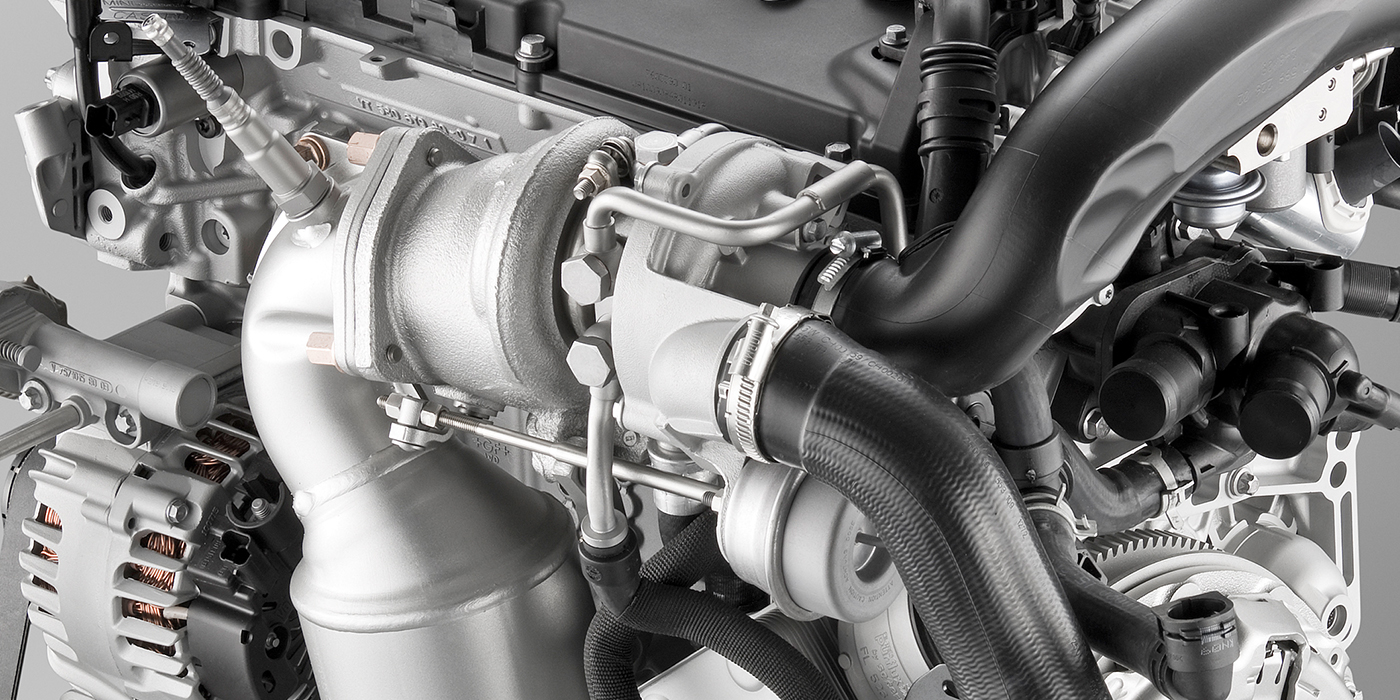
Some turbocharger failures on some GM Duramax 6.6 diesel engines from 2011-2017 are quick and catastrophic. It could start with smoke from the tailpipe or even a catalytic converter clogged with oil and debris. The customer may notice the engine is down on power. These are easy to diagnose.
Some turbocharger failures for these engines are less dramatic and might not require a replacement unit. Instead, they start with a code and a check engine light. These are typically caught by the engine management system when it senses the turbocharger is no longer producing the expected level of boost for a given engine speed or load.
No matter the symptoms or damaged parts, the root cause of the failure must be diagnosed and resolved. The cause of the failure or drivability problem might be related to the oil supply required to lubricate and cool the turbocharger’s bearings. In rare cases, a piece of debris can damage the compressor or the exhaust turbine. Vane Position Sensor can fail and not command the variable vanes in the turbine housing which control the speed of the turbine. Further to that, this variable geometry turbocharger contain an oil control solenoid that commands vane position, this too can fail and be a fault mode on this unit.
One of the most common codes for the Duramax is DTC P0299. The engine management system knows the expected level of boost pressure for a given condition. DTC P0299 indicates the boost pressure is below expectations. To set a P0299 code it requires multiple incidents over one or two key cycles. If you have a scan tool, you can access the freeze-frame information when code P0299 was set. A P0299 is not an automatic sign the turbocharger needs to be replaced. It is just a starting point for further inspection and diagnostics.
Mechanical failures of a turbocharger are usually related to the lubrication system. For the oil to cool and lubricate the turbo, it must flow. Restrictions in the oil feed or return lines can cause excessive heat along with shaft and bearing wear.
Oil restrictions are typically caused by carbon deposits in the lines and passages. When an engine stops turning, the oil flowing to the turbocharger stops. The oil inside the turbocharger might drain out of the center section through the return line. The remaining oil in the center section is heated to the point where it’s turned to carbon deposits. This process can happen even faster if the driver is using low-quality oil.
When the bearings and shaft wear, the ring lands and steel ring seals and be damaged causing oil to enter the turbine and compressor side of the turbocharger. This oil can clog the Diesel Particulate Filter particulate filter and even restrict the flow of exhaust gases. This can cause low boost pressure and a P0299 code.
On the intake side, the air filter may fail due to excessive pressure differential that rips the filter media from the frame. The pressure differential is typically caused by a clogged air filter. It is cheap insurance to replace the air filter when the turbocharger is replaced and highly recommended.
On the exhaust side, foreign objects can come from anything that can exit the exhaust port. If you deal with an engine failure with catastrophic damage, the turbocharger’s turbine and variable geometry vanes could be damaged.
For all diesel pickups made after 2007, the performance and fit of the turbocharger are critical for the operation of the Diesel Particulate Filter or DPF. In addition, any leaks in the exhaust system from the turbocharger to DPF will lead to codes and problems.
The DPF uses pressure sensors before and after the filter to measure restriction and determine when to perform a regeneration cycle. If the downpipe is leaking, the readings will not be accurate. In some cases, a code P2463 for excessive soot might be active. In other cases, the ECM will not run the regeneration cycle due to the plausibility of the reading from the two sensors. If you encounter one of these leaks, follow the procedures in TSB 15457 to align the downpipe and DPF. The method discussed involves removing the clamps, supporting the exhaust system, installing new gaskets and realigning the pipes.
As an extra quality check, perform a forced DPF regen cycle and check for any resulting codes.
There are several ways to protect a new turbocharger. The lines that supply and return it the oil pan should be replaced if available, or thoroughly flushed and cleaned to guarantee they are free and clear of any blockages inside them. Before the engine is started, the turbocharger should be pre-lubricated with a large syringe in the oil supply line.
The most important thing is to educate the customer on proper maintenance and oil changes. Most OEMs have specific grades and certifications for vehicles with turbocharged engines. Using the least expensive or what is available at a gas station can damage the turbocharger.
Also, if you encounter a Duramax with a blocked DPF or damage to the turbocharger due to high temperatures, you might need to educate the customer on avoiding extended idle times. While older diesel engines might have benefited from letting them idle for an extended period, newer diesel engines could clog the DPF and the turbocharger might experience higher than average temperatures. Also, customers may abort the regen process because it is inconvenient, or they fear the higher idle is rough on the engine. The reality is not performing the regen process could damage the new turbocharger.
The most critical item to address before replacing the turbocharger on a Duramax engine is to find the root cause of the failure. If you fail to do this, chances are you will have to do the job over at your own cost.
This video is sponsored by Cardone.